The confusion with carbohydrates comes when people try to create a one-size-fits-all approach and claim it is the only thing that works for everyone in every situation, regardless of body size, activity level, health, metabolism, or goals.
The truth is, there is no perfect diet for everyone. There are several effective and simple hikes that take into account where you are now and where you want to go. Confusion and problems arise when nutrition is considered separately, in a vacuum.
There's a hierarchy to creating an effective weight loss diet, and it doesn't start with carbs.
Calories
While carbohydrates are on the minds, calories come first. The only way to force your body to burn fat is to burn more calories than it takes in.
You can cut carbs or fat to zero, but if you go overboard on calories, you won't lose weight.
What happens if you cut out carbs but eat too many calories?
Decreased glucose and insulin levels increase fat oxidation. But with an excess of calories, the body will use dietary fats for energy and will not reach body fats. In other words, the body turns into what they like to call a “fat burning machine,” but this has nothing to do with body fat. Only calories determine which fat will be used for energy - dietary or subcutaneous.
Excess calories from fat will be stored as fat, no matter how low your insulin levels are. The body can store fat even without high levels of insulin.
Proteins, fats
The second most important point of a proper diet is a sufficient amount of protein. It helps preserve muscles - what shapes the figure. This is also one of the most “filling” foods, it reduces the feeling of hunger and helps you better adhere to your diet without breaking into rolls and chocolate in a fit of acute hunger.
In third place are fats, which are important for all types of cellular functions and for maintaining the natural production of hormones.
Fiber, vitamins
Fruits and vegetables are a source of vitamins, minerals and fiber. Fiber saturates well, like proteins, and helps fight hunger and glucose surges.
Carbohydrates
Starchy carbohydrates (cereals, breads, legumes) are a source of energy, so they should be supplied depending on your activity level, training, metabolism and goals. That is, they are definitely not in first place in the hierarchy.
Types of carbohydrates
The simplest unit of carbohydrate is the monosaccharide, a sugar molecule made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. These "building blocks" can be combined into structures that have different sizes, shapes and degrees of complexity. They are called polysaccharides.
- 171
More details - 234
More details
- 171
More details
- 234
More details
Based on their chemical structure, carbohydrates can be divided into three types: sugar, starch and fiber. Although some foods (such as white sugar) are made entirely of sugar, many foods contain two or three types of carbohydrates. Sugar is commonly called a simple carbohydrate because it has a simple structure. Starches and fiber are called complex carbohydrates because they are made up of long chains of simple sugars. Starches are found in foods such as beans, whole grains, and some vegetables (such as potatoes and corn), while fiber is found in fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts and seeds.
Carbohydrate-rich foods

Proper consumption of carbohydrates involves a balanced consumption of “fast” and “slow”. For the convenience of creating an individual menu and characterizing products from a “carbohydrate point of view”, an indicator was introduced - the glycemic index, it is often denoted by the abbreviation GI. It shows how quickly your blood glucose level will change after a certain food.
Find out more about where carbohydrates are found with a detailed table.
The higher the quantitative value of this level, the more insulin is produced, which, in addition to glucose metabolism in the body, performs the function of accumulating fat reserves. The more frequent and severe fluctuations in blood glucose occur, the less likely the body is to store carbohydrates in the muscles.
Slow, complex carbohydrates are characterized by low and medium GI, fast (simple) - high.
Low GI:
- cabbage
- legumes
- apples
- apricot
- drain
- grapefruit
- peaches
- apples
Average GI have:
- oatmeal and oatmeal cookies
- pineapples
- green pea
- rice
- millet
- pasta
- buckwheat
High glycemic index foods:
- sweets
- grape
- bananas
- honey
- dried fruits
- potato
- carrot
- White bread
Why do we need carbohydrates
The human body needs all three types of carbohydrates - sugar, starch and fiber. All of them are used differently by our body. Sugars and starches are broken down to use and store energy in cells, tissues and organs. Fiber passes through the body undigested, but helps regulate digestion and blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
During the process of digestion and metabolism, the body is able to break down all carbohydrates (except fiber) into glucose. Glucose is used by the body to produce energy.
Why are carbohydrates needed?
It should be remembered that all carbohydrates in foods are broken down in the body into glucose, which is a source of energy, stimulates thinking and mental activity, nourishes nerve cells, starts the processes of digestion and respiration, and is spent on physiological needs.
Therefore, it is not recommended to give up carbohydrates under any circumstances. You just need to determine which carbohydrates are healthy and which are harmful.
A deficiency of carbohydrate-containing foods in the diet leads to diseases of the heart and blood vessels, impairs memory, provokes headaches, muscle cramps, reduces concentration and the ability to perform mental stress. Therefore, it is important to know the optimal carbohydrate intake.
What happens when we eat carbohydrates
Although all carbohydrates travel through the same pathway, depending on the structure of the molecules, it takes different amounts of time and requires different amounts of effort from the body. For example, sugar, which has a simple structure, quickly breaks down into glucose, and this does not require the body much time and effort. Therefore, sugar is the fastest form of energy.
The process of breaking down starch into glucose occurs over a longer period of time due to its complex structure. This type of carbohydrate provides a slower, more sustained form of energy and is less likely to cause blood sugar spikes.
The duration of digestion depends on the type of carbohydrate. Simple sugars are absorbed quickly; the process of assimilation of complex carbohydrates requires more time and more effort.
Carbohydrate requirement calculator
Age Gender Height Weight Goal Activity
If you're not sure what percentage of carbs is right for you, just follow the rule of thumb:
For weight loss, start with 45-50% and reduce the percentage. If you are actively training for more than an hour every day or preparing for an event that will require remarkable endurance from you (for example, a marathon), then you are better off increasing the percentage to 55-65%.
| Type of activity | Recommended rate |
| Very light weight exercises | 3-5 g/kg |
| Moderate intensity exercise, 60 min/d | 5-7 g/kg |
| Moderate/high intensity endurance exercise, 1-3 hours/day | 6-10 g/kg |
| Moderate to high intensity exercise, 4-5 hours/day | 8-12 g/kg |
Carbohydrates in bodybuilding
To build muscle mass you should follow these tips:
- Consume the daily amount of carbohydrates required for athletes.
- When creating a menu for the day, it is important to select products based on their GI index. Products with low and/or medium GI should be consumed based on the calculation of 2.5 g of carbohydrates per 1 kg of human weight. Products with a high GI should be supplied with food in quantities of no more than 2 g per 1 kg of weight.
- The ideal time to eat a high GI food is within 3 hours after training.
- The body actively stores carbohydrates in the form of intramuscular glycogen in the morning, no later than 6 hours after a person wakes up.
Low-carbohydrate diet and cycle disorders in women
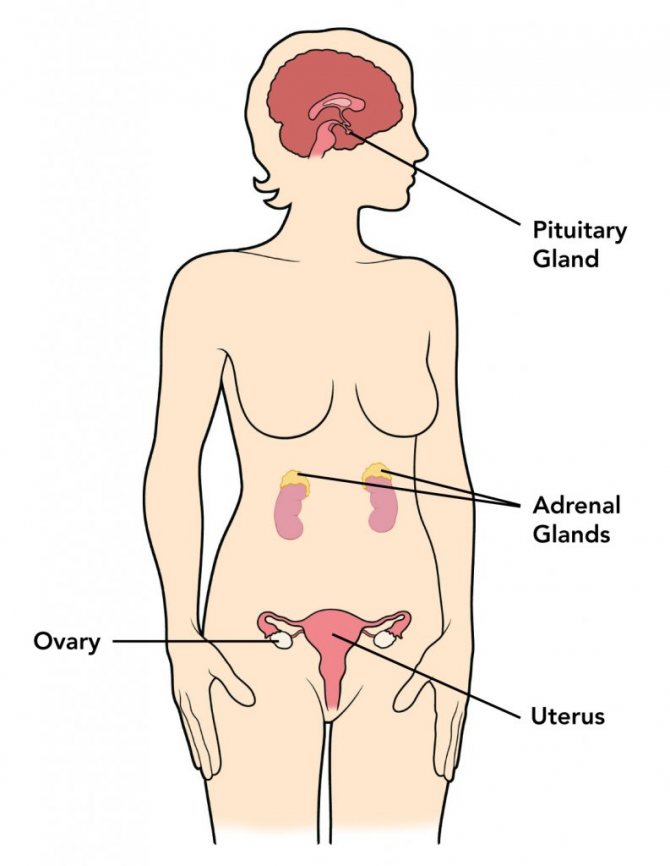
Refusal of carbohydrates during a calorie deficit can lead to hormonal imbalances in women. It is assumed that a woman's body is more sensitive to low levels of calories in food and percentage of body fat.
The hypothalamus and pituitary gland, which are located in the brain, are extremely sensitive to things like energy availability and stress (this includes not only psychological stress, but also starvation diets and strength training).
Quite often, so-called hypothalamic amenorrhea occurs, that is, the absence of menstruation, caused by severe restriction of calories and carbohydrates, sudden weight loss, a decrease in the percentage of body fat to a minimum level, stress or excess physical training ().
For example, many women involved in professional bodybuilding suffer from cycle disorders during extreme preparations for competitions.

This occurs due to a drop in levels of various hormones, including gonadotropin-releasing hormone, which starts the menstrual cycle (). This leads to a decrease in the levels of other hormones - luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estrogen, progesterone and testosterone ().
The amount and type of carbohydrates consumed are associated with a woman's ability to conceive. So, equally very much and very little carbohydrates are associated with decreased fertility ().
Long-term severe reduction of carbohydrates can disrupt hormone levels, causing amenorrhea or irregular menstrual cycles, which reduces a woman's ability to become pregnant (, , ,).
Low leptin levels are another cause of amenorrhea and menstrual irregularities (,).
Leptin is a hormone produced by fat cells in the body and through which they “communicate” with the brain. Leptin tells the brain how the body is doing with its energy reserves. When there is a lot of leptin, the brain understands that the body has enough fat (energy), so there is no point in urgently replenishing its reserves. When leptin is low, it is a signal to the brain about hunger and the risk of death. As a result, it reduces metabolism and increases the feeling of hunger.
Severely reducing calories and especially carbohydrates can lower leptin levels and interfere with its ability to manage reproductive hormones. This is especially true for women who are very thin or who are losing extreme weight on a low-carb diet (,).
CARBOHYDRATES: THEIR TYPES, IMPORTANCE FOR HUMANS AND DIGESTION FEATURES

Our body cannot exist without energy, and the brain is especially sensitive to this deficiency. Carbohydrates are the best and, from a biological point of view, correct sources of energy. The main sources of carbohydrates are various foods: grains, potatoes, sweets, fruits, confectionery, milk and its derivatives and other foods. What is the value of carbohydrates, how can the body store them, and how does carbohydrate metabolism occur?
What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are organic substances that make up living organisms, containing in their chemical structure a carbonyl group and several hydroxyl groups. According to the postulates of proper nutrition, it is this group of substances that should cover about 60% of the daily need for food energy, that is, calories.
Carbohydrates can be divided into 2 large groups:
- Digestible
They are completely digested and provide every cell with glucose - this is the main form of energy. These carbohydrates enter the liver in the form of glycogen, which maintains normal blood sugar levels during hunger and increased energy expenditure.
- Indigestible
This type of carbohydrate is not digested, but is very important for the intestinal microbiome. Firstly, it forms the substrate necessary for the life of the microbiome. Secondly, dietary fiber is partially broken down by the intestinal microbiome, which supports their vital function, and all this together stimulates normal intestinal function - peristalsis.
The sources of carbohydrates in the diet are varied, for example, indigestible dietary fiber is found in plant foods: fruits, vegetables and legumes, etc. These carbohydrates ensure the movement of food mass, prevent constipation, and can be considered as a preventive measure against certain types of cancer. The digestible type of carbohydrates is found in fruits, vegetables, dairy products, pasta, and grain products.
Based on the degree of digestibility, carbohydrates are also divided into several groups:
- Easily digestible
Fructose, glucose, galactose are types of simple carbohydrates that are quickly and easily digested, hence their name. Excessive consumption of these carbohydrates can cause spikes in blood sugar levels, since easily digestible carbohydrates have a high glycemic index, that is, their absorption rate is increased.
- Difficult to digest
These carbohydrates are digested slowly, maintain stable blood sugar levels and keep you full for a long time. These include bread, legumes, potatoes, that is, all products containing starch, pectin and glycogen.

All of the above are a type of digestible carbohydrates.
Functions of carbohydrates
Contrary to popular belief, those who want to lose weight do not need to give up carbohydrates in their diet; they perform an important function, and their intake should be carried out in full, according to the principles of proper nutrition. An adult needs 313–375 g of carbohydrates daily. First of all, because these are the main and most correct sources of energy for the body - this is exactly how nature “intended”.
The fact is that with a nutritional deficiency, proteins and fats can also be digested into sugars, that is, through complex metabolic processes they can be “converted” into carbohydrates. But at the same time, the body is deprived of the most important structural nutritional elements - amino acids, fatty acids, etc. And this can cause deficiency conditions and even serious diseases. It should also be noted that the digestion of proteins to sugars is an energy-consuming process, and as a result, the body receives less energy than was spent on its production. Protein diets are, in fact, aimed at creating such an artificial energy deficit. But for most people, practicing them is very harmful, especially for a long time.
Carbohydrates also perform other functions:
- necessary for the construction of cells, and these functions are no less significant in comparison with proteins;
- influence the blood group, because when determining it, attention is paid specifically to specific carbohydrates and proteins included in the membranes of red blood cells;
- found in many hormones that regulate metabolic processes, as well as antibodies that protect the body;
- Carbohydrates in the human body are stored in the form of glycogen, which can then be converted into glucose and used for certain needs. This mechanism is activated during hunger, carbohydrate metabolism disorders, certain diseases, etc. The main “depot” of glycogen is the liver.
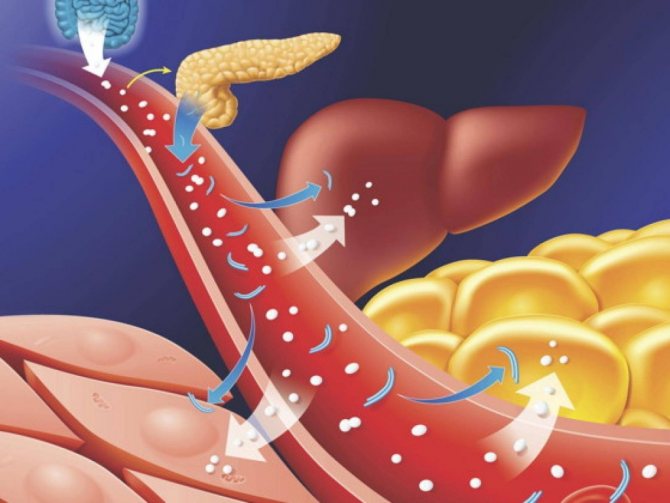
Digestion and metabolism of carbohydrates
Digestion of carbohydrates is the totality of the process of assimilation of carbohydrates and carbohydrate-containing substances, their synthesis, breakdown and excretion of metabolic products from the body. And this process begins in the mouth under the action of the enzyme alpha-amylase. This is why if you chew bread for a long time, you can feel the sweet taste. Why is this happening? It's simple: already in the mouth, carbohydrates are broken down into glycosine, which gives sweetness.
Starch is a complex carbohydrate, an example of which can be used to consider the process of its digestion. Already in the oral cavity, starch is digested into simpler components from a chemical point of view. But carbohydrates such as sucrose and lactose do not undergo any changes in the oral cavity.
Next, the food enters the stomach, but due to the fact that the acidity of the gastric juice is too strong, the digestion of carbohydrates does not occur. As the food bolus moves into the duodenum, pancreatic amylase, which is produced by the pancreas, enters the duodenum. It is this enzyme that is the main one in the digestion of carbohydrates, because it breaks down the bulk of starch.
It is this amylase, in combination with enzymes from the small intestine, that carries out the process of digesting starch into glucose. Sucrose and lactose are broken down in the intestines.
When the digested bolus of food is in the middle section of the small intestine (jejunum), glucose and fructose are absorbed. These sugars enter directly into the blood or lymphatic system and travel through the portal vein to the liver. Some of the glucose goes through the process of glycogenesis - the conversion of glucose into glycogen, and this is how the reserve is formed. The remaining part of the glucose “runs” through the bloodstream to the heart, brain, muscles, organs, etc.
Carbohydrates in the body are stored in the form of glycogen, precisely due to this ability, conditions are created for the accumulation of a certain reserve of energy, and this reserve is consumed when energy costs increase. And then the reverse process begins - the conversion of glycogen into glucose, which is spent on the needs of providing the body with energy.
As soon as glucose has penetrated into the cells with the help of the hormone insulin, the complex process of assimilation of energy and the release of metabolic products - water and carbon dioxide - begins, which are then removed from the body.
Text: Yulia LAPUSHKINA.
What are nutrients?
The term nutrients refers to biologically active substances and elements involved in the life of the body. All their diversity is usually classified into 2 more groups:
- Macronutrients
These are sources of energy, as well as “building materials” for the body: proteins, fats, carbohydrates.
- Micronutrients
These are vitamins, minerals, bioflavonoids contained in food in microdoses.
If they are deficient, health and well-being deteriorate. If the diet is low in calories, then all nutrients are processed into sugars in order to make up for the energy deficit - the body’s basic vital need.
Let's look at the functions of macronutrients and micronutrients in general terms.
Bananas
Bananas come from plants with one ovary and several seeds, so scientifically they are berries. They are good for skin health because they are high in vitamins C, B6 and A. The latter, an antioxidant, helps hydrate the skin and also speeds up the healing process, preventing breakouts.
According to Zara Risoldi Cochrane, PharmD, MS, FASCP, vitamin A may help those who suffer from acne. “It all depends on the source and how you use it,” she says. "Eating foods rich in vitamin A can promote better skin health from the inside out, while topical formulas can directly combat breakouts."
Carbohydrates and weight loss
Many people associate carbohydrates exclusively with sweets, and, consequently, with excess weight. However, there is an easy way to channel your energy into losing weight. We are not talking about so-called carbohydrate diets; however, restriction in protein and healthy fats can negatively affect the health of the body. Therefore, such radical diets are possible only after an individual consultation with a doctor.
You can and should adjust your diet on your own. However, this must be done correctly and, first of all, you should give up fast carbohydrates. Those involved in sports are allowed to eat some foods with a high GI (their daily dosage should not exceed 1 g per kilogram of weight). Products with a low and/or medium glycemic index should be consumed at the rate of 2 g of carbohydrates per 1 kg of weight.
You can’t deny yourself any food group. Carbohydrates must come from cereals, vegetables, fruits, and bread.
Carbohydrates should be an essential part of any person's diet, especially if they engage in physical activity. After all, they are the main source of energy! Plan your diet correctly. Be energetic and beautiful!
Sources: C. A. Rosenbloom, E. J. Coleman (Eds.) Sports Nutrition A Practice Manual for Professionals. 5th edition. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Chicago, IL; 2012.
How many carbohydrates do you need per day: weight loss, weight gain
The norm of carbohydrates for weight loss
According to many studies, low-carb diets can be very effective for weight loss. Reducing your carbohydrate intake can lead to decreased appetite and weight loss, even without the need to count calories.
For some people, this is a very comfortable option because on a low-carb diet, they eat until they are full, feel satisfied, and lose weight at the same time.
However, the daily
amount of carbohydrates for weight loss
is also very individual and depends on age, gender, body type and activity level.
Some people choose to eat a low-carb diet and reduce their daily carbohydrate intake to 50-150
gr. in a day.

Let's look at some of the benefits of low-carb diets:
- Research shows that low-carb diets can reduce a person's appetite, causing them to eat fewer calories, which can help them lose weight. The Effects of a Low-Carbohydrate Diet on Appetite: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Additionally, low-carb diets have benefits that go beyond just weight loss. They may help lower blood sugar, blood pressure, and triglycerides. And also help increase the level of HDL (good) cholesterol and improve the structure of LDL (bad) cholesterol. Health Effects of Low-Carbohydrate Diets: Where Should New Research Go?
- Low-carb diets often benefit from low-calorie, low-fat diets. They cause greater weight loss and improve health. Low-carbohydrate nutrition and metabolism
There are different carbohydrate standards for low-calorie diets, let's look at some of them:
100-150 gr. in a day
– This is a moderate consumption of carbohydrates. This may be appropriate for thin, active people trying to stay healthy and maintain their weight.
Carbohydrates that can be consumed at this rate
:
- all vegetables;
- a few pieces of fruit a day;
- moderate amounts of healthy starches such as potatoes, sweet potatoes and grains such as rice and oats.
We recommend
“Products to increase hemoglobin: diet and dietary features” Read more
50-100 gr. in a day
- this range is more severe and is not suitable for everyone.
Carbohydrates that can be consumed at this rate
:
- lots of vegetables;
- 2-3 pieces of fruit per day;
- minimal amount of starchy carbohydrates.
20-50 gr. in a day
– the most extreme version of the low-carb diet. Under no circumstances should you switch to this diet on your own, only under the supervision of a specialist and according to indications.
When consuming less than 50 g of carbohydrates per day
The body goes into
ketosis
, supplying energy to the brain through so-called ketone bodies.
Carbohydrates that can be consumed at this rate
:
- lots of low-carb vegetables;
- some berries, perhaps with whipped cream;
- need to watch out for carbohydrates from other foods such as avocados, nuts and seeds
It must be remembered that when switching to a low-carbohydrate diet, you need to be very careful; it is best to do this under the supervision of a specialist. This diet has its contraindications
and side
effects
that you may not be aware of and harm yourself.
One-size-fits-all advice: Simply eliminate the worst sources of carbohydrates from your diet, such as refined wheat and added sugar, so you'll be on the right track to better health and weight loss. Replace high-calorie refined foods
carbohydrate sources,
whole
healthy foods:
- vegetables;
- greenery;
- berries;
- fruits;
- cereals;
- fish;
- seafood;
- meat;
- eggs.
Choose carbohydrate sources that include fiber, try unrefined sources of starch: potatoes, sweet potatoes, oats, brown rice.
The norm of carbohydrates when gaining muscle mass
Carbohydrates are an important source of calories
for people wanting to build muscle mass.
- Some research suggests that eating carbohydrates along with protein within a few hours of exercise may help increase protein synthesis. Timing of postexercise protein intake is important for muscle hypertrophy with resistance training in elderly humans
- When you lift weights, the body relies heavily on carbohydrates for fuel, so a carbohydrate-rich pre-workout meal or snack can help you perform better in the gym. International society of sports nutrition position stand: nutrient timing

- Additionally, carbohydrates have a protein-sparing effect, which means the body prefers to use carbohydrates for energy instead of protein. As a result, he can use the protein for other purposes, such as building muscle, if his carbohydrate intake is sufficient. The Important Role of Carbohydrates in the Flavor, Function, and Formulation of Oral Nutritional Supplements
- Eating carbohydrates post-workout may slow down the protein breakdown that occurs after exercise, which may promote muscle growth. Intake of Protein Plus Carbohydrate during the First Two Hours after Exhaustive Cycling Improves Performance the following Day
Therefore, if your goal is to gain
muscle mass
, increasing your carbohydrate intake may be a good solution. The main thing is not to get carried away, remember the upper permissible level of consumption and train efficiently and regularly.
Blueberry
Perhaps one of the most famous berries, blueberries are the best thing for your skin. At least because it is rich in antioxidants.
Antioxidants fight cell damage caused by free radicals. Essentially, unstable atoms, free radicals, are associated with the development of chronic diseases, as well as the acceleration of the aging process.
According to nutritionist Katie Davison, MScFN, RD, blueberries are especially rich in anthocyanins. These are plant compounds that "have strong antioxidant properties and give blueberries their natural purple-blue hue."
Blueberries can also help improve circulation, Davison notes, as well as reduce inflammation associated with acne and boost collagen production, which helps strengthen the skin and plays a key role in maintaining elasticity, which reduces wrinkles.











