If you want to lose weight or get rid of body fat, the main thing you need to achieve is a calorie deficit. The human body, like a machine, needs energy and burns it. Accordingly, a calorie deficit occurs when you burn more than you consume.
So, in order to calculate your target calorie deficit, you need to know two key parameters: how many calories you consume through food and drink, and how many calories you burn during physical activity.
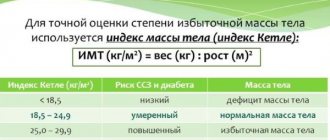
Weight standards
Before calculating what calorie deficit a person needs to lose weight, you need to know what a weight norm is and how it is calculated. There are several basic formulas by which norms are calculated.
- For a non-athletic person, a height of 110 is considered normal weight.
- For athletes, a formula is usually used in which the weight is calculated to be 10 kilograms more than usual.
Note: despite the fairly close approximation of these formulas, if you look at CrossFit athletes, their weight is really in the range of height -100+-5 kilograms. The same Richard Froning, with a height of over 180 centimeters, at the peak of his career weighed only 85 kilograms.
Naturally, this approach is not completely correct, since it does not take into account many factors, including:
- Initial metabolism.
- Weight and bone thickness, which can adjust weight by 8 kilograms in any direction.
- Amount of muscle mass.
- The amount of glycogen in the blood.
- Fat percentage.
In particular, we may see two people of the same weight who will look completely different. Therefore, when calculating the optimal weight, we will use more advanced statistical formulas.
For men
How to calculate normal weight for a man, and determine whether he needs to create a calorie deficit to lose weight? On average, a weight of 75-80 kilograms is considered the norm for an active man. No matter how strange it may be, this figure practically does not depend on a person’s height. On average, people who are shorter have a thicker bone structure, which puts them on par with tall and thin people. The normal amount of adipose tissue for a non-athlete is considered to be up to 22% with its even distribution throughout the body. If you have a large muscle mass (for mesomorphs), the value of adipose tissue can be up to 30%, and the person will still not be considered fat or overweight. In general, it is necessary to measure the percentage of fat tissue and its ratio to muscle volume.
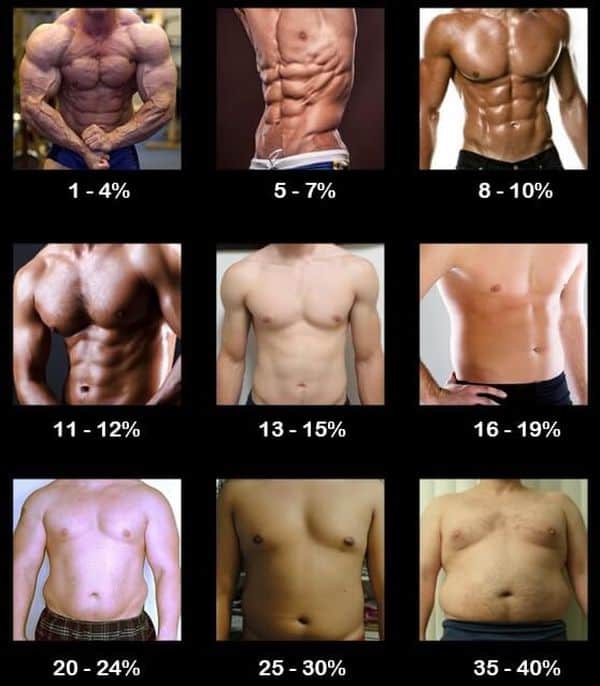
Interesting fact: Ronnie Coleman, at the peak of his career, failed the police exam because he was considered overweight and classified as terminally obese. At the same time, this fact was recorded almost immediately after the Olympia, when the total body fat barely reached 10%.
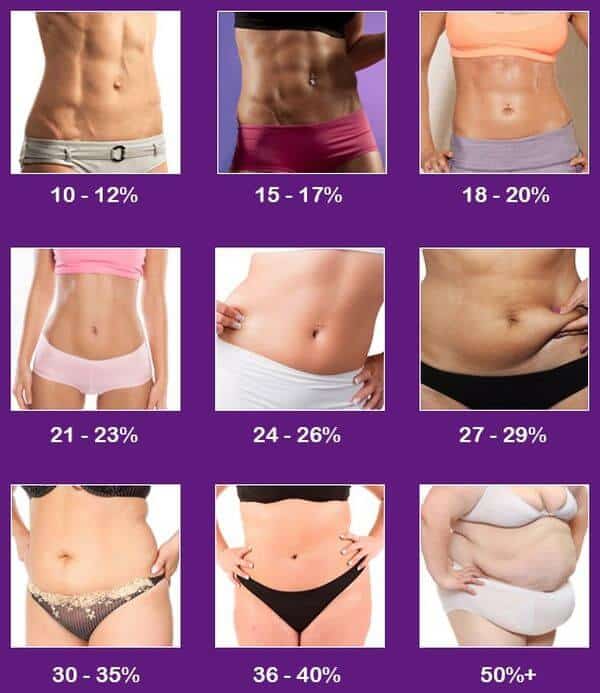
For women
In the case of women, two factors need to be used at once.
- Height/weight ratio. It should be standard (height -110).
- Body fat percentage.
In the case of his calculations, women are given certain concessions. Since their body is configured to store energy in case of childbirth or hunger, the normal distribution for a woman who is not an athlete is considered to be 23-24% of the tissue.
For athletes
Calculating normal weight for athletes is complicated by many features:
- Type of sports discipline.
- Body type.
- Determination of glycogen levels.
For example, serious bodybuilders need to maintain a high percentage of body fat in the off-season (up to 30%), as it allows them to:
- Increase the synthesis of the hormone testosterone.
- It is a shock absorber and lubricant for ligaments and tendons.
At the same time, in the period before the competition, they dry out their body to 4-8% fat tissue. Such fluctuations in weight and percentage of fat tissue are unhealthy, and are achieved exclusively through a set of extreme fat burning during a cutting course (6-10 weeks), after which they return part of the mass. For athletes of other specialties, the weight norm is calculated so that the total percentage of body fat is less than 16%.
Types of Deficiency
Before you go on any specific diet and create a calorie deficit, you need to understand what types of deficits exist. This will allow you to lose weight correctly without nerves, setbacks, and stress for the body.
- Nutritional deficiency. Usually the result of diets that cause insufficient amounts of nutrients and nutrients to enter the bloodstream.
- Increased activity. Allows you to increase energy expenditure, which also leads to a calorie deficit.
- Extreme decrease in sleep and rest. If you need to lose 10 kilograms in 3 days, you can reduce the amount of sleep. Already on the third day, the body, in an attempt to obtain a sufficient amount of energy, will double its energy consumption.
In addition, artificially created deficits can be divided by intensity.

Stable
A stable calorie deficit is an ideal solution for those who are not in a hurry. You can start it in September and stay on this diet until May. A diet properly enriched with proteins and vitamins will provide an adequate level of satiety. At the same time, the body will lose up to 1-2 kilograms per week.
But the most important thing with this diet is that you won’t even notice how the extra pounds leave your body. In addition, this approach allows you to avoid skin stretch marks and other unpleasant side effects. Well, and the most important thing is that with such a deficiency, you don’t have to limit yourself to any one type of food; you can eat exactly the same as before – only less.
A stable calorie deficit, which allows the use of adipose tissue without loss of metabolic rate, is considered to be 10-17% of the total calorie content.
Increased
An increased calorie deficit is based on slightly different nutritional principles. In particular, this is the first approach in which the deficit is defined not as total calories minus expenses, but rather a nutritional deficit is created.
Accelerated deficiency nutrition has the following features:
- Significant predominance of protein products.
- Almost complete absence of carbohydrates.
- Low fat content.
- Huge amount of fiber.
- The total deficiency should reach 50% of the energy consumed.
An increased calorie deficit is intended solely for short-term weight loss. The target audience is athletes who know how to calculate basic calorie content, BJU, glycemic index, etc. When using an increased deficit, it can be noted that already 2-3 weeks after starting the diet, the body begins to adapt to such a lack of nutrients, which leads to reduction of metabolism, as well as destruction of energy consumers in the body. In particular, from such diets you can already lose some muscle tissue. At the same time, with a properly designed accelerated calorie deficit in the diet, you can absolutely safely get rid of up to 10% of your weight in a short time.

Prominent representatives of professional diets designed for an increased caloric deficit are:
- Low carbohydrate diet.
- Carbohydrate rotation.
- Keto diet.
- High protein diet.
And any other forms in which calories and nutrients are calculated on an individual basis.
Extreme
Unfortunately, among all the methods of proper weight loss and cutting, the most harmful ones have become the most popular. In particular, this is modern dietetics, which is published in magazines and on the Internet.
In order not to be included in the list of victims of the newfangled “apple and corn” diets, you need to understand how such diets work correctly, what they are fraught with, and why they are so popular. Any mono diet involves extreme calorie cutting. Very often on the Internet you can see very specific recommendations for “dumpling diets”, where it is recommended to eat no more than 900 kcal per day. With an average consumption of 2000-3000 kcal per day, 900 kcal is more than 60% of the deficit. And very often, they significantly exceed this threshold.

Why from 10 to 20%?
A smaller calorie deficit simply will not produce results, since the body will be able to overcome such a calorie deficit. At the same time, a huge deficit of more than 20% of normal calories will have a negative effect in the future.
Of course, now you will lose weight on a deficit, even if it is a 25% or even 30% deficit. However, a total lack of calories will be a total stress for your body, which needs to be responded to in a timely manner and eliminated.
Appetite will increase, the risk of breakdowns will increase, mood will worsen, the balance of hormones will be disrupted, and much more. The body needs all these defense mechanisms against starvation. It will be extremely difficult to leave such a diet while maintaining the results.
What happens to the body?
In the first days, metabolism is accelerated, producing a huge amount of adrenaline, which allows you to use fatty tissue (precisely intended for a hunger strike) to maintain strength. All this is done so that a person finds a source of food and is able to restore the calorie balance.
All this can last up to a week. During this time, the body leaves the lion's share of salt, fat and muscle tissue. The body optimizes all resources. And yes, you can really lose up to 15 kilograms in a week. In return you have to pay with your health. After all, the body burns out the main energy consumer, “muscle tissue,” which leads to dystrophy.
Actual fat loss is limited to 25% of the total weight lost, which means that immediately after normalization of nutrition, the weight will increase by at least ¾ of what was lost.
In addition, when trying to optimize the body’s resources, the work is disrupted:
- Gastrointestinal tract.
- Of cardio-vascular system.
- Ligamentous apparatus.
- Endocrine system.
Each time, diet can lead to irreversible changes.
Calculation of nutritional deficits
How to correctly calculate nutritional deficits. Everything is very simple, even if you decide to create an extreme deficit, remember the simple rules:
- Calculate calorie consumption.
- Subtract a percentage for your goals (10 to 75).
- Divide the resulting calorie content into 5-7 meals.
- Choose foods with a minimum glycemic index and high digestion time.
- Use an abundance of protein and fiber to maintain basic body functions.
You're getting fat
Now imagine that calories are a salary. Every day you spend money on food, transportation, housing, utilities, etc. In reality, this is energy expenditure for walking, thinking, digesting food and much more.
So, if your salary exceeds your expenses, you accumulate financial resources - calories. Where should the accumulated funds go? That's right - they need to be put aside in reserve.
You can store excess unused energy in the human body by creating fat stores. This is how you gain weight.
Lifehacks
One of the main life hacks that will allow you to painlessly create a calorie deficit for weight loss is the consumption of caffeine-containing drugs. It can be:
- Actually coffee.
- Strong tea without sugar.
- Energetic drinks.
- Decoctions from ginger root.
- Pre-workout complexes.
Note: green coffee is not particularly effective at burning fat, like other very specific foods.
Why does drinking coffee increase fat burning? Everything is very simple. Drinking in large doses (no more than 2 cups in 2 hours), caffeine affects the body as follows:
- Increases heart rate. This increases passive kcal expenditure.
- It opens the fat depot, the excess energy of which goes into the general bloodstream. The body strives to spend such an excess of energy as quickly as possible.
- Creates an insulin surge in the absence of sugar.
- Increases energy, and therefore calorie consumption in certain cases.

Another interesting life hack is to increase the number of meals, which allows you to trick the body for a short time. As a result, even with a severe calorie deficit (up to 80% of the norm), the body does not slow down metabolism, but with the help of insulin releases, it opens a fat depot, from where excess energy passes directly into the blood, accelerating weight loss.
With extreme diets, the recommended number of meals is considered to be 5 or more.
Losing weight
It's quite simple. Now imagine that you are not paid as much as you would like. There is not enough money for your daily expenses, so you have to spend your nest egg. In our case, its role is played by fat on the abdomen, waist, and hips. If you continue to receive less, you will begin to waste your nest egg, that is, accumulated fat.
When you eat fewer calories than you need to cover energy costs, the body creates a calorie deficit , and the body makes up for the lack of energy from its fat reserves. This is how you lose weight.
Calorie consumption calculation
For many, caloric intake is calculated exclusively experimentally. In particular, someone uses formulas to calculate calorie deficit . Some people select calorie intake individually based on performance. However, the general schemes that are used in bodybuilding and powerlifting do not work, since the following factors must be taken into account:
- Daily activity during the day.
- Consumption of caffeine carriers.
- Amount of sleep per day.
- Presence of mental activity.
- Availability of glycogen reserves in muscles and blood sugar.
All this is quite complex, and, usually, if you are not a competitive athlete, it is not necessary to take everything into account; it is enough to have a sign of calorie consumption on hand for a particular type of activity.
Note: the table shows values per pure kilogram of weight, excluding fat tissue. Even if you are a fairly athletic person, remember that if you are not cutting, the percentage of fatty tissue in your body is up to 25% of your total weight.
| Kind of activity | Calorie consumption per kilogram of weight kcal/hour |
| Dream | 1.5 kcal/hour |
| Walking | 5 kcal/hour |
| Digestion of food | 0.5 kcal/hour |
| Low intensity workout | 12 kcal/hour |
| Cardio load | 25 kcal/hour |
| Mental activity | 30 kcal/hour |
| Sitting at the computer | 0.07 kcal/hour |
| Reading | 6 kcal/hour |
| Writing texts manually | 4 kcal/hour |
| Writing texts using the keyboard | 3 kcal/hour |
| Gaming | 0.9 kcal/hour |
| Office work | 1.2 kcal/hour |
| Cybergaming (increased adrenaline) | Up to 50 kcal/hour |
| Going to the grocery store | 3.5 kcal/hour |
| Squats | 25 kcal/hour |
| Push ups | 27 kcal/hour |
| Pull-ups | 32 kcal/hour |
| Playing a musical instrument | 1.9 kcal/hour |
| Remembering information | 7.9 kcal/hour |
| Lengthy discussions | 3.5 kcal/hour |
| Passive flow | 0.5 kcal/hour |
| High intensity workout | 18 kcal/hour |
| Climbing stairs | 16kcal/hour |
| Cleaning the apartment | 9 kcal/hour |
| Washing dishes | 6 kcal/hour |
Based on these data, you can calculate the required daily consumption base. Let us remind you that for a normal deficit (with fat burning up to 1.5% of the total weight) per month it is enough to create a 10% calorie deficit in the diet.
How to calculate the required number of kilocalories per day? Which calorie deficit should you choose?
At the same time, fortunately or unfortunately, in addition to the main metabolism, we have physical activity, which also requires a certain amount of energy.
The required number of kilocalories spent on daily physical activity and basal metabolism can be determined by multiplying the basal metabolism by the coefficient depending on the intensity of physical activity. A sedentary lifestyle will correspond to a coefficient of 1.2; if a person exercises 1-3 times a week, then the coefficient will be equal to 1.3.
There are also more accurate formulas that allow you to determine the daily need for kilocalories. These include the Harris Benedict formula. It takes into account the person’s gender, body weight, height and age. All these characteristics are multiplied by the corresponding coefficient, and thus the basal metabolic formula is calculated, which is also multiplied by the corresponding coefficient of physical activity, which makes it possible to determine the daily rate of kilocalorie consumption to maintain the existing body weight.
Calorie consumption example
Based on the tabular data, we will calculate the approximate consumption for a person with an athletic build (up to 20% fat tissue) weighing 75 kilograms. The net weight of such a person is 60 kilograms.

- Sleep 8 hours – up to 720 kcal. Why so much? Everything is very simple. During sleep, the body rearranges all functions, launches intense anabolism, and in some phases of sleep, on the contrary, catabolic processes begin.
- High intensity training – 1 hour – 1080 kcal.
- Office work – 8 hours – 576 kcal.
- Meals (5 pieces) for 15-20 minutes. -60-80 kcal.
- Walking to work and back – 1 hour 210 kcal.
- Gaming – 2 hours a day – 100 kcal.
- Passive consumption – 720 kcal.
The total consumption, not counting small activities, is 3500-3700 kcal. To create the correct deficit, it is necessary to limit food to 3000-2800 kcal. In the absence of training, the consumption per day is 2500-2700. Accordingly, nutrition on days without training is 2000-2200 kcal.
Let's say today you ate for lunch:
- Vermicelli soup - 270 kcal - Two fried pork chops - 530 kcal - French fries (140 g) - 420 kcal - A glass of sweet compote - 170 kcal
As a result, we get as much as 1390 kcal.
Let's try to choose other dishes and create a small calorie deficit:
- borscht (250 ml) - 200 kcal - one fried pork chop - 265 kcal - mashed potatoes with butter 170 kcal - a glass of dried fruit compote - 130 kcal
As a result, we will get less - 765 kcal
If you can’t lose weight, let’s try to further increase the calorie deficit and take it for lunch:
- lean borscht (200 ml) - 100 kcal - salad of tomatoes, cucumbers and green leaves - 50 kcal - a little beef stew (115 g) 210 kcal - mashed potatoes with butter - 170 kcal - glass of water - 0 kcal
The result is a meal for 530 kcal
Which lunch to choose? How much should you reduce your calorie intake to lose weight?