What are carbohydrates and what are they for?
Carbohydrates are organic substances, an essential chemical element that is necessary for the construction of a number of important complexes in the body. They are a key component of most foods and serve as the main source of energy for humans.
Already in the very term “carbohydrate” we hear the word water. In fact, there is no water as such in these organic chemical compounds. In 1844, a Russian chemist from the Baltic states first gave such a definition to the compound of carbon (C) with a hydroxyl group (H2O). This word is firmly rooted in world science. There is another name for carbohydrates - sugars.
This is interesting!
Carbohydrates make up the bulk of all dry mass of living things, plants, bacteria and inorganic compounds on Earth. The cells of animals, plants and humans consist of carbohydrates in different quantitative ratios. For example, if for plants this figure reaches 80% of the dry mass of the plant, then for an animal this ratio is approximately 5%.
The carbohydrate class is so vast and diverse that it is difficult to imagine any organism on our planet without these substances.

Carbohydrates, as a constructor, consist of elementary particles, which in chemistry are called saccharides. The entire classification of carbohydrates is divided depending on their properties, or more precisely on the ability to dissolve in water - this process is called hydrolysis. During this process, sugars are broken down into monomers. Monomers are the smallest units of carbohydrates.
Thus, they distinguish:
- Monosaccharides contain one single unit of sugar, which quickly dissolves in water and enters the bloodstream. Blood glucose levels rise sharply. Monosaccharides have a high glycemic index.
- Oligosaccharides are slightly more complex carbohydrates; they contain two or more monosaccharide components. The most popular and in demand in industry is raffinose, which contains fructose, glucose and galactose. A high content of these substances is found in ordinary beets.
- Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates that contain tens or even hundreds of monomers. They dissolve in water over a longer period of time and break down into their components for quite a long time.

Types of carbohydrates
Saccharides are a large group of substances that vary in molecular composition. It determines a wide variety of glucides.
Depending on the complexity of the molecules, glucides are classified as follows:
- monosaccharides;
- disaccharides;
- polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are carbohydrates that contain only one type of molecule. These are the following substances:
- glucose (found in honey and fruits);
- fructose (also found in honey and fruits);
- galactose (found in milk).
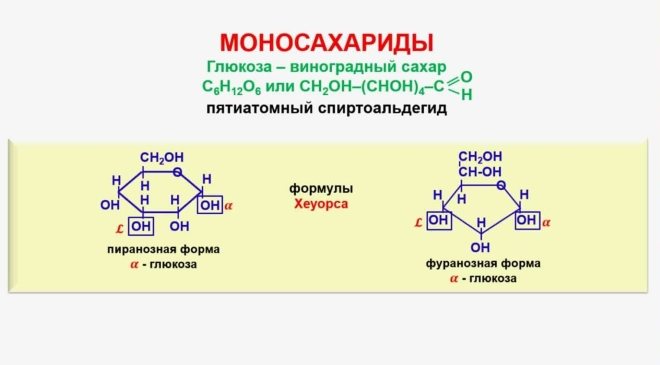
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are carbohydrates containing 2 molecules. These include:
- Sucrose (white sugar made from sugar beets or cane). It includes glucose and fructose.
- Lactose (consists of glucose and galactose), which is present in the milk secreted by animals of the class mammals.
- Maltose (includes 2 glucose molecules), which is found in beer and corn.

Oligosaccharides
Oligosaccharides are carbohydrates containing from 2 to 10 molecules. Along with disaccharides, their most common type are trisaccharides:
- Raffinose. It contains galactose, glucose and fructose. Contained in sugar beets and cotton seeds.
- Gentianose – contains 2 molecules of glucose and 1 fructose. It is extracted from the root part of plants of the gentian genus.
3 polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are carbohydrates with several molecules. These include:
- glycogen (found in the liver);
- starch containing many glucose molecules.
Starch includes:
- cereals (wheat, corn, rice);
- root vegetables (potatoes, pears, fodder beets);
- grains and legumes (beans, lentils, green peas, chickpeas, beans, soybeans).

Functions of carbohydrates in the body

- The main role of carbohydrates in the body of many living beings, including humans, concerns the replenishment of energy reserves. Their absence in the diet leads to depression of all organs and systems of the body. It is important to understand that not only carbons have an energy function - it is the joint work of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. When there is an excess of glucose, it is deposited into glycogen, and then through complex biochemical transformations into adipose tissue.
- Carbohydrates are very necessary for the central nervous system. Brain cells function only thanks to large amounts of glucose. If the body receives the right amount of carbohydrates, the nervous system works properly, but as soon as the glucose level drops, the person becomes absent-minded, and is plagued by weakness and dizziness. This condition is common for people with low blood sugar syndrome or women on a carbohydrate-free diet.
- Muscle tissue really needs clean energy during work. When contracting and relaxing, smooth muscle tissue myocytes use carbohydrate energy. Growth and increase in muscle mass are provided by protein, but in the direct presence of carbohydrates. If there is not the required amount of sugar in the blood, then the muscles are destroyed and a complete metabolic disorder occurs.
- Complex carbohydrates, which include cellulose, regulate the functioning of the digestive system. Fiber itself does not provide any nutritional benefit, but it creates pressure on the intestinal wall and this stimulates its work. In addition, coarse fibers play an important role as a sorbent for the body. This removes toxins, other harmful substances and your own metabolic products. The growth of beneficial bacteria in the intestines is also ensured by fiber, because it is their food.
- Fats, proteins and carbohydrates are closely interrelated. For example, for the oxidation of fat breakdown products - acetate, oxaloacetic acid is extremely necessary, which in turn is a breakdown product of carbohydrates. If there are no carbohydrates in the diet or they do not enter the body’s cells, then the body is filled with fat processing products, ketone bodies. This has a very bad effect on the human condition. If we talk about metabolic diseases, ketoacidosis is a dangerous and life-threatening condition.
Choose the right carbohydrates
When it comes to food and drinks, choose options filled with beneficial micronutrients and vitamins. The three rules below will help you with this. But, let us finally note that if you are a very active person who wants to increase your productivity, then not all of these rules will suit you.
- Eat more complex carbohydrates from natural foods
Vegetables, legumes, nuts and seeds, 100% whole grain bread, pasta, brown rice - these foods are a good source of fiber, vitamins, minerals and protein.
- Eat less processed food
Foods like white rice, white bread and regular pasta are more processed and therefore lack fiber.
- Eat simple carbohydrates in moderation
Most sources of simple (fast) carbohydrates are considered “empty calories” because they contain virtually no micronutrients but are high in calories. They are also the most common cause of blood sugar spikes. Fruits and milk are exceptions because they are high in vitamins and minerals.
The path of carbohydrates in the body

To make the metabolic process, namely carbohydrate metabolism, more understandable, you need to know what path these nutrients take in the human body and what transformations they undergo.
Carbohydrates in the form of food enter the mouth. If these were monosaccharides, then they remain unchanged. But if these were polysaccharides and complex carbohydrates, then in the oral cavity they begin to transform into simpler forms: oligosaccharides and monosaccharides. Saliva contains ptyalin with an alkaline environment and it is this that begins the digestion of carbohydrates. There are practically no changes in the stomach with carbohydrates.
Final digestion and breakdown into elemental sugars occurs in the small intestine. In the duodenum, pancreatic enzymes act on the food bolus. At the distal end of the small intestine, glucose is absorbed into the blood. Its further path lies to the cells through the main barrier of our body, the liver.
The final cleansing of the blood from harmful and toxic substances takes place in the liver, and the level of glucose in the blood is stabilized there. If its level exceeds 3.3-5.5 mmol/l of blood, then the liver converts the excess into glycogen.
In case of deficiency, glucose is replenished from glycogen stores in the liver. Thus, glucose is sent to all cells of the body without exception. There, through complex transformations, energy is extracted from it to form.
Quality carbohydrate sources

Carbohydrates are an integral part of any diet. The body receives most of its energy and many vitamins and nutrients from them. Foods where carbohydrates are found in abundance include many plant foods such as rice, pasta, beans, potatoes and many other grains and vegetables.
When choosing grain products, we highly recommend choosing whole grain options such as whole grain bread, brown rice, whole grain pasta, quinoa, oats, and bulgur.
Sources of complex carbohydrates
What carbohydrates contain that are slowly digested:
- vegetables;
- legumes;
- cereals*;
- fruits;
- beet;
- carrot;
- corn;
- peas;
- potato;
- turnip;
- beans;
- lentils;
- lima beans;
- pinto beans;
- split peas;
- barley;
- oats;
- rice;
- rye;
- wheat;
- edible seeds.
*as well as grain products - whole grain wheat bread, crackers or pasta.
Sources of simple carbohydrates (Natural)
- Fructose (fruit sugar)
- Lactose (milk sugar)
- Fruits and juices such as apples, oranges, pineapples.
- Dairy products such as milk and yogurt.

Complex carbohydrates

While monosaccharides in their pure form are rarely found in nature, polysaccharides make up the bulk of food for humans and animals. They can consist of tens of hundreds of monomers.
Chemists distinguish these substances according to the general principle of their structure. Among them are:
- Homopolysaccharides are substances containing the same type of monosaccharides.
- Heterosaccharides consist of sugars that differ in structure and function. The group of homopolysacchorides includes known monomers.
Organic homopolysaccharides of plant origin include:
- starch;
- cellulose;
- pectin substances.
To organic compounds of animal origin:
- glycogen;
- chitin.
Hormones that regulate carbohydrate metabolism in the body
For the body, the main task is to maintain the functionality of the brain, as a central organ that regulates all processes. Therefore, it is the brain that absorbs glucose the most.
The end product of glucose breakdown, or in the words of glycolysis biochemists, is an ATP molecule. It is energy in its purest form that causes muscles to contract, the heart to pump blood, and neurons to perform their important function in the brain so that a person can speak, hear and think. Everything is very cyclical and continuous. When energy production is not possible or the regulation of this process is impaired, death occurs.
This is important to know!
In the process of evolution, spare or backup pathways for producing glucose have been established in cells that produce ATP. In other words, if a person stops eating carbohydrates, then glucose is obtained from proteins and fats.
Our amazingly intelligent body does not trust such an important process as regulating blood sugar levels to the human mind. But in order to determine whether it’s time to eat or not, special cells called receptors are located in the internal organs, namely the gastrointestinal tract and liver. They, like microscopic laboratories, determine the level of drop in blood glucose.
To prevent glucose levels from rising above normal, when carbohydrates enter the body excessively, it is consumed by the liver, muscles and, last but not least, adipose tissue. About 20% of carbohydrates broken down in the intestines enter the liver and become glycogen. Some goes into adipose tissue, and some is broken down into energy molecules.
Approximately 40% of glucose from the intestines simply enters the bloodstream and, due to its special permeability, is absorbed by skeletal muscles and adipose tissue. This entire complex process is regulated by insulin and glucagon.
Insulin
This hormone is known to a wide range of people. Its deficiency leads to such a serious disease as diabetes.
Insulin is produced in the pancreas, but leaves it inactive. Activates its protein breakdown products. Insulin acts only through specific receptors located in cells. There is a type of diabetes mellitus in which a lot of insulin is produced, but there are no receptors, and similar symptoms occur.
The effect of insulin on carbohydrate metabolism:
- reduces blood glucose levels to 3.3-5.5 mmol;
- promotes the deposition of fats in the body by converting excess glucose into fat;
- stimulates the formation of fatty deposits in the liver and fatty tissue;
- affects the formation of cholesterol;
- has a positive effect on the synthesis of new proteins;
Glucagon
It is also produced in the pancreas. Glucagon consists of amino acids and affects the following processes in the body:
- increases the level of glucose in the blood when it decreases;
- affects the active breakdown of glycogen;
- affects the formation of glucose from protein and lipids;
- actively stimulates the breakdown of adipose tissue;
Adrenalin

It is synthesized in the adrenal gland, namely in its medulla layer, when the hormone is released and in what quantity the brain regulates - this is a stress hormone.
When a dangerous situation arises, which, according to the brain, threatens life, a command is sent to the adrenal glands and adrenaline enters the blood:
- the accumulation of glycogen in the muscles is activated, followed by its transition to glucose;
- Glucose is needed by skeletal muscles for intense work, fighting or running;
- reduces the amount of insulin.
Cortisol
This is also a hormone of the adrenal glands, but of the cortical part. Cortisol performs important functions:
- increases blood glucose levels;
- affects the redistribution of adipose tissue in the body, namely, it leads to a decrease in fat accumulation in the arms and legs and stimulates the appearance of fat on the back and abdomen;
- causes the death of lymphocytes;
- reduces the level of inflammation.
Thyroid hormones
The thyroid gland is perhaps the most important organ that actively influences the metabolism in the body. It is also called the cardinal gray, because many processes in the body do not occur without the influence of thyroid-stimulating hormones.
The synthesis of hormones directly depends on the supply of iodine from the external environment and this is necessary for such important functions in the body:
- basal metabolism increases - the amount of energy required for digestion and the production of digestive enzymes increases;
- energy metabolism in cells accelerates.
Somatotropic hormone
This is a special hormone that is produced in the pituitary gland. During the period of child growth and development, it is this hormone that affects everything. On the child’s height, weight, muscle development and skeletal growth.
In an adult body, the presence of somatotropic hormone is dangerous; when it is produced, it indicates the presence of a brain tumor and is manifested by acromegaly.
Somatotropic hormone performs the following functions in the body:
- reduces glucose consumption in muscles;
- increases glucose production in the liver;
- increases insulin production;
- the hormone makes skeletal muscle and adipose tissue cells insensitive to insulin and this leads to the accumulation of glucose in the blood.
Fast carbohydrates
Simple (fast) carbohydrates are sweet-tasting organic compounds that consist of two or one molecule of monosaccharides or disaccharides:
- Monosaccharides : fructose (honey, ripe fruits and vegetables), glucose (grapes, carrots, watermelon, berries), galactose (dairy products, celery)
- Disaccharides : lactose (milk and dairy products), sucrose (beets and sugar cane), maltose (sprouted grains, beer)
Fast carbohydrates are primarily foods with a high glycemic index. To prevent foods high in fast carbohydrates from being transformed into fat, they should be eaten in small portions and only in the first half of the day. In this way, blood sugar spikes and insulin spikes can be effectively prevented. Fast carbohydrates should be completely excluded from the diet in the second half of the day.
Give preference to slow carbohydrates. It is better to consume fast carbohydrates in limited quantities and only in the first half of the day.
Harm of fast carbohydrates:
- fat accumulation
- weight gain
- sudden spikes in blood sugar
- rapid onset of hunger
- intense insulin release
- increased risk of developing diabetes
Products that are classified as fast carbohydrates
Most foods with a lot of fast carbohydrates are very tasty. That's why it's hard to give them up. In addition, foods with fast carbohydrates are generally more accessible to the average person. For example, unpolished rice is more expensive than white rice, whole grain bread is more expensive than white bread, hard pasta is more expensive than soft pasta, etc. But if you want to lose weight and improve your health, it is important to reduce your intake of fast carbohydrates.
Due to their high glycemic index, simple carbohydrates negatively affect the human body. Fast carbohydrates for the most part do not supply the body with nutrients, but only satisfy hunger for a short period of time. With excess and low activity, simple carbohydrates are transformed into subcutaneous fat. Consumption of fast carbohydrates in the first half of the day is especially dangerous for your figure.
Fast carbohydrates include:
- white bread and flour products made from white flour (cakes, buns, cookies)
- sugar and sugar-containing products
- confectionery, ice cream, preserves, jams
- milk chocolate and bars
- pasta made from durum wheat
- white milled rice
- instant porridge and muesli
- cornflakes and popcorn
- alcohol (especially beer and spirits)
- store-bought sauces (ketchup, mayonnaise, etc.)
- carbonated drinks, sweet lemonades and juices
- fast food and almost all dishes in fast food restaurants
- boiled starchy vegetables (potatoes, pumpkin, carrots and beets)
- sweet fruits (bananas, grapes, persimmons, watermelon, mango)
- canned fruits
- dried fruits
- honey
Also, some foods that have undergone strong heat treatment can be classified as fast carbohydrates. Due to the destruction of fiber (dietary fiber) during cooking, even complex carbohydrates can be obtained into simple ones. For example, if you overcook porridge until it becomes pureed or boil hard pasta.
Do not overcook grains and try to eat fresh vegetables and fruits. This is useful not only for losing weight, but also for preserving maximum nutrients in foods.
Why are fast carbohydrates dangerous to health?
Once in the stomach cavity, simple carbohydrates are transformed into sugar in just a couple of minutes. An excess of sugar poses a danger to the brain and its functionality. In this state, the body tries to neutralize the problem as quickly as possible and converts excess fast carbohydrates into fat reserves.
The process is accompanied by sharp jumps in sugar levels, which leads to the re-emergence of hunger and encourages a person to satisfy it with something tasty and sweet. When consuming a large amount of fast carbohydrates, a vicious circle arises: the body feels a constant feeling of hunger due to sugar fluctuations, satisfying it with food with a high glycemic index. These spikes in sugar levels seriously increase your risk of developing diabetes. When there is an excess of glucose, it is deposited into glycogen, and then, through complex biochemical transformations, into adipose tissue.
In addition, carbohydrates in this form stimulate the release of endorphin, or the pleasure hormone, which suppresses stress reactions in the body. Therefore, foods high in fast carbohydrates and glycemic index can cause psychological dependence.

In what cases are fast carbohydrates necessary?
Scientific research shows that sugar in the form of fast carbohydrates is necessary for the body, but in reasonable doses. Thanks to sugars, proteins and fats are absorbed, so balance is important in everything. As we noted above, the total amount of fast carbohydrates when losing weight should be kept within 10-15% of the total daily caloric intake.
Also, simple carbohydrates can be indispensable in situations of rapid energy recovery. A sharp increase in blood glucose levels can help cope with conditions such as:
- nausea
- dizziness
- faintness
The main task of fast carbohydrates is to give our body quick energy. If this energy is not used, then the body will accumulate it “in reserve” in the form of subcutaneous fat. If you want to minimize the harm from consuming fast carbohydrates, then increase physical activity (fitness, walking, sports, exercise).
Fast carbohydrates help:
- replenish glycogen stores
- cope with difficult mental tasks
- neutralize toxins
- quickly restore energy
- get rid of acute stress
Fast carbohydrates are often consumed by athletes after training. In the first 30 minutes after intense exercise, the protein-carbohydrate window opens in the body. This period makes it possible to consume fast carbohydrates without risk to your figure and health - to restore muscles and activate their growth.
Not eating after a workout is not very beneficial, since there is a surge in catabolic processes that destroy muscles and interfere with quality growth. For example, a smoothie with banana and cottage cheese after an active workout would be the right choice.
Fast carbohydrates and training:
- If a person leads an active lifestyle, then a moderate amount of fast carbohydrates will not harm the body. Regular physical activity or good daily activity (outdoor walks and walking) will help avoid situations where fast carbohydrates are converted into subcutaneous fat.
- If a person is losing weight, but does not exercise and leads a sedentary lifestyle, then it is better not to get carried away with fast carbohydrates. Insufficient levels of physical activity while consuming simple carbohydrates increases the risk of weight gain and obesity.
We recommend watching:
- Morning exercises fully standing without a mat: 20 exercises
- Active morning exercises for losing weight in the stomach: 20 exercises
- Joint gymnastics: why you need to do + 20 exercises
Is it possible to eliminate fast carbohydrates completely?
As a rule, fast carbohydrates are excluded during strict diets. However, this is unlikely to become a permanent norm of life. Sugar is simply irreplaceable as a source for mental and physical activity. It is most rational to follow the basics of proper nutrition and be more attentive to sources of fast carbohydrates. After all, these include both bananas and chocolates. Of course, constantly eating donuts and french fries has nothing to do with proper and healthy nutrition, but we still recommend including some simple carbohydrates in the menu.
So, according to the principles of PP, complex rather than fast carbohydrates should predominate in the diet. Many fast carbohydrate foods can be interchanged. Instead of sweets and baked goods, it is better to eat berries, dried fruits or fruits, instead of baked goods - starchy vegetables, instead of fried potatoes - boiled potatoes in their jackets.
Avoid the following fast carbohydrates:
- white bread and white flour products
- sugar and sugar-containing products
- confectionery and baked goods
- fast food and processed foods
- sweet drinks and alcohol
What can be replaced:
- pasta made from durum wheat ==> pasta made from durum wheat
- instant cereals and muesli ==> regular cereals
- white rice ==> brown or dark unpolished rice
- canned fruit ==> fresh fruit
- sweet fruits ==> unsweetened fruits, especially green apples
- ketchup, mayonnaise ==> healthy sauces, prepared yourself
- French fries and mash ==> jacket potatoes (in moderation!)
- milk chocolate ==> dark chocolate above 70% (moderate!)
- sugar ==> honey, dried fruits (in moderation!)
We consume the last products on this list very moderately when losing weight. Don't forget that they still remain fast carbohydrates, so you shouldn't abuse them.
It is important to understand that products such as boiled carrots, beets, pumpkin, corn, as well as watermelon, melon, dates, bananas, and grapes have a high glycemic index and are most often classified as fast carbohydrates. But these products are healthy, they contain important micro- and macroelements. Therefore, it is not recommended to completely exclude them from the diet. However, if you are in the process of losing weight, then it is better to consume the listed products no more than twice a week in small portions. You don't have to completely eliminate fast carbohydrates when losing weight. It is important to choose the safest ones!
Top 10 most useful fast carbohydrates:
- Honey
- Grape
- Dates
- Dried apricots
- Prunes
- Raisin
- Watermelon
- Pumpkin (cooked)
- Carrots (cooked)
- Beets (cooked)
The list above shows the most useful foods from the group of simple carbohydrates for weight loss. They successfully satisfy the craving for sweets and will be especially useful for those who cannot live a day without something tasty. Although such products contain fast carbohydrates, they are healthy, rich in microelements, vitamins and minerals.

What is the glycemic index

The glycemic index is a very arbitrary calculation system that relates only to carbohydrates. Thanks to it, you can determine which foods contain carbohydrates that can change blood glucose levels.
In other words, there are foods that contain large amounts of simple or complex carbohydrates with a short chain of monomers. For example, potatoes, its index is 95, which means that when 100 grams of potatoes enter the body, starch is quickly broken down and a lot of glucose enters the blood.
But the glycemic index does not determine the rate at which blood sugar rises. This indicator is calculated relative to glucose injected directly into the body.
This is interesting!
For the first time, Canadian scientist David J. A. Jenkinson proposed determining the glycemic index. He took the change in blood sugar levels after administering glucose intravenously or orally as the gold standard and took this figure as 100. All other foods with carbohydrates are calculated relative to one hundred.
For example, if you eat 100 grams of honey with a glycemic index of 90, it turns out that your blood sugar level will rise to the same level as if a person ate 90 grams of pure glucose.

Fortunately for us, all products have been converted to the glycemic index system, and there is no need to calculate it yourself. This classification of carbohydrate-containing products was developed specifically for patients with diabetes in order to correctly adjust their diet. But for people who watch their weight and lead a healthy lifestyle, this indicator is just as important.

It is generally accepted that there are two types of food distribution according to the glycemic index.
The first one is suitable for products and is divided:
- low - glycemic index 55 and below;
- average from 56 to 70;
- high - 71 and above.
The second is designed for diets accordingly:
- high - 61 and above;
- average - 45-60;
- low - 45 and below.
Why it is important to observe and know glycemic index levels. Because numerous studies by nutritionists and endocrinologists have proven that people whose diet is in the range of 40-55 are less likely to suffer from diabetes and heart disease.
Application of knowledge about the glycemic index

From all that has been said above, it is clear that the higher the glycemic index of a product, the higher the level of sugar in a person’s blood after consuming it.
Accordingly, the higher the glycemia, the more insulin is released from the pancreas. Insulin prevents the breakdown of stored fats and promotes the accumulation of unclaimed glucose in fat deposits.
It is important
Thus, to keep your weight within acceptable limits, you need to know what foods to eat. In addition, excess weight and increased deposition of adipose tissue negatively affects the condition of the entire body.
Therefore, there are a number of reasons why you should eat a diet with a low glycemic index:
- Prevention of diseases of the visual analyzer.
- Prevention of heart and vascular diseases.
- Maintaining a balanced level of the body's energy reserves.
- Prevention of breast cancer.
- Maintaining normal weight.
- Prevention of late hystosis in pregnancy and the development of diabetes in pregnant women.
- To improve performance during sports training.
This is not the entire list of useful recommendations from nutritionists and therapists for maintaining the reasonable use of carbohydrates.
With the advent of fashion for healthy eating and lifestyle, the Internet has been filled with many tables indicating the glycemic index of a particular product. It is difficult for the average person to navigate rather contradictory information.
Let’s say in one source the index of pasta is 40 and classified as low, and in another source, the same pasta is assigned a glycemic index of 70. This occurs as a result of incorrect interpretation of the tables, as well as due to different types of the same product .
It is important to know!
Perhaps the most accurate and authoritative source for publishing tables with the glycemic index level should be considered the University of Sydney. This institution conducts independent research and publication of databases.
For example, in Russia and the CIS countries there are traditional and rather beloved products with a glycemic index higher than that of glucose itself.
- White bread;
- cornflakes;
- cooked white rice;
- sucrose (honey, gingerbread, refined sugar, dates, raisins);
- maltose (honey, kvass, muesli, beer, marmalade and others).
To be one hundred percent sure of the result, you can conduct research on the products you are interested in yourself. To do this, you will need a healthy subject, a certain amount of pure glucose and the foods of interest. Glucose levels can be measured independently using a glucometer or in a laboratory.
High GI foods
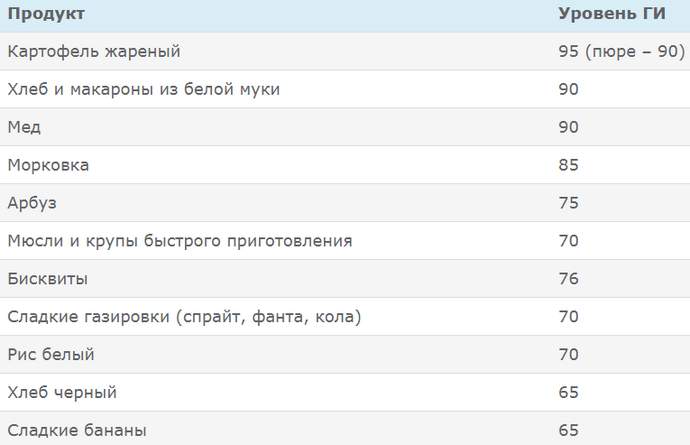
Low GI foods
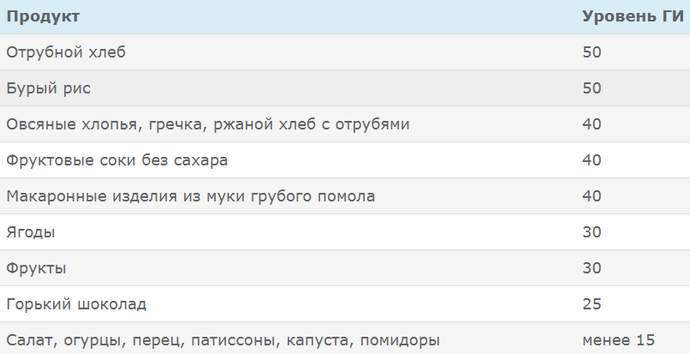
Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, what is it?
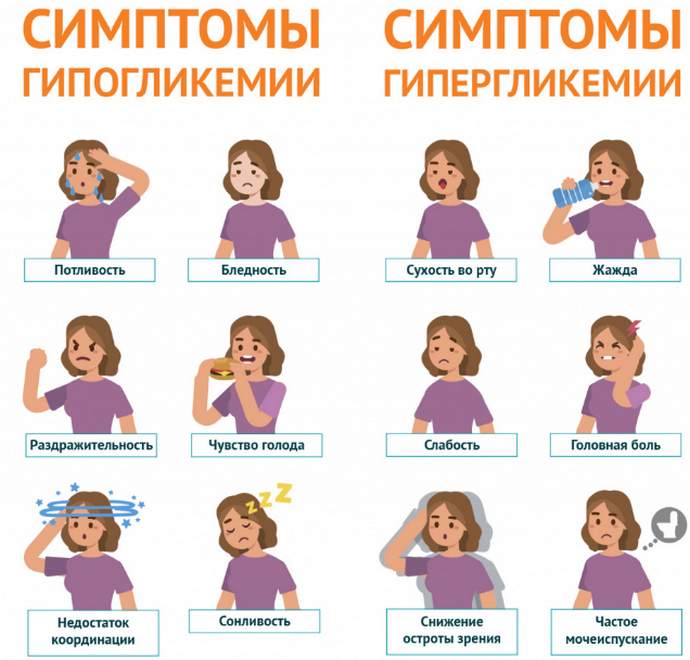
If a person does not have problems with the pancreas, which causes disruption of hormone synthesis, then the symptoms of hyperglycemia do not appear.
It’s a different matter if this condition is chronic and is caused by the fact that insulin does not have time to convert excess glucose into glycogen. Then three main symptoms appear that should alert a person:
- Polyuria is an increased amount of urine and urination.
- Polyphagia - a person eats often and a lot because the cell cannot receive glucose.
- Polydipsia - a person often drinks a lot due to dry mouth and thirst caused by changes in the osmotic composition of the blood.
These are direct indications for a visit to a therapist or endocrinologist.
Another thing is hypoglycemia, a condition in which there is a lack of glucose in the peripheral blood. The cells do not receive the required amount of energy material and therefore the entire body suffers. Other reasons include:
- Fluid deficiency.
- Abuse of refined carbohydrates.
- Using insulin or another glucose-lowering drug in excess of the required dose.
- Wrong number of meals when treating diabetes.
- Heavy physical activity.
- Systematic alcohol consumption.
- Hunger.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms of the pancreas.
Hypoglycemia syndrome manifests itself in different ways, depending on the severity. Symptoms include:
- hand tremors and unsteadiness of gait;
- feeling of hunger, thirst;
- nausea and general weakness;
- increased excitability or, on the contrary, inhibition;
- increased sweating, arrhythmia;
- in severe cases, coma and profound neurological impairment.











