Why are carbohydrates needed?
It should be remembered that all carbohydrates in foods are broken down in the body into glucose, which is a source of energy, stimulates thinking and mental activity, nourishes nerve cells, starts the processes of digestion and respiration, and is spent on physiological needs.
Therefore, it is not recommended to give up carbohydrates under any circumstances. You just need to determine which carbohydrates are healthy and which are harmful.
A deficiency of carbohydrate-containing foods in the diet leads to diseases of the heart and blood vessels, impairs memory, provokes headaches, muscle cramps, reduces concentration and the ability to perform mental stress. Therefore, it is important to know the optimal carbohydrate intake.
Carbohydrates are good and bad
Oh, our people love, love to look for the guilty! And in such a matter as excess weight, it would be a sin not to look for it. Carbohydrates have long been among the main culprits in the appearance of fatty deposits.
On the one hand, this is in vain, because the calorie content of carbohydrates is half that of fats: only 4 kcal per 1 g. On the other hand, the image of carbohydrates is seriously damaged by the reputation of sugar, the guilt of which in the global obesity epidemic has been absolutely proven.
Energy from carbohydrates
It's no secret that carbohydrates are the most accessible and convenient source of energy for the body. After all, the cycle of their conversion into glucose (cellular “fuel”) is fast and simple. By the way, it is very convenient to store glucose - directly into the muscles and liver, and from there, quickly pull out the reserve as needed. However, if there is too much reserve, glucose, like other nutrients, is stored for longer - in fat deposits.
Everything seems to be simple. Consume carbohydrates in moderation, spend enough - and no excess fat. But it seems there is some kind of secret - otherwise the Internet would not be full of materials about low-carb, low-carb, strange-carb and generally no-carb diets. And they seem to somehow even work. True, with serious side effects - increased fatigue, nausea, weakness and even depression. And the “rebound” after such a diet is not long in coming - the extra pounds quickly come and bring friends with them.
Complex and simple carbohydrates
In fact, not all carbohydrates are created equal. Some are, so to speak, simpler, while others are more complex.
Simple carbohydrates
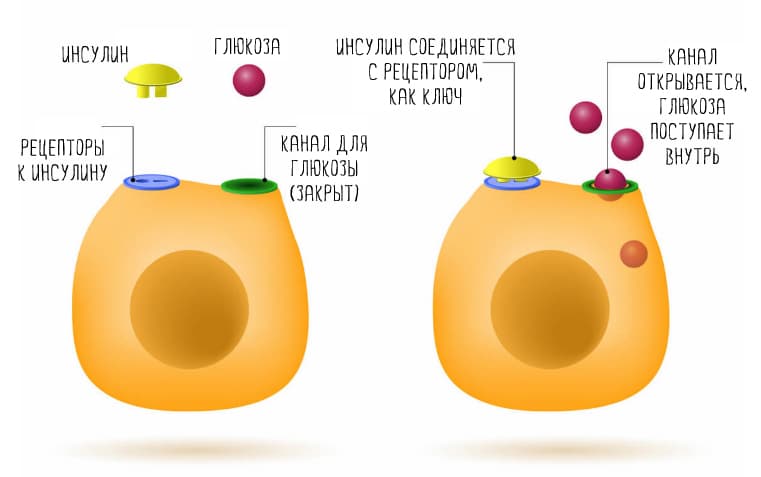
are sugars that are very easy to find in sweets, baked goods and dairy products. The babaika called “refined sugar” is also a simple carbohydrate obtained from plant products. What's good about them? It is their simplicity - to process them into fuel, the body does not need to work for a long time. Just produce the required dose of insulin - and now a stream of glucose pours into the blood. Perhaps this is why almost every person loves sugar-containing products so much - the “memory of ancestors” suggests that this is the most profitable source of energy.
The benefits and harms of carbohydrates
The structural unit of all carbohydrates is saccharides. Healthy carbohydrates differ from harmful ones in their chemical composition and number of structural units. In this regard, they distinguish:
- Monosaccharides - consist of one structural unit (fructose or glucose) and are absorbed in the body instantly.
- Disaccharides are a combination of two structural units and, like monosaccharides, are classified as simple carbohydrates.
- Polysaccharides contain three or more units, and due to their complex molecular formula, they are broken down slowly in the body, which is why they are called slow carbohydrates.
Simple carbohydrates
Simple carbohydrates are harmful to the body. They instantly appear in the blood and increase sugar levels. These include glucose, fructose and their various compounds. Products containing quickly digestible carbohydrates are:
- Sugar is a combination of glucose and fructose (sucrose).
- Fruits, sweets, milk (it contains lactose - milk sugar), some vegetables.
Among vegetables, potatoes are considered a conditionally harmful product, since the breakdown of starch-containing substances produces maltose - it contains two glucose molecules, which are fast carbohydrates.
Complex carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates include: fiber, dietary fiber, glycogen, pure starch. Their advantage is their slow absorption. The body receives the energy it needs and manages to spend it, so fat is not deposited.
Sources of slow digestion carbohydrates are:
- Cereals, durum pasta.
- Bread products made from wholemeal flour.
- Legumes (except soybeans).
- Vegetables (cabbage, greens, pumpkin, cucumbers, tomatoes).
- Unsweetened varieties of fruits, berries.
Healthy carbohydrates are absorbed slowly and do not cause spikes in blood sugar. The absorption of a well-thought-out carbohydrate breakfast takes 3.5-4 hours - the entire period the person feels full.
What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are found in almost any food and have an energy value of 4 cal/g. But they are not all created equal, and different types have different effects on your body. Food usually contains a combination of two types of carbohydrates: simple and complex.
Carbohydrates are complex chemical compounds consisting of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. The first discoveries by science were described by the formula: Cx(H2O)y, as if carbon atoms were bonded to several water atoms (hence the name). It has now been proven that in a carbohydrate molecule, carbon atoms are connected separately to hydrogen, hydroxyl (OH) and carboxyl (C=O) groups. However, the former name stuck firmly.
Absorption of healthy carbohydrates
Due to the fact that complex carbohydrates are absorbed gradually, they participate in a weight loss program and promote weight loss. To assess the usefulness of products, the glycemic index is used, which characterizes the rate of absorption of substances by the body. The amount of carbohydrates consumed per day is also important.
Potatoes are included in the list of complex carbohydrates, however, their glycemic index is high and they are quickly absorbed. In addition, potatoes contain large amounts of sugar. This must be taken into account when drawing up a carbohydrate menu for a diet.
Watermelon
Yes, watermelon is actually a berry. Scientifically named pepos, these fruits are a special category of berry—with a tough skin, lots of flat seeds, and fleshy pulp—and they're also good for your skin. While the inside of the watermelon is deliciously juicy, sweet and nutritious, the rind is especially beneficial for the skin as it is rich in vitamins B6 and C.
B vitamins are good for the skin because they help with both cell turnover and stress relief. Vitamin B deficiency can cause skin symptoms such as acne, dryness, rashes and wrinkles. As an antioxidant, vitamin C can help repair and protect cells from free radical damage.
If you don't want to eat the watermelon rind, you can juice it and add it to a smoothie or simply rub it directly into your skin.
According to dermatologist Anna Guanche, Koreans have been using watermelon rind for skin care for decades. She told Business Insider: "Korean grandmothers would rub watermelon rind onto sunburn, rashes or irritated skin to soothe it and help it recover faster. "Cooling masks that combine watermelon rind with avocado or banana may help promote healing." This is why watermelon-based cosmetics are so popular in K-beauty.
Healthy carbohydrates for weight loss
Foods containing carbohydrates that are healthy and promote weight loss are:
- Bran, oats, peas, lentils, beans.
- Apples, citrus fruits, berries.
- Barley, buckwheat, brown rice.
- White cabbage and all other types of cabbage.
Unlike fast carbohydrates, the substances in these products contain dietary and plant fibers, which improve intestinal motility, normalize metabolic processes, and create beneficial microflora in the intestines.
Norm of carbohydrates per day
To create a healthy menu, it is important to adhere not only to the correct list of products, but also to take into account the amount of food consumed. It is necessary to develop a weight loss program taking into account the carbohydrate intake.
If you do not take this indicator into account and consume slow carbohydrates in excessive quantities, your body weight will inevitably increase. Strict consumption monitoring is required.
Effective in matters of weight normalization is interaction with a nutritionist-endocrinologist, who, based on the patient’s current state of health, develops a personal scheme and table of carbohydrate consumption in foods.
In Zelenograd, such care is provided at the Axis Medical Center. Consultations with a nutritionist will help you determine the sources of carbohydrates and their quantity.
What affects the amount of carbohydrates in food?
Activity level
Carbohydrates are good for fueling intense workouts and recovery. Or harmful if they come in large quantities, but there is nothing to spend them on.
Carbohydrates should be looked at as fuel. They are stored in muscle cells in the form of glycogen and serve as energy during training (strength, sprint, interval), as well as for recovery after.
But all this is not unsuitable for a sedentary person. Unless you exercise and deplete your glycogen stores, you don't need a lot of carbohydrates in your meals.

A simple analogy is a car. If it's in a garage, you don't need gas. The tank has a certain volume and anything in excess will simply spill out. In the body, this manifests itself as excess glucose in the blood, which leads to fat accumulation and many other problems - increased cholesterol, insulin resistance and, ultimately, type II diabetes and/or atherosclerosis.
But if you drive your car every day, you should fill it up often. No gas - the car doesn't move. In the body, this manifests itself as a feeling of fatigue, apathy, irritability, depression, impaired performance in training, muscle loss, insomnia, low testosterone levels, impaired production of thyroid hormones, and decreased metabolism.
Metabolism
If you are overweight to the point of obese and are planning to lose weight, carbs should be reduced - this is the safest way to reduce calories.
The muscles of an untrained fat person do not take carbohydrates well. And if they come in excess, they will primarily be stored as fat, or at least block the body's ability to burn fat.
Lean and muscular people have good insulin sensitivity—it can efficiently supply glucose to muscle cells.
Metabolic state may change over time. Once you lose weight, improve your health biomarkers, and build muscle with strength training, the need to limit carbohydrates will go away.
But even an obese person should not completely eliminate carbohydrates.
Lifestyle and personal preferences

The best diet is one that you can stick to for a long time. This variable is often ignored.
Here are a few scenarios that require adjustments to the “optimal diet”:
A cook whose job is to taste food while cooking
Most restaurant dishes are fatty. Although this man's activity level and metabolism required a high-carbohydrate diet, his meal plan could be adjusted to account for his high fat intake, and his calories were kept in check by lowering carbs, so his personal plan was very different from some "ideal" plan.
Office worker who eats out during the day
Again, most restaurant, cafeteria and fast food meals are high in fat. So portion sizes and carbohydrate intake will have to be reduced to keep calories under control. A working strategy is to focus on protein, leave out the grains, and eat as little bread, carbohydrate snacks, and desserts as possible.
A person who is simply used to eating a lot of carbohydrates
This person is overweight and sedentary, and a low-carbohydrate diet would be ideal. But drastic changes here do not help adherence to the diet.
- The first step is to increase your protein intake with each meal.
- The second step is to reduce (but not completely eliminate) portions of cereals.
- To control calories, reduce fat in your diet.
- The fourth step involved strength training - as a way to increase the body's sensitivity to insulin.
Grape
Grape berries are classified as "true berries" because the wall of the fruit, known as the pericarp, is entirely fleshy. Like blueberries, grapes are rich in antioxidants. It also contains vitamin K, which helps maintain healthy bones and muscles.
In addition to their nutritional value, grapes are also good for hydration since they are 82% water. Staying hydrated is key to good skin health. If you don't drink enough water, your skin can become tight and dry, as well as less elastic and more prone to wrinkles.











