Fats are organic compounds that are a combination of esters, including trihydric alcohol, as well as monobasic fatty acids.
Many people associate this substance with excess weight and bad cholesterol, which clogs blood vessels. Therefore, most people who are losing weight refuse fat-containing foods, but this is not always justified. Almost everyone is interested in what the role of fats is in the human body, what they are needed for and how they are classified.
What are fats
The scientific concept of fats (lipids) implies a combination of all kinds of fat-like substances. In biology, the definition is as follows: fats are complex organic compounds that have different internal structures, but similar properties.
What types of fats are there?
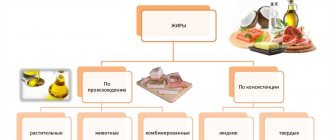
Types of fats by appearance:
- From vegetable raw materials, these are mainly liquid fats, with the exception of coconut and cocoa bean oil. This type includes all types of vegetable oil (sunflower, soybean, olive, cottonseed, rapeseed, flaxseed and others). The substances contain a lot of unsaturated fatty acids that melt at low temperatures. Easily digestible by humans.
- Animal fats are solid fats other than fish fats. Lamb, pork, beef and other types of fats melt at high temperatures. The substances contain a lot of saturated fatty acids. Animal triglycerides provide energy and increase bad cholesterol levels.
It is recommended not to combine plant and animal triglycerides in food.
Types of fats by fatty acid content:
- Substances with monounsaturated fatty acids (palmitic acid, oleic acid). Necessary for the body because it removes harmful cholesterol. Protect the cardiovascular system from heart attacks, strokes, and atherosclerosis. The body uses monounsaturated fatty acids rather than storing them in reserve in the subcutaneous layer. Such acids are found in olive, rapeseed, peanut, sunflower oil, avocados, olives, and nuts.
- Substances with polyunsaturated fatty acids: linoleic - Omega 6, alpha-linoleic - Omega 3, eicosapentoenoic - EPA, docosahexaenoic - DHA, conjugated linoleic - CLA. Needed by a person to protect the heart. They also promote the growth of muscle tissue. The most useful products with Omega 3 are fish (red fish, herring, sardines, tuna), flaxseed oil, hemp oil, and nuts.
- Substances with saturated fatty acids (palmitic, stearic, lauric). They increase cholesterol levels and contribute to the formation of excess deposits under the skin if consumed together with carbohydrates. When used correctly, they promote the production of testosterone and increase muscle endurance. Sources of saturated fatty acids: beef, poultry, pork, lard. Dairy products, chocolate, coconut and palm oil are rich in them.
- Trans isomers of fatty acids (trans fats). The industrial way of creating margarines is called hydrogenation, when vegetable fats are saturated with hydrogen. The use of trans isomers in nutrition causes problems in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, risks diabetes, and reduces muscle volume. Fast food is made on the basis of margarines. They are most used in the production of chips, crackers, donuts, crackers, candies, cakes, and cookies. There are a lot of trans fats in mayonnaise, ketchup, instant soup, French fries, in all fried foods, in fast food.
What are the types of fats - classification
Classification of the composition and structure of triglycerides is difficult due to the abundance of substances. They are united by hydrophobicity, that is, the ability to not dissolve in water. Depending on how the substance interacts with water, fats can be saponified or unsaponifiable.
- Saponified triglycerides contain at least two structural components. Their components: alcohols, higher fatty acids. More complex structures also include phosphoric acid, amino alcohols, mono- and oligosaccharides. When hydrolysis occurs under the action of acids, alkalis or lipase enzymes, it breaks down into components.
- Unsaponifiable triglycerides do not result from the combination of fatty acids and are therefore not subject to hydrolysis. These are natural compounds united by a similar base structure. The carbon skeleton of an unsaponifiable fat molecule is made up of isoprene units, with a “head” adjacent to a “tail.”
Composition of fats
Triglycerides are part of plants and animals. Their molecular composition contains higher carboxylic acids: palmitic, stearic, oleic, linoleic, linolenic. Fats contain almost no lower acidic compounds: they are rare. An example is butter: it contains butyric acid.
Structure of fats:
CH2−O−CO−R
I
CH−O−CO−R
I
CH2−O−CO−R
This is the general formula of fats, where C is carbon; H – hydrogen; O – oxygen; R – particles containing one or more unpaired electrons, they are also called carboxylic acid radicals. Particles can be represented by different formulas: C15H31, C17H33, C17H35.
Monounsaturated fatty acids
The main types of MUFA are myristoleic, palmitoleic, and oleic. These acids can be synthesized by the body from saturated fatty acids and carbohydrates. One of the most important functions of MUFAs is lowering cholesterol levels in the blood. The sterol contained in MUFAs, p-sitosterol, is responsible for this. It forms an insoluble complex with cholesterol and thus prevents the absorption of the latter.
The main sources of MUFA are fish oil, olive, sesame and rapeseed oils. The physiological need for MUFA is 10% of the daily calorie intake.
The role and functions of fats in the human body
The role of fats in the human body is significant. They perform several vital functions for humans. The importance of fats in the body is evident from their participation in the work of various organs.
- The main function of fats is energy. A person receives most of their energy from carbohydrates; triglycerides contain reserve energy, which is required in case of a lack of carbohydrates.
- Fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K move, dissolve, and are absorbed due to the transport function of triglycerides.
- Subcutaneous fat is stored as an energy reserve and is used when there is a deficiency of nutrients, so triglycerides have a storage function.
- Triglycerides are a good heat insulator that protects against hypothermia. They have a thermal insulation function.
- The protective function of triglycerides helps protect human organs from harmful mechanical influences.
- Structural function. Triglycerides are the building blocks of cells.
- Regulatory function. Triglycerides help regulate the production of steroid hormones necessary for metabolism, reproductive organs, and the immune system.
Therefore, it is necessary to know the importance of fats for a person so as not to give them up completely. What are triglycerides needed for? For proper, full functioning of the body.
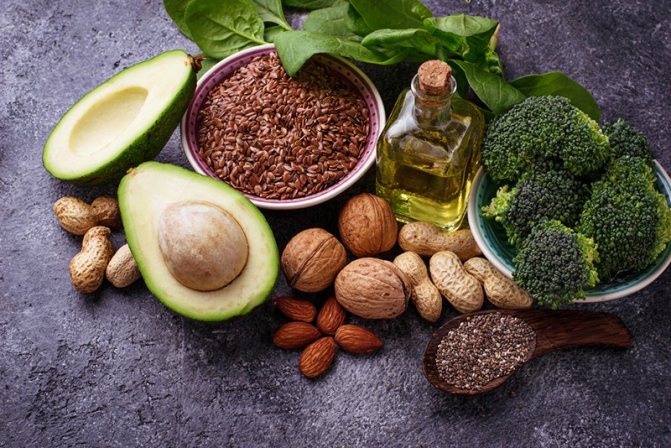
What do healthy fats mean?
Healthy triglycerides contain monounsaturated fatty acids: palmitic, oleic, and polyunsaturated fatty acids: linoleic - Omega 6, alpha-linoleic - Omega 3, eicosapentoenoic, docosahexaenoic, conjugated linoleic. A person gets useful triglycerides from food because the body does not generate them in the required quantities.
We need useful triglycerides for the growth and strengthening of muscles, for the proper functioning of the heart and blood vessels, for strengthening the immune system, for metabolic processes, and for the production of testosterone.
Sources of healthy fats: vegetable oil, avocados, olives, fish, nuts, seeds, olives.
Beneficial functions of lipids
Give up the idea of sticking to a low-fat diet, such a system will probably be effective - your body weight will decrease. But as a result, you will get a sickly, exhausted appearance, and health problems are possible. The daily fat intake for women when losing weight ranges from 60-80 g (including 20 g of plant origin), you can get more accurate figures after consulting with a nutritionist who will take into account all the important features of your body.
Why do you need fatty foods:
- gives energy, allows you to perform mental and physical work with enthusiasm and good results, promotes endurance and productive training;
- important for the nervous system - lipids are actively involved in the formation of brain neurons and nerve endings;
- increases immunity;
- promotes calcium absorption;
- gives a long-lasting feeling of satiety, which helps you stick to your diet and not break down;
- helps to well absorb many vital compounds - animal fat is useful because it delivers vitamins A and O, and vegetable oils are a source of tocopherol;
- stops the inflammatory process;
- promotes tissue regeneration, since cell membranes are made of lipids;
- normalizes hormonal levels, provokes the production of sex hormones, as well as dopamine and serotonin.
There is no need to strive to completely get rid of the fat layer; a person needs it, as it plays an important role. Namely, it protects against hypothermia, ensures reliable fixation of internal organs in the correct place in the abdominal cavity, and protects against injury.
If you ignore food that is a source of healthy fats, you will not be able to preserve:
- youth and elasticity of the skin, strength of nails, beauty of hair;
- reproductive function;
- good vision;
- high stress resistance and emotional well-being;
- healthy joints;
- clarity of mind and good mood;
- normal production of vitamin D by the body, as well as the ability to absorb vitamin compounds A, E, K;
- a firm commitment to stick to proper nutrition - because without lipids in your diet, you will constantly feel hungry.
We must also educate people about the consequences of eating too much fatty food. If you regularly exceed the norm of fat when losing weight, it is difficult to achieve the desired result, and in addition there is a risk of developing the following diseases:
- gallstones;
- stroke;
- gout;
- atherosclerosis.

And if you overuse foods containing trans fats, this can lead to deterioration of your skin and digestion. It is worth giving up chips and chocolates not only because of their high energy value, but also because of the negative impact on well-being and appearance.
Foods rich in fats
Triglycerides are of animal and plant origin. Information about where one of the main substances is contained and in what volumes makes it possible to balance the diet.
Plant foods rich in fats:
| Product name | What type of fatty acids predominates? | Content per 100 g (in grams) | Content in 100 g (%) of the norm | Share of fats in calories |
| Avocado | monounsaturated | 14.7 | 21.6 | 0.9 |
| Walnuts | polyunsaturated | 65 | 96 | 0.87 |
| Almond | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 54 | 79 | 0.79 |
| Pistachios | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 45 | 67 | 0.74 |
| Pine nut | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 68 | 100.6 | 0.87 |
| Peanut | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 49 | 72 | 0.77 |
| Hazelnut | monounsaturated | 61.5 | 90.5 | 0.85 |
| Olive oil | monounsaturated | 100 | 147 | 1 |
| Peanut butter | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 50 | 73.5 | 0.72 |
| Rapeseed oil | monounsaturated | 100 | 147 | 1 |
| Sunflower oil | polyunsaturated | 100 | 147 | 1 |
| Linseed oil | polyunsaturated | 100 | 147 | 1 |
| Hemp oil | polyunsaturated | 100 | 147 | 1 |
| Olives | monounsaturated | 15 | 22.5 | 0.96 |
| Flax seeds | polyunsaturated | 42 | 62 | 0.83 |
| Soybean fruits | polyunsaturated | 18 | 26 | 0.43 |
| Sunflower seeds | polyunsaturated | 53 | 78 | 0.79 |
| Chia seeds | polyunsaturated | 31 | 45 | 0.54 |
| Dark chocolate | polyunsaturated saturated | 28 | 41 | 0.5 |
| White dried mushrooms | rich | 14 | 21 | 0.45 |
Animal foods rich in fats:
| Product name | What type of fatty acids predominates? | Content per 100 g (in grams) | Content in 100 g (%) of the norm | Share of fats in calories |
| Salmon | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 8 | 12 | 0.48 |
| Acne | polyunsaturated | 30.5 | 45 | 0.83 |
| Tuna | polyunsaturated | 4.5 | 6.5 | 0.3 |
| Saira | polyunsaturated | 14 | 21 | 0.62 |
| Herring | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 8.5 | 12.5 | 0.53 |
| Salmon | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 10 | 15 | 0.52 |
| Sturgeon | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 4 | 6 | 0.36 |
| Som | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 5 | 7.5 | 0.4 |
| Gobies | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 4 | 6 | 0.34 |
| Sturgeon caviar | polyunsaturated | 14.5 | 21 | 0.45 |
| Chum salmon caviar | polyunsaturated | 13 | 19 | 0.48 |
| Pork | monounsaturated saturated | 33 | 49 | 0.84 |
| Beef | monounsaturated saturated | 3.5 | 5 | 0.3 |
| Mutton | monounsaturated saturated | 16 | 24 | 0.7 |
| Rabbit meat | monounsaturated saturated | 11 | 16 | 0.54 |
| Turkey meat | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 6 | 8 | 0.37 |
| Chicken's meat | monounsaturated polyunsaturated | 2 | 3 | 0.15 |
| horsemeat | monounsaturated saturated | 4.5 | 7 | 0.33 |
| Beef liver | rich | 4 | 25 | 0.26 |
| Pork liver | monounsaturated saturated | 4 | 6 | 0.27 |
| Pork lard | monounsaturated saturated | 93 | 136 | 0.99 |
| Buzhenina | monounsaturated saturated | 27 | 39 | 0.78 |
| Raw smoked sausage | monounsaturated saturated | 47 | 70 | 0.86 |
| Eggs | monounsaturated saturated | 11 | 17 | 0.66 |
| Natural milk | monounsaturated saturated | 4 | 6 | 0.55 |
| Sour cream 15% | monounsaturated saturated | 15 | 22 | 0.85 |
| Tofu cheese | polyunsaturated | 5 | 7 | 0.37 |
| Parmesan cheese | monounsaturated saturated | 25 | 37 | 0.59 |
| Natural yogurt | rich | 3 | 5 | 0.4 |
| Kefir 2.5% | rich | 2.5 | 4 | 0.45 |
| Butter | rich | 82.5 | 121 | 0.99 |
| Mayonnaise "Provencal" | polyunsaturated | 67 | 98 | 0.96 |
| Cottage cheese 5% | rich | 5 | 7 | 0.32 |
The body's daily requirement for fats
How much fat should you consume per day according to doctors' advice?
The daily fat intake for each person is calculated individually depending on age, physical activity, and health status.
The only rule is that 20-25% of your daily calories should come from triglycerides.
But they should not be more than 30%, because otherwise excess fat will become an unnecessary reserve, weaken the immune system, reduce reproductive function, slow down metabolic processes, and cause chronic fatigue.
- For men aged 18 to 29 years with light physical activity, the daily fat intake is 50 grams.
- For men aged 30 to 39 years with light physical activity, the daily intake is 48 grams.
- For men aged 40 to 59 years with light physical activity, the daily intake is 45 grams.
- For men aged 18 to 29 with average physical activity, the daily intake is 53 grams.
- For men aged 30 to 39 with average physical activity, the daily intake is 51 grams.
- For men aged 40 to 59 years with average physical activity, the daily intake is 48 grams.
- For men aged 18 to 29 with vigorous physical activity, the daily intake is 61 grams.
- For men aged 30 to 39 with vigorous physical activity, the daily intake is 58 grams.
- For men aged 40 to 59 years with vigorous physical activity, the daily intake is 56 grams.
- For women aged 18 to 29 years with light physical activity, the daily intake is 42 grams.
- For women aged 30 to 39 years with light physical activity, the daily intake is 41 grams.
- For women aged 40 to 59 years with light physical activity, the daily intake is 39 grams.
- For women aged 18 to 29 years with average physical activity, the daily intake is 45 grams.
- For women aged 30 to 39 years with average physical activity, the daily intake is 43 grams.
- For women aged 40 to 59 years with average physical activity, the daily intake is 41 grams.
- For women aged 18 to 29 with intense physical activity, the daily intake is 48 grams.
- For women aged 30 to 39 years with intense physical activity, the daily intake is 46 grams.
- For women aged 40 to 59 years with intense physical activity, the daily intake is 44 grams.
In addition to following the correct intake of triglycerides, it is important to maintain a balance between the consumption of Omega 3 and Omega 6 polyunsaturated fatty acids. They should be supplied to the body in equal shares, or Omega 3 may be greater. Stewed, baked or steamed dishes will help with this. The balance between proteins, fats, and carbohydrates is also important.
Excess fat in food
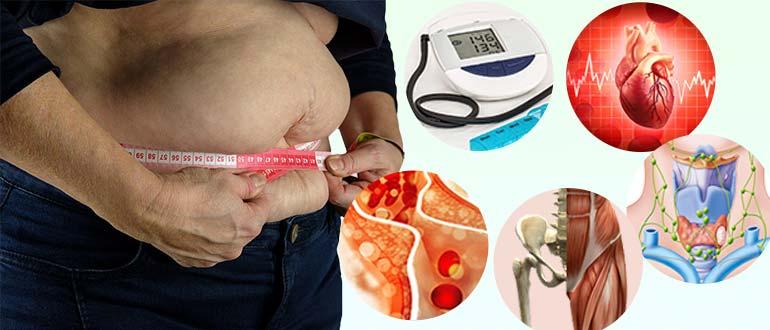
An excess of triglycerides in human food leads to the formation of excess deposits - obesity. This negatively affects the body. The consequences may be an increase in blood clotting, the formation of stones in the liver and gall bladder, and deterioration in the functioning of internal organs. Obesity will lead to increased blood pressure, disruption of the heart and blood vessels, thyroid gland, ovaries, negative changes in bone and muscle tissue, and increased cholesterol levels.
List of products that will help you become slimmer
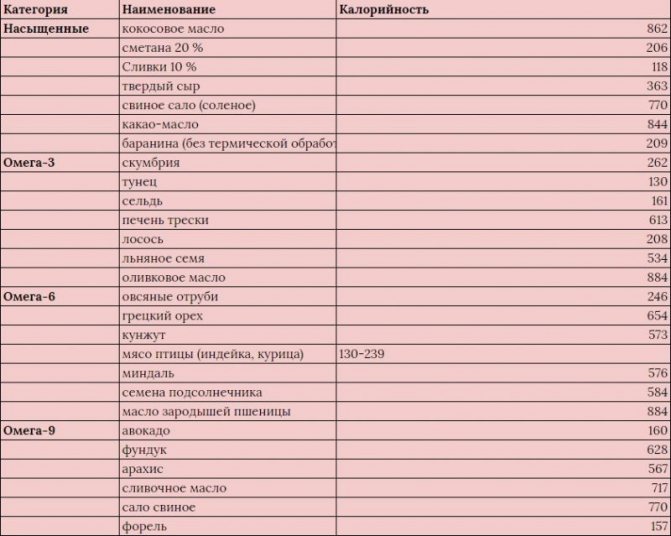
Based on the table of food products presented, you can select the healthiest ingredients for your menu with the optimal composition of fats; this list is incomplete and is for informational purposes only. If you want, you can supplement your diet with other tasty and nutritious ingredients.
Look at our Clients' Acknowledgments and Success Stories - View
To lose weight, you don’t need to torture yourself with hunger, just eat mindfully, get enough sleep and move more. For recommendations on proper nutrition and proper diet planning, contact Elena Morozova’s weight loss clinic. Experts will help you identify all the shortcomings of your lifestyle and menu and tell you how to make the path to weight loss enjoyable and beneficial for the body.
Digestibility of fats
Scientific research has shown that vegetable and animal fats are absorbed differently. The absorption of plant triglycerides occurs quickly, and energy is also obtained quickly. Animal fats are digested more slowly, which allows you to feel full for a long time.
Statistics show that men prefer fats of animal origin, and women prefer vegetable fats. A person who cares about his health should know why fats are needed. This will help him avoid many diseases and prolong his youth.