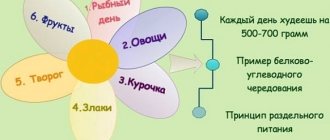
Most people who want to get their body into ideal shape can resort to low-calorie eating . This does not require expensive products, there is no need to prepare complex dishes, you can use simple, affordable food products that are always available for sale.
Quick navigation through the article:
- Diet menu for the week
- Calorie table for low-calorie foods
- Food diary
- Physical exercise
- Reviews and results of losing weight
The main point of a low-calorie diet is to limit fats and easily digestible carbohydrates . Everyone can create their own diet, limiting themselves to flour, fatty and sweet dishes.
Sample diet menu for a week
When using a low-calorie menu, you need to eat 5-6 times a day, in small portions , the weight of which does not exceed 200-250g.
First you need to use a kitchen scale, then you will learn how to determine the weight of portions by eye. Low-calorie diet for a week menu minus 5 kg (for people with very high weight).

1
The first day:
- Breakfast: rice porridge, boil 3-4 tablespoons, add a little low-fat milk. You can add a handful of raisins, dried fruits;
- Second breakfast: grated apple;
- Lunch: chicken soup, cabbage salad;
- Afternoon snack: kefir 1-2%;
- Dinner: baked fish, tomato and cucumber salad.
2
Second day:
- Breakfast: omelet of one yolk and two whites with low-fat milk;
- Second breakfast: grated carrots;
- Lunch: boiled chicken, cucumber and herb salad;
- Afternoon snack: tomato juice;
- Dinner: beef meatballs, lettuce with olive oil.
3
Day three:
- Breakfast: low-fat cottage cheese with chopped orange;
- Second breakfast: baked apple;
- Lunch: stewed vegetables (carrots, cabbage, onions, herbs, zucchini, eggplant, pumpkin, whatever is available) with the addition of minced chicken;
- Afternoon snack: orange;
- Dinner: stewed fish, green pea and herb salad.
4
Day four:
- Breakfast: oatmeal with hot low-fat milk and berries;
- Second breakfast: baked or fresh pear;
- Lunch: vegetarian soup, boiled turkey, cauliflower salad with herbs and olive oil;
- Afternoon snack: kefir with berries, can be whipped in a blender;
- Dinner: boiled veal, grilled vegetables: tomatoes, carrots, onions, zucchini.
5
Day five:
- Breakfast: buckwheat porridge with low-fat milk and a little butter;
- Second breakfast: grapefruit;
- Lunch: chicken cutlets, salad of Chinese cabbage, herbs and fresh cucumbers;
- Afternoon snack: apple juice;
- Dinner: salmon steak or salmon, tomatoes.
6
Day six:
- Breakfast: millet porridge with milk, you can add some dried fruit;
- Second breakfast: low-fat yogurt without additives;
- Lunch: soup with veal meatballs, vegetable salad;
- Afternoon snack: bifidokefir with fresh berries;
- Dinner: two boiled eggs, cucumber salad, greens.
7
Day seven:
- Breakfast: cottage cheese casserole with one raw egg and chopped fruits or berries;
- Second breakfast: grated apple;
- Lunch: boiled or baked chicken breast, stewed vegetables (cabbage, carrots, zucchini, onions, peas, tomatoes);
- Afternoon snack: low-fat fermented baked milk;
- Dinner: boiled turkey, two tomatoes, two cucumbers.
Having understood the basic principle of this diet , it is not difficult to select products yourself. You can choose your favorite ones that you personally like and cook them more often than others. In addition to the main menu, you need to supplement your diet with weak tea or coffee without sugar . You can add low-fat milk. The total daily calorie content should not exceed 1200 kcal. Also pay attention to the 1200 kcal diet, its principles will also be useful to you.

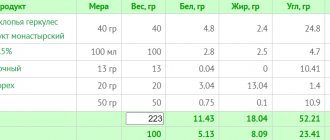
In order for weight loss on a low-calorie diet to be successful, you need to know which low-calorie foods should form its basis. In the table you can find a list of products that can be used in the low-calorie diet menu .
The table is convenient to use when choosing side dishes from vegetable dishes for protein dishes.
How to make a menu correctly
Before you create a weight loss menu for a week or a month, you need to:
- Assess your level of physical activity.
- Calculate the kcal norm for the day.
The level of physical activity can be:
- Minimum - sedentary work, no sports (coefficient 1.2).
- Light - sedentary work, but there are light workouts up to 3 times a week or long walks (coefficient 1.3).
- Medium - work that requires little physical effort, light training up to 5 times a week, morning or evening exercises (coefficient 1.5).
- High – work with physical activity, active lifestyle, intense sports up to 5 times a week (coefficient 1.7).
- Extremely high - hard physical work, hard training every day (coefficient 2).
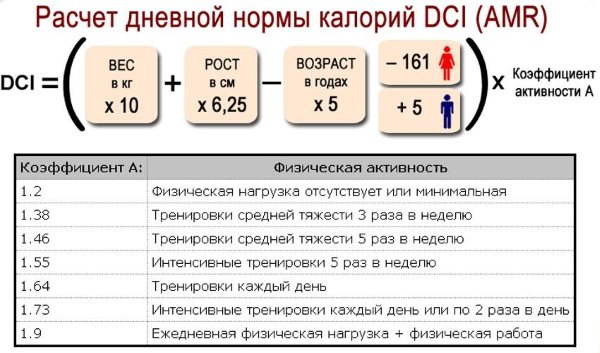
Once the level of physical activity is determined, you can calculate the kcal norm using the formula:
(9.99 * weight in kg) + (6.25 * height in cm) - (4.92 * age in years) -161 * coefficient. physical activity
Calorie table for low-calorie foods
| Product category | Product Name | Calorie content per 100g | Product category | Product Name | Calorie content per 100g |
| Vegetables | broccoli | 33 | Meat (protein) | beef | 187-144 |
| carrot | 35 | veal | 90 | ||
| chilli | 20 | horsemeat | 143 | ||
| artichoke | 40 | lamb | 191 | ||
| cauliflower | 30 | rabbit | 199 | ||
| kohlrabi | 36 | beef liver | 98 | ||
| cucumbers | 15 | veal tongue | 163 | ||
| tomatoes | 23 | beef sausage | 165 | ||
| zucchini | 23 | chickens | 159 | ||
| eggplant | 24 | chicken category 1 | 238 | ||
| pumpkin | 28 | chicken category 2 | 159 | ||
| spinach | 22 | turkey | 197 | ||
| celery | 21 | chicken liver | 139 | ||
| radish, green onion | 19 | chicken heart | 158 | ||
| lettuce | 12 | chicken eggs | 157 | ||
| asparagus | 20 | egg white | 44 | ||
| greenery | 13 | egg yolk | 64 | ||
| bulb onions | 41 | quail eggs | 168 |
| Product category | Product Name | Calorie content per 100g | Product category | Product Name | Calorie content per 100g |
| Fish and seafood (protein) | fruit juice cabbage | 5 | Milk and dairy products (protein) | cow's milk | 62 |
| squid | 75 | milk n/w | 35 | ||
| shrimps | 83 | goat milk | 67 | ||
| crabs | 69 | kefir | 31-59 | ||
| mussels | 77 | yogurt | 52-112 | ||
| pollock | 69 | cottage cheese n/w | 86 | ||
| flounder | 87 | cottage cheese 10% | 170 | ||
| sea bass | 117 | Ryazhenka | 40-85 | ||
| tuna | 101 | cream 10% | 115 | ||
| cod | 75 | sheep milk | 107 | ||
| blue whiting | 72 | serum | 25 | ||
| mackerel | 153 | buttermilk | 40 | ||
| icy | 74 | grain cottage cheese | 105 | ||
| herring | 121 | sour cream 10% | 115 | ||
| Argentina | 88 | sour cream 15% | 160 | ||
| sprat | 137 | chocolate milk | 81 | ||
| hake | 86 | drinking yogurt | 82 | ||
| oysters | 72 | "Activia" | 104 |
| Product category | Product Name | Calorie content per 100g | Product category | Product Name | Calorie content per 100g |
| Fruits | apples | 48 | Mushrooms (protein) | white dried | 34 |
| pears | 42 | boletus | 20 | ||
| plums | 43 | boletus | 22 | ||
| grape | 69 | Honey mushrooms, saffron milk caps | 22 | ||
| Peach, apricot | 45 | Chanterelles, boletus | 19 | ||
| quince | 48 | Russula, milk mushroom | 18 | ||
| cherry | 52 | Champignon | 27 | ||
| Grapefruit, melon | 35 | nigella | 9 | ||
| 35 | Berries | blueberry | 39 | ||
| mandarin | 38 | strawberries | 41 | ||
| a pineapple | 52 | cranberry | 29 | ||
| lemon | 34 | blueberry | 40 | ||
| banana | 96 | rose hip | 101 | ||
| kiwi | 47 | currant | 39-43 | ||
| persimmon | 67 | raspberries | 46 | ||
| figs | 54 | cowberry | 46 | ||
| pomegranate | 72 | gooseberry | 45 | ||
| cherry plum | 34 | strawberry | 34 | ||
| mulberry | 53 | cherries | 50 |
Minus 5 kg per week - is it possible?

- Losing 5 kg in a week is really possible. Especially for those whose initial weight was too high and exceeded the norm by 20-30% or more.
- If you need to lose 5-10 kg , then a large weight loss will result in a rapid return of lost kilograms and a further decrease in metabolism. The fact is that the body does not like such sudden changes in diet, therefore, it begins to spend energy very sparingly, and losing extra pounds with each new diet becomes more and more difficult.
- In addition, with sudden weight loss, a problem arises with the appearance of excess skin , which does not have time to tighten along with the disappearance of subcutaneous fat. As a result, unsightly folds of skin appear, which can sometimes only be removed with the help of a surgeon.
Conclusion: you need to lose weight gradually, losing no more than 0.5-0.7 kg per week.
Options
Depending on the timing:
- short-term: for 3 or 5 days;
- average duration: 7, 10, 14, 21 days;
- The longest low-calorie diet is 1 month (doctors do not recommend losing weight on such an energy-deficient diet for longer than this period).
If you need to lose 3-4 kg, a short-term option is suitable. To lose weight by 5-9 kg, choose a medium-long diet. If your excess weight is 10 kg or more, you will have to be on a low-calorie diet for a month.
Depending on complexity:
- gentle (light, simple): reducing the daily intake by 300-500 kcal (on average, caloric intake will be about 1,800 kcal);
- medium difficulty: reduction by 600-800 kcal (1,500 kcal);
- hard (strict): reduction by 900 kcal or more (less than 1,200 kcal);
- An emergency low-calorie diet involves maintaining a daily caloric intake of 400-500 kcal for a short period of time (3-5 days).
The safest ones are gentle and medium difficulty. But in the first case, the results will be minimal. Therefore, nutritionists recommend nutritional systems with a daily calorie content of about 1,500 kcal. As this indicator decreases, health risks will proportionally increase.
Depending on the diet:
- high protein/protein;
- no-carb/low-carb;
- fat free/low fat;
- vegetarian/lenten;
- drinking.
Daily calorie intake for weight loss. Food diary
Below is a step-by-step weight loss plan , which is recommended for every patient in clinics when contacting a nutritionist.

Calories per day should be calculated as follows:
- first, you write down in a notebook everything you eat during the day on normal days (without a diet);
- calculate your usual caloric intake for several days, a week;
- find out what exactly you should give up, which foods are too high in calories, and why your weight increases or does not decrease;
- Gradually reduce your daily calorie intake . First, remove all fatty, floury, and sweet foods. Eliminate smoked meats and pickles, which retain liquid. Calculate your current caloric intake;
- Follow this diet until your weight drops steadily;
- when you notice that the weight has stabilized and measured, reduce the calorie content by 400-500 kcal from the previous values. To lose weight, calories must be reduced.
Basic principles
Any low-calorie diet requires compliance with a number of general rules, without which it may be ineffective.
- Fractional meals (rules and principles).
- Dinner - 3 hours before bedtime.
- Prohibited methods of cooking: frying, salting, marinating.
- The basis of the diet is proteins, a minimum of fats, mainly of plant origin, and some complex carbohydrates.
- Entry and exit should be gradual, with a gradual decrease and, accordingly, increase in the daily calorie intake.
- Drink 1.5-2 liters of regular water per day.
- Sports activities are required. Strength loads in them should be at least 30% (for women) and 50% (for men) of the entire program, provided there is a sufficient amount of protein in the diet.
The main rule: with a low-calorie diet, you must lead a healthy lifestyle, otherwise side effects and deterioration in well-being cannot be avoided. Adequate sleep, fresh air, a clear daily routine, a schedule of alternating work and rest, a minimum of worries - all these are necessary components of this nutrition system.
Smoking and alcohol are incompatible with it. If there is an excess of nicotine against the background of insufficient daily calorie intake, intoxication of the body can occur, which will have to be treated in a hospital setting.
Structure of a low-calorie diet
Using the products from these tables will help you adjust your diet and independently select products for your daily menu.

The structure of a low-calorie diet should be built as follows:
- In the morning - porridge, fruits, allowed sweets.
- Lunch – liquid hot dishes, protein dishes, vegetables.
- Dinner – protein and some low-calorie vegetables.
- Snacks – low-fat dairy products, fruits and vegetables in small quantities (100-150g).
The closer it gets to the evening, the less caloric the food should be .
In the evening, activity usually decreases, so it will no longer be possible to burn a large number of calories and, as a result, they will be deposited in your problem areas.
Questions and answers

How to properly organize the entrance?
Suppose you need 2,400 kcal per day for normal functioning of the body, and 1,500 for weight loss (calculated using formulas taking into account individual parameters). The difference is 900 kcal. Login will take 6 days if you reduce your caloric intake by 150 kcal daily. This can be done by eliminating harmful foods from the diet (one or two every day) and limiting portions (by 50-60 g for each meal daily).
How to get out?
If you organize the entrance correctly, exiting the low-calorie diet will be problem-free, since it will completely mirror it. In 6 days you need to overcome the corridor of 900 kcal (if we take the figures given in the example above as a basis - 2,400 and 1,500 kcal). To do this daily:
- increase daily caloric intake by 150 kcal;
- we include in the diet 1-2 products from the list of prohibited, but least harmful: these can be fatty fish, meat, dairy, high-calorie fruits and vegetables;
- increase the serving size by 50-60 g at each meal.
Why does weight gain?
Unfortunately, this problem is quite relevant. There may be several reasons, and only after eliminating them can you get rid of this unpleasant phenomenon.
- Reason 1
With the occurrence of energy deficiency, the body switches the functioning of organs to a special mode when metabolism is inhibited. This reduces the rate of both lipolysis and fat burning. Slow metabolism is the main provocateur of weight gain.
How to eliminate it: include foods that accelerate metabolism in your diet, take special medications or use folk remedies, choose a different diet, review your training program.
- Reason 2
With intense training and a protein diet, an increase in muscle mass is observed, which is much heavier than fat tissue. This is what leads to weight gain.
How to eliminate: reduce the intensity of training, limit strength training, reduce protein intake. If you want a beautiful, sculpted figure and you do not plan to slow down the growth of muscle mass, just wait for the burning of the main fat tissue by choosing a long-term diet option.
Weight can also be gained due to swelling (if, for example, the drinking option is chosen or the basis of the diet is watermelon), taking medications (hormonal contraceptives, glucocorticosteroids), and the development of certain diseases. Solving this problem in each individual case must be approached individually.
What side effects should I expect?
If you have chosen a diet with a daily caloric content of at least 1,500 kcal and entered it correctly, in the absence of contraindications, usually no unpleasant sensations arise. Otherwise, you will have to deal with side effects such as:
- lethargy, decreased performance;
- irritability;
- insomnia;
- muscle spasms and pain;
- dizziness, headaches;
- pressure surges;
- nausea, pain in the stomach;
- problems with stool.
How to deal with side effects?
If the main side effects (lethargy, irritability, poor health) are pronounced and reduce the quality of life, slightly increase the daily calorie intake by introducing carbohydrates into breakfast. Start your day with oatmeal, allow yourself to eat a bun or donut, add a teaspoon of sugar or honey to your coffee. It is better to make such concessions than to break off the diet ahead of time and never achieve results.
Sometimes on low-calorie diets, quite severe muscle pain occurs. It can be caused by two factors: either they are too intensively broken down instead of adipose tissue (with a lack of physical activity and a too low-calorie diet), or it is a sore throat (with intense exercise, if before that they led a predominantly sedentary lifestyle). In the first case, you need to increase both physical activity and the level of daily caloric intake. In the second, endure it; this pain is temporary and should pass soon. If this does not happen, you may have chosen the wrong training program, consult a trainer.
If you are constipated, there are many low-calorie laxatives that can help relieve the problem. You can drink a glass of kefir or 100 ml of fresh beet juice in the evening - they will not disrupt your diet, but if you use them regularly in the morning, you will be able to go to the toilet normally. If they do not help, this may be due to more serious disorders of intestinal motility, in which case contact a gastroenterologist or therapist.
Physical activity on a low-calorie diet
As a complement to a low-calorie diet, it is necessary to include any physical activity in your daily program . This could be fitness, aerobics, cycling, swimming, etc. If you don’t have time for exercise, then:
- walk quickly;
- take the stairs without an elevator;
- overcome long corridors at work by running;
- do muscle exercises while in transport, alternately tensing and relaxing your muscles;
- buy a small ball, and while sitting at your office desk, squeeze it with your feet;
- find time for 15 minutes of morning exercises, getting up a little earlier or doing it in the evenings;
- do exercises while watching TV, combining business with pleasure.
If you wish, you can always find time for exercise by canceling some unimportant and non-urgent matters.
Here is a video about how important physical activity is when eating a low-calorie diet:
Limit fats and easily digestible carbohydrates
A low-calorie diet is always associated with limiting fats and easily digestible carbohydrates . You should give up all types of fatty foods. Avoid buying and eating the following foods:
- Fatty meat, sausages, frankfurters.
- Duck, goose, offal from them.
- Chicken skin.
- Cooking fat, margarine, lard.
- A large amount of vegetable oils.
- Fatty dairy products, glazed curd cheeses.
You should also avoid easily digestible carbohydrates.:
- Flour products, rolls, pastries, fried dough (pies, pancakes, pancakes, etc.)
- Confectionery (cakes, candies, cakes, cookies, etc.)
- A large number of cereals, porridges with butter, pasta. Porridge can be eaten only in the morning in the amount of 100-150g per serving.
- Large volumes of fruits and berries. We often think that if fruits and berries are low in calories, then we can eat as much of them as we want. But this is absolutely not true. During the season, many people try to fill up on fruit, eating 0.5-1 kg at a time. At the same time, the stomach stretches, and the body requires increasingly larger portions.
- Sweet carbonated drinks that contain about 5-10 tablespoons of sugar per 1 glass of liquid or harmful sweeteners.
What to avoid while eating healthy
The PP menu for a week for weight loss will be easier to follow if you avoid situations that provoke breakdowns:
- Lack of sleep and overexertion. Losing weight is stressful for the body, and it tries with all its might to save energy. Therefore, you want to sleep more, and the feeling of fatigue comes earlier than usual. During this period, you should not exhaust your body; it is better to sleep an extra few hours.
- Avitaminosis. To maintain good health during the transition to proper nutrition, you need to drink vitamins, since the body is in a stressful state. It is also recommended to drink fish oil, which replenishes essential fatty acids.
- Alcohol. Alcoholic drinks have a high sugar content, so it is better to avoid them altogether.

- Don't go to the store hungry.
- Monotony. You cannot create one PP diet for a week for weight loss and eat like that for a month. The menu needs to be changed every week to avoid breakdowns.
What other low-calorie diets are there?
Low-calorie diets that are recommended for people who control their weight include the following:
- Japanese diet for two weeks;
- diet 1200 kcal per day;
- diet for the lazy or water diet;
- chocolate diet;
- spicy diet, etc.
Each of the proposed diets has its own characteristics. But each of them has disadvantages.

For example, a chocolate diet involves eating only chocolate and coffee , which in principle cannot be beneficial, since the body does not receive vitamins, proteins, and minerals. A spicy diet is only suitable for those who do not have stomach problems, because abundantly flavoring all dishes with hot pepper can provoke inflammatory processes and lead to gastritis.
Did you know that
American nutritionists have proven that a low-calorie diet prolongs life. Doctors noted that if fewer calories enter the human body, the level of one of the most important hormones decreases. The lack of this hormone provokes a slowdown in metabolism and, accordingly, aging is slowed down. In addition, according to qualified nutritionists, it is a low-calorie diet that can increase stress resistance.
Cons of the diet
But a low-calorie diet, like all others, has its drawbacks . A typical low-calorie diet includes a variety of foods, although they are low in fat and carbohydrates. Therefore, it is considered the most useful and easy to use , suitable for those who do not have large funds to purchase expensive food products. However, many people neglect the simple rules of a low-calorie diet. For example:
- they are too lazy to prepare meat dishes, buying low-fat beef or chicken sausage or frankfurters;
- instead of natural vegetables and fruits, use canned ones;
- knowing that many fruits and vegetables are low in calories, eat them in kilograms;
- They use only those foods that they love more than others, and eat monotonously.
The main disadvantages are:
- Refusal of many favorite dishes, confectionery, sweets, fried and smoked foods, sauces and mayonnaise.
- The need to constantly weigh food and count calories.
- The need to have a constant supply of healthy products to eliminate the possibility of failure.
- It is difficult to give up your usual dishes if you are in a company or your family continues to eat high-calorie dishes.
- Lack of essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants. Be sure to additionally consume mineral-vitamin complexes, which contain a daily dose of the necessary vitamins and minerals.
If you overcome these difficulties and learn how to properly combine low-calorie foods with each other , then the diet will have no contraindications.
Obesity and the possibilities of its dietary correction in children

It is closely related to the lifestyle of modern man, with his inherent physical inactivity, overeating, refined nutrition with a large quota of fats and easily digestible carbohydrates, and eating disorders. Epidemiology and causes of obesity
Currently, obesity is one of the most common diseases: every 4th inhabitant of our planet is overweight or suffers from obesity. In all countries, there is a progressive increase in the number of patients both among adults and children. In this regard, WHO has recognized obesity as an epidemic of the 21st century.
In Western European countries, up to 20% of men and 25% of women are overweight or obese. The leader is the United States, where increased body weight is recorded in 60% of the population, and obesity in 27%. According to scientists' forecasts, by the end of the first decade of the 21st century. 40% of men and 50% of women on the planet will already suffer from obesity.
Unfortunately, in-depth epidemiological studies on the prevalence of obesity have not been conducted in our country. According to rough estimates, currently in Russia at least 30% of the working population are overweight and 25% are obese.
The leading symptom of obesity is generalized excess fat deposition in subcutaneous tissue and other tissues and organs, accompanied by neurohormonal and metabolic disorders, which are defined by the term “metabolic syndrome” (MS). The basis for its identification was studies that showed a pathogenetic connection and frequent combination of obesity, essential hypertension, insulin resistance, and lipid metabolism disorders.
Metabolic syndrome includes the following main components:
- abdominal type of obesity (android, visceral, “apple type”);
- insulin resistance;
- impaired glucose tolerance (IGT);
- arterial hypertension;
- hyperinsulinemia and high levels of C-peptide;
- hypertriglyceridemia;
- decreased levels of high-density lipoproteins and/or increased levels of low-density lipoproteins.
Often, signs of MS appear in childhood and adolescence. In middle age groups, its prevalence increases and reaches a maximum among older people.
The formation of certain constitutional parameters is influenced by both genetic factors and lifestyle. It has been established that more than 40% of the variability in constitutional characteristics is genetically determined. Obesity is likely a multifactorial disease: more than 250 genes, markers and chromosomal regions are responsible for the development of obesity in humans. However, the clinical significance of each combination of factors is not fully understood. To date, the role of several individual genes in the development of obesity has been studied: mutations in the genes of leptin, leptin receptor, hormone precursor convertase 1, pro-opiomelanocortin, melanocortin-4 receptor and SIM 1. These studies help to some extent to understand the molecular mechanisms regulating energy balance in the body person.
According to M.Guillaume et al. (1995), the severity of nutritional obesity in children correlates quite clearly with obesity in their parents. This relationship is stronger than the relationship between childhood obesity and energy intake or physical activity. The development of obesity in children is more closely related to the presence of this disease in the mother than in the father.
The likelihood of developing obesity in adults increases depending on the age of onset and severity of obesity in childhood. Children who are obese at age 1 or 2 but have thin parents are at virtually no risk of developing obesity in adulthood. At the same time, if obesity developed over the age of 6 years, then the risk of its worsening in adulthood is already 50%. Additionally, having one or both parents being obese also increases this risk. Thin children with at least one obese parent have a higher risk of becoming obese in adulthood.
The development of obesity in children can be facilitated by excessive nutrition of the mother during pregnancy or overfeeding of the child in the first year of life (metabolic programming). It can develop at any age, but most often manifests itself in the first year of life, at 5-6 years and during puberty.
Even at a very early age, living conditions can influence changes in body weight or the development of metabolic abnormalities in the future. Studies have shown that boys and girls born prematurely or with low birth weight subsequently had a higher body mass index (BMI) and were more likely to develop metabolic syndrome than those children who were born at normal weight and at term. The nature of nutrition in early childhood can also affect changes in body weight in the future. Studies have shown that breastfeeding for 1 year of life reduces the risk of gaining excess body weight or developing obesity at the age of 5-6 years.
The content of adipose tissue in humans ranges from 5 to 50% and above. Normally, the content of adipose tissue is in the range of 10-30%. 1 kg of fetal weight accounts for 2.5% adipose tissue, and at the birth of a child - 12%. By 6 months its content reaches 25%. Subsequently, until the onset of puberty, the ratio of fat and muscle tissue decreases. In girls, after 8-9 years and up to 17 years of age, the percentage of fat mass increases rapidly. In boys, fat mass increases slowly during puberty and begins to decline after age 13. Girls are born with more developed subcutaneous adipose tissue than boys. With age, this difference increases, reaching a maximum in adults, and causes a higher incidence of obesity in girls and women.
According to modern concepts, one of the main pathogenetic mechanisms leading to the development of any type of obesity is an energy imbalance, which consists of a discrepancy between the amount of calories supplied from food and the body’s energy expenditure. Most often this occurs due to the consumption of large quantities of flour and confectionery products, the so-called. fast-foods or eating disorders - moving the main share of food consumed to the evening hours.
In obesity, there are disturbances in the central mechanisms of metabolic regulation, changing eating behavior and causing neurohormonal changes in the body. In the hypothalamus, mainly in the areas of the paraventricular nuclei, the integration of many impulses coming from the cerebral cortex, subcortical formations, and the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system occurs. Disruption of any part of this regulatory mechanism can lead to changes in food intake, fat deposition and mobilization and, ultimately, to the development of obesity.
The main depot of energy reserves is adipose tissue, therefore excess energy supplied from food is deposited in fat cells - adipocytes, causing an increase in their size and an increase in body weight. In recent years, great importance in the pathogenesis of obesity has been attached to brown adipose tissue, which, with excess nutrition, hypertrophies, converting excess energy from food into heat, thereby preventing the deposition of lipids in fat depots. Brown adipose tissue is one of the main sites of adaptive and diet-induced thermogenesis. In children with excess body weight, there is a violation of the specific dynamic action of food, probably caused by a decrease in thermogenesis processes in brown adipose tissue.
There is a direct relationship between the development of obesity and a violation of the principles of a balanced diet. Excessive intake of nutrients causes depletion of adaptive mechanisms and the occurrence of persistent metabolic disorders.
Clinical manifestations of obesity in children
With exogenous constitutional obesity in children, there is not only an excess of fat mass, but also higher growth rates compared to healthy peers, and accelerated “bone” maturation. Often the facial skull has somewhat disproportionate features, and there is excessive development of adipose tissue in the area of the mammary glands.
In obese boys, the genitals appear disproportionately small, the penis is often “sunk” in fatty tissue, and puberty occurs earlier. In girls, the external genitalia do not have specific features; menarche occurs on time or slightly earlier.
In school-age children and adolescents, the most common cause of obesity is the hypothalamic syndrome of puberty (synonyms: juvenile hypercortisolism, juvenile diencephalic syndrome, etc.).
Hypothalamic obesity is observed in diseases of the central nervous system with damage to the hypothalamus (tumors, due to trauma, neuroinfection). This type of obesity is characterized by the rapid development of obesity. Fat deposition is observed mainly on the abdomen (in the form of an apron), buttocks, and thighs. Trophic changes in the skin often occur: dryness, white or pink stretch marks on the skin of the thighs, breasts, buttocks, and inner surface of the shoulders. As a manifestation of hypothalamic disorders, along with obesity, various signs of autonomic dysfunction are observed - increased arterial and intracranial pressure, sweating disorders, autonomic, adrenergic crises.
Endocrine obesity develops in patients with hypothyroidism, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, etc. Upon examination, along with obesity, which is usually characterized by uneven deposition of fat on the body, other clinical signs of hormonal disorders are revealed (for example, masculinization or feminization, gynecomastia, hirsutism, etc.) .
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is usually established during the first examination of a sick child, and is clarified after measuring height and determining body weight. Differential diagnosis of various types of obesity is based on medical history, the distribution of fat deposits in the body, and the presence of clinical and laboratory signs of damage to the endocrine glands. The degree of obesity in childhood is assessed using sigma or percentile tables of the ratio of linear height and body weight for a certain age and each sex.
The distribution of the subcutaneous fat layer in children largely depends on gender, age, severity and duration of the disease. In general, fat deposition is relatively uniform. However, by the period of puberty, in girls the fat layer is more pronounced in the pelvic area, and in boys - on the torso (waist and trunk types of obesity).
In accordance with the classification adopted in Russia (Kliorin A.I., 1989), there are 4 degrees of obesity.
Currently, excess weight is increasingly assessed by body mass index (BMI, Quetelet index). It is determined by dividing body weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. BMI quite reliably characterizes excess body weight in adult men and women with average height (150 - 185 cm). With normal body weight, BMI is less than 25.0. If it is more than 25, but less than 27, it is overweight, but not yet obese; if it is more than 27, it is obesity.
These BMI values can be used to assess the degree of obesity in children over 2 years of age.
In patients with degree II-IV obesity, changes in the cardiovascular system, lungs, and digestive organs are noted. Tachycardia, muffled heart sounds, and increased blood pressure are often observed. Sometimes respiratory failure develops due to the high position of the diaphragm. Most obese patients have a tendency to constipation, the liver is enlarged due to fatty infiltration, and symptoms of chronic cholecystitis and chronic pancreatitis are often detected.
Basic principles of management of children with obesity and overweight
To achieve sustainable weight loss, the following principles must be observed:
- formation of the correct nutritional stereotype for the child and his family;
- psychological support and creation of motivation for weight loss;
- gradual introduction of dietary regimens with reduced energy value (adaptation period, subcaloric diet, maintenance diet);
- correction of the diet (increasing the frequency of meals, shifting the food load from the second half of the day to the first, slow pace of eating);
- increased motor load.
An important factor in developing a correct eating pattern in an obese patient is regular contact between the doctor and the child and his parents, psychological preparation and support of the child by all family members. Treatment turns out to be ineffective if it is not motivated by anything and sick children do not understand the purpose, meaning and necessity of the dietary therapy. It is advisable that all family members, in the presence of the child, also limit the consumption of hot, spicy, fatty, fried foods, confectionery and flour products, include a wider variety of vegetables and fruits in their diet and bring its composition as close as possible to the diet recommended for an obese child.
The main principle of diet therapy for obesity is to reduce the energy value of food and achieve a negative energy balance.
An obligatory component of the treatment of obesity in children is increased physical activity, because muscle activity has a beneficial effect on blood circulation, breathing and the activity of the endocrine system, helps normalize metabolism and increase immunity.
For constitutional exogenous obesity, which is the most common form of obesity in childhood, the main method of treatment is nutritional therapy.
For endocrine obesity, in addition to diet therapy, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease and carry out hormone replacement therapy as indicated (for hypothyroidism - thyroid hormones, for hypogonadism - sex hormones, etc.). In case of hypothalamic obesity, which has developed as a result of a neuroinfection, anti-inflammatory therapy is necessary. For obesity in children with hypothalamic syndrome during puberty, drugs are prescribed that normalize the activity of the central nervous system, etc.
The task of therapeutic nutrition for any form of obesity comes down, first of all, to restoring the disturbed correspondence between the enzyme systems of the patient’s body and the chemical structures of food by adapting them to the metabolic characteristics of the body of a child suffering from this pathology.
Adaptation period of the dietary regime
During this period, primary correction of the sick child’s nutrition is provided. As a rule, the diet of obese children contains excess amounts of all essential nutrients, so their nutrition should not be sharply limited, but should be brought closer to the age-related physiological norm. This period largely determines the positive result of dietary treatment; its duration is on average 10-14 days. In the first days of treatment, weight loss is especially intense. An indicator of the correctness of the treatment regimen should be not only a decrease in body weight (on average by 1-3 kg), but also the associated improvement in general well-being and emotional tone.
Subcalorie diet
In a subcalorie diet, the reduction in energy value is ensured by reducing the content of carbohydrates and partly fat; the protein quota must correspond to the physiological needs of the child, taking into account the need to ensure his full growth and development. Moreover, in some cases, for children of high school age who are on a diet with reduced energy value, the amount of protein should be slightly increased (by about 10% compared to the age-related physiological norm). Protein foods create a feeling of fullness, which makes it easier for the child to tolerate a hypocaloric diet regimen with restriction of a number of foods.
The ratio of essential nutrients that should be maintained in the diet of school-age children with varying degrees of obesity.
The daily menu of a child with overweight or obesity should contain lean meats (beef, veal, rabbit, hens, chickens) and fish (cod, pollock, hake, etc.), as well as milk and dairy products with reduced fat content, preferably in in the form of fermented milk drinks (kefir, biokefir, bifidok, unsweetened yogurt with a fat content of 0-1.5%, cottage cheese with a fat content of 0-4%, cheeses with a fat content of 10-20%).
Depending on the degree of obesity, the amount of fat in the diet should be reduced by 15-30%. The administration of diets reduced in energy value leads to the activation of lipolysis and the mobilization of fat from fat depots.
The subcalorie diet does not use refractory animal fats (beef, lamb, pork), gastronomic products (sausages, sausages, sausages, etc.), milk and dairy products with a high fat content (cream, sour cream, fatty cottage cheese, curd mass, fatty varieties cheese).
The amount of butter and vegetable oils with a low degree of obesity may be within the age norm. Of great importance are vegetable oils (sunflower, corn, olive, soybean, etc.), which are rich in linoleic acid, which plays an important role in normalizing lipid metabolism, bile secretion, and promotes better bowel movements. In addition, food containing a sufficient amount of vegetable fats lingers longer in the stomach and reflexively reduces the excitability of the food center. Vegetable oil is used for dressing salads, vinaigrettes and added to dishes prepared without fat. However, in case of obesity of III-IV degree, the content of both butter and vegetable oils is limited.
Foods and dishes that should be used or excluded from the diet of an obese child are given in.
The correct selection of carbohydrates as part of a subcalorie diet requires great attention. Reducing the amount of carbohydrates, especially easily digestible ones, creates an energy deficit in the body of an obese child and stimulates the use of its own fat reserves. Therefore, depending on the degree of obesity, the total amount of carbohydrates in the child’s daily diet is reduced by 25-40% compared to the age norm. The proportion of carbohydrates is reduced by significantly limiting the diet of sugar, sweets, confectionery, and partially reducing the amount of cereals, pasta, and bread, primarily wheat.
However, excessive restriction of carbohydrates in the diet is not justified, since a lack of carbohydrates in the diet can lead to the formation of ketone bodies in the blood.
Cereals, vegetables and fruits form an important part of a low-calorie diet. The dietary fiber they contain is practically not absorbed by the human body: they form feces, stimulate intestinal motility, promote the elimination of cholesterol, and are a substrate for the growth of normal intestinal microflora. Foods rich in dietary fiber create a feeling of fullness and satiety in the stomach and affect the regulation of carbohydrate and fat metabolism.
Fruits and vegetables provide the child’s body with a number of minerals and vitamins and have a diuretic effect, removing excess fluid from the body. The diet of an obese child should include cucumbers, cabbage (cauliflower, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, kohlrabi), zucchini, tomatoes, pumpkin, radishes, carrots, turnips, asparagus, leafy greens, unsweetened fruits and berries. The amount of potatoes containing a high percentage of starch should be limited to ?-? recommended age norm, replacing it with other vegetables.
In a subcalorie diet, it is preferable to use wholemeal bread, as well as buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley, millet and barley cereals, which contain a significant amount of dietary fiber. To further enrich the diet with dietary fiber, it is advisable to use rye and wheat bran - 15-20 g per day.
Products rich in dietary fiber are presented in.
It is important to change the quality of the drinking regime: replace commonly used sweet drinks (juices, compotes, carbonated water) with degassed alkaline mineral waters, laxative and diuretic herbal teas, apple and pear compotes. In the diet of obese children, jelly should not be used, as well as canned compotes, fruit purees and industrial and homemade juices containing large amounts of sugar. Preference is given to natural freshly squeezed sweet and sour juices, fresh and dry (soaked) fruits and berries without added sugar. Xylitol and sorbitol are high in calories and should not be consumed by obese children.
In school-age children with grade III-IV obesity, as well as in the absence of effect from a subcalorie diet (for 1 month), fasting days can be used (no more than 1-2 times a week). A sharp, short-term transition to a diet with low energy value (about 1000 kcal) causes a restructuring of metabolism and stimulates the mobilization and use of energy resources of reserve fat.
Fasting days should be alternated. Usually they start with more satisfying ones (meat, fish, cottage cheese and dairy), and then move on to fruit and vegetable days. Good results are obtained by using double fasting days, for example, first a meat day is prescribed, and then an apple day. The amount of liquid these days is not limited.
Unloading therapy as an active method of treatment requires strict adherence to the daily routine, dietary prescriptions and general regimen. When prescribing fasting days, it is necessary to convince the sick child of the expediency and necessity of this therapeutic measure, because children with unstable mental health can easily break the fasting diet.
One of the main factors in the treatment of obesity in children is the suppression of increased appetite by consuming large volumes of low-calorie, predominantly protein-vegetable, monotonous foods. It is advisable to increase the number of meals to 5-6 times a day, while the volume of single servings decreases. Small meals interrupt appetite and increase satiety.
To reduce appetite and dull the feeling of hunger, avoid foods with a pronounced juice effect (broths and fried foods containing extractives, flavorings, spices, hot, sour, salty and smoked foods, etc.).
For breakfast, lunch and dinner, you should serve dishes made from raw and cooked vegetables (salads, vinaigrettes with vegetable oil, boiled and stewed vegetables, vegetable stews, etc.).
As snacks, obese children can eat vegetable salads and mild, low-fat cheeses in small quantities.
First courses should be vegetarian; meat, chicken, fish and mushroom broths are completely excluded.
Meat and fish dishes are served in the form of boiled portioned pieces or steamed cutlets, meatballs, and meatballs. It is recommended to use a variety of vegetables as side dishes for main courses. Crumbly buckwheat, pearl barley, rice and millet porridges are allowed in limited quantities.
Eggs can be consumed hard-boiled or as part of cooked dishes, but not more than 1 egg per day.
The child’s daily diet should be distributed in such a way that the bulk of it falls in the first half of the day, i.e. during hours of greatest physical activity. The last meal should be no later than 2-3 hours before bedtime.
With the given diet, the child will receive 65-70% of the total daily calorie intake in the first half of the day.
Maintenance diet
After reaching a body weight corresponding to the harmonious physical development of the child, you can switch to a maintenance diet, the duration of which is not limited. During this period, it is possible to carefully gradually expand the range of products and increase the energy value of the diet to values at which the child will stably maintain the proper body weight. Against the background of this diet, fasting days can also be used.
For all types of obesity, children are recommended to take long daily walks, and, in the absence of contraindications, to go swimming; General massage and contrast baths are effective. Physiotherapy exercises are an important component of complex therapy for obesity. It is indicated for all types and degrees of obesity, if the general state of health allows increasing physical activity. The therapeutic effect of physical exercise is based on increasing energy consumption, normalizing all types of metabolism, and increasing fat utilization. However, physical activity should not be excessive.
Fluid restriction for obese children is not necessary, and may even have a negative effect, because... In obese children, relative cellular dehydration has been detected. However, the amount of liquid and salt in a child’s daily diet should not exceed the age norm.
The criteria for the adequacy of the prescribed hypocaloric diet should be a uniform, not very rapid decrease in body weight with continued growth gains and proper development of the child, his good health and ability to work.
Source: Medical Council magazine No. 4 2007.
Reviews about the diet
Here are some low-calorie diet reviews to help you make your own decision:
Alisa, 34 years old, manager: My childhood years were spent in a constant struggle with excess weight, but my family kept repeating that I didn’t eat enough and prepared me such “delicacies” that it was impossible to refuse. As a result, by the age of 17 I weighed 94 kg. Not a single guy looked in my direction. Then I went to study in another city and settled in a rented apartment with one girl, who taught me to choose low-calorie and healthy foods. Literally in the first three months I lost 12 kg, then in two years another 26! I didn’t recognize myself, and when I finally went home, my family was shocked. Instead of a fat woman, a slender woman stood in front of them. Now I eat only this way, it’s healthy and I like it, and it’s inexpensive!
Arthur, 35 years old, mechanic I lost 15 kg in one year on a low-calorie diet. I made up my own menu, combining, for example, meat with lettuce or cabbage. I don’t like to cook, but that’s the good thing about a low-calorie diet – put the meat in water and cook for yourself. I cook it for 3-4 days and eat it piece by piece. I take it with me to work in the garage, at the buffet I only buy kefir or tea without sugar, and I often take apples with me. And our people at the buffet eat fast food and beer, all fat, with bellies as one. They are surprised when they look at me.
Anya, mother of 2 children, 26 years old After giving birth to my second child, I was simply devastated. I already had a belly, and here... I couldn’t fit into any dress, I didn’t even dream of trousers. She wore some enormous robes. 105-106kg was on the scales. My husband said that if I don’t lose weight, we will be divorced. I was offended by him then, but now I’m glad he said that, otherwise I wouldn’t have lost weight. I pulled myself together out of anger at him, I wanted to prove to him out of spite that I could become slim and then I would leave him myself. So, in the first 4 months I lost 25 kg by eating a low-calorie diet. The menu was 600 kcal per day, it was difficult, but I quickly got used to it, my stomach shrank, and my appetite also disappeared. Now I already weigh 65 kg, I continue to lose weight, I want to weigh 55-57. It was only difficult at the beginning, so anything is possible.
Watch the video about how a guy managed to lose 35 kg in a few months thanks to proper nutrition and calorie counting:
Does PP help with weight loss?
The PP menu for a week for weight loss is the main assistant in the fight against excess weight. Firstly, the loss of kilograms occurs due to the fact that fast carbohydrates, such as cakes and sweet buns, are completely removed from the diet. They are called fast because they are absorbed in a short time, but do not provide useful substances, but immediately go into fat deposits.
Excluding such carbohydrates from the menu gives the body the opportunity to process existing fats rather than accumulate new ones.
Secondly, nutrition occurs in small portions, at short intervals. Thanks to this eating schedule, you always feel full, and, therefore, the body does not need to accumulate reserves in case of a hunger strike.
The PP menu, developed for the day and week, for high-quality weight loss includes certain foods that need to be consumed at certain times of the day. For example, citrus fruits should not be eaten for breakfast, since the acid they contain irritates the mucous membranes, but it is not recommended to eat them for dinner because of the sugar.

The best time to eat an orange is lunch or dinner. The same goes for other products. Carbohydrates should be eaten in the first half of the day, while vegetables are much healthier for dinner. Fish is well digested in the evening, and you can eat meat for lunch. Thanks to this nutritional pattern, the body can get the maximum benefit from the food it receives.
As a result, all of the above actions accelerate metabolism, due to which the process of losing weight occurs. Proper nutrition is the basis of a beautiful figure
Low-calorie recipes (can be printed on the refrigerator)
Here are some recipes to help you get started on your diet.
Cottage cheese casserole
Take 300g of low-fat cottage cheese, add one raw egg, one chopped apple or pear, or orange, plum, pineapple or apricot, whatever you have. Grease the mold with vegetable oil and spread the curd mixture. Place in the oven.

Fish baked with vegetables
Clean the fish, salt, season with spices, place on a baking sheet, top with onion rings, tomato slices, slices of zucchini, eggplant, and herbs. From vegetables, you can choose what is available. Bake in the oven.

Chicken in molds or chicken muffins
Chop the chicken fillet into small pieces, add one raw egg, spices, salt, pieces of tomatoes and sweet peppers, herbs, place in silicone molds and bake in the oven.

Book “Low-calorie desserts”
On our website you can also download the book “Low-calorie desserts” by Alexander Seleznev. He is an excellent pastry chef, as well as a “star guru”. His dishes receive the highest ratings from celebrities. In the book, he compiled a collection of original and at the same time low-calorie desserts that you can treat yourself to on a diet. The book contains many beautiful illustrations that will appeal to every reader. You can download the book “Low-calorie desserts” for free