Daily protein intake
Each person needs an individual amount of protein daily. It depends on gender, weight and other factors. It is important not to overdo it and not eat only protein-rich foods. In any case, nutrition should be balanced and rational. Eating too much protein will not lead to increased muscle growth, although some people believe it will. Even 300 grams of pure protein per day will not cause the body to produce muscle tissue faster than possible.
Research says that for athletes and people who are trying to gain weight, the protein norm is equal to 1.5-2.5 g per 1 kg of weight. That is, with a weight of 70 kg, a man needs about 200 g of protein, a woman with a weight of 60 kg needs 165 g per 1 kg of weight. For weight maintenance or weight loss, this value is reduced by 10% or 20% respectively. But do not forget that this is purely individual, and you should rely on your feelings, observing changes in your figure and well-being. It is impossible to understand from the first day whether the diet has been chosen correctly; at least a month must pass, after which you can adjust your diet.
Where are animal proteins found?
Now let's talk about the main sources of fast proteins, what common foods contain them in maximum quantities?
The main sources of fast proteins are meat products. Let's list them and how much protein they contain:
- Chicken meat (fillet), ideally white meat chicken breast. It contains 25 g of pure protein per 100 g of product. The digestibility index of chicken is 0.92.
- Turkey meat is a source of fast protein, similar to chicken fillet in terms of the amount of proteins and the speed of processing by the body.
- Rich sources of fast proteins are lean beef and veal - these types of meat delicacies contain about 30 g of fast protein. The digestibility coefficient is 0.92.
- Milk and fermented milk drinks also contain fast proteins. The first contains 3 g of protein, yogurt is enriched with slow protein by 5 g, kefir - by 4.5 g. This also includes whey. The main thing is that all these products have a low fat content. They are 100% digestible. From whey protein, the body absorbs up to 10 g of amino acids per hour.
- A rich source of fast proteins is fish (perch, pollock, flounder, cod, pike) and seafood (crab meat, shrimp, squid). The amount of protein in them is equal to 17-21 g. These delicacies are absorbed by the human body by 90%.
- Egg white is considered the fastest of all existing ones. It is completely absorbed and contains 15 g of proteins, of which the human body takes up to 1.5 g of amino acids per hour.
List of Protein Rich Foods

Not all foods have the same nutritional value and calorie content, and, accordingly, the amount of protein. Animal products (meat, fish, poultry), legumes, cereals and other products are richest in it. Proper protein nutrition for muscle growth is built on protein-rich foods; there are recipes for dishes (for example, boiled chicken fillet with lentils) that are considered “impact” dinners for athletes. With one such meal, you can reach the normal amount of protein consumed. Eating such food is best in the evening, since fats are too heavy for the digestive system and digestion during sleep, and carbohydrates provide energy that is absolutely not needed at night; consuming carbohydrates at night will only lead to the gain of fatty tissue, not muscle tissue. Let's find out which foods contain protein
10 foods with the highest protein content
There are foods that contain practically no protein, such as sweets and desserts; such dishes are not eaten on a protein diet, but there are record-breaking foods for protein content. It is on the basis of this food that proper protein nutrition is built.
List of foods rich in protein:
- Soy – up to 35 g;
- Boiled veal – up to 31 g;
- Peanuts – 26 g;
- Chicken breast – 25 g;
- Tuna – 23 g;
- Beans and peas – 22 g;
- Cheese – 19 g;
- Shrimp – 18 g;
- Cottage cheese – up to 17.5 g;
- Chicken egg – up to 14 g.
From this list it is clear that not only animal products are rich in protein, but also plant-based ones. This means that vegetarians, vegans, and other people who follow certain diets for moral reasons or health reasons can keep their body in good shape and build muscle, despite the fact that there is a popular myth about the lack or absence of protein in plant foods.
Such a variety of products allows you to combine them with each other and create more and more new dishes that will help diversify the menu even on a protein diet.
Types of proteins, their characteristics and what foods they contain
All proteins found in food products are divided into simple and complex . Simple proteins are also called proteins, and complex proteins are called proteids . They differ in that simple ones consist only of polypeptide chains, while complex ones, in addition to the protein molecule, also contain a prosthetic group - a non-protein part. Simply put, proteins are pure proteins, but proteids are not pure proteins.
Each individual type of protein has a different effect on the body and promotes muscle growth in different ways. This is due to the different chemical composition and structural features of the molecules.

The best protein food is considered to be that of animal origin, as it contains more nutrients and amino acids, but plant proteins should not be neglected. Ideally the ratio should look like this:
- 70-80% of food is of animal origin;
- 20-30% of food is of plant origin.
If we consider proteins according to their degree of digestibility, they can be divided into two large categories:
Fast protein
Fast protein molecules are broken down into their simplest components very quickly. The main sources of such proteins are usually animal products , such as:
- Fish;
- Chicken breast;
- Eggs;
- Seafood.
Slow protein
Slow-acting proteins are very useful for people who have set themselves the goal of losing weight. They perfectly and for a long time satisfy the feeling of hunger, restore muscles, enrich them with amino acids and protect muscles from destruction. In slow proteins, molecules are broken down to their simplest components extremely slowly.
Animal products rich in slow-acting proteins :
- Cottage cheese
Plant-based foods rich in slow-acting proteins :
- Legumes: peas, beans, soybeans, peanuts
- Cereals, cereals and flakes: oatmeal, wheat, buckwheat, rye, rice and corn
If we look at protein through the lens of bodybuilding, it means highly concentrated protein (protein). The most common proteins are considered to be (depending on how they are obtained from foods):
- From whey - is the fastest absorbed, extracted from whey and has the highest biological value;
- From eggs - absorbed within 4-6 hours and is characterized by a high biological value;
- From soybean – high level of biological value and rapid absorption;
- Casein is absorbed longer than others.
Vegetarian athletes need to remember one thing: vegetable protein (from soy and mushrooms) is incomplete (particularly in terms of amino acid composition).
It is also important to be able to combine different types of proteins to obtain maximum absorption of food entering the stomach . Good results in this regard are obtained by the combined consumption of egg whites and dishes made from corn grits, a combination of soy and millet, rye and milk.
Fast and slow proteins are equally needed by both the body of a person losing weight and someone who wants to gain weight.
Protein compatibility
However, without the goal of building muscle, you should not combine high-protein foods very often. To process proteins from different sources, gastric juice of different acidity and different enzymes are needed. A constant combination of proteins + proteins will lead to some problems with the gastrointestinal tract, for example, the process of breaking down starch may be disrupted.
A combination of proteins and carbohydrates is not the best option, since the digestion of carbohydrates occurs in an alkaline environment, and proteins in an acidic environment with a high pH. Mixing these two substances leads to fermentation of foods, heartburn, heaviness and general malaise.
It is best to combine proteins with vegetables that contain little starch, as this also inhibits the digestion of food. These are vegetables like
- Cabbage;
- Radish;
- Bell pepper;
- Celery;
- Zucchini;
- Tomatoes;
- Spinach and other salads.
Thus, if necessary, you can occasionally correct the lack of protein with a combination of two or more high-protein foods, but in ordinary life it is better to replace such a combination with protein + fiber, that is, non-starchy vegetables.
Meat protein table
Different types of meat have different amounts of protein. In particular, meat protein is distinguished by its high content of amino acids, which practically do not decompose during heat treatment.
| Protein content in meat products | |||
| Veal | Up to 31 g | Pork lean | 25 g |
| Goose | 29 g | Mutton | 21-24 g |
| Chicken (no skin) | 25 g | Rabbit / hare | 24 g |
| Turkey | 24 g | Chicken stomachs | 20-22 g |
| Smoked sausage | ≈20g | Duck stomachs | 19.5 g |
| Beef | 19-23 g | Lamb liver | 19 g |
| Chicken liver | 18-21 g | Beef liver | 17 g |
| Chicken heart | 15-22 g | Beef tongue | 16 g |
| Pork liver | 18 g | Lamb heart | 15 g |
| Duck | 17.5 g | Lamb kidneys | 14 g |
| Beef/pork heart | 15 g | Beef kidneys | 12.5 g |
| Pork kidneys | 14 g | Boiled sausage | 10-12 g |
Fish and seafood proteins
| Protein content in fish, fish and seafood | |||
| Chum salmon caviar | 27 g | Beluga / Cod liver | 24 g |
| Sardine | 23.7 g | Tuna | 23 g |
| Mullet | 21.4 g | Pike-perch / Pink salmon / Bream | 21 g |
| Carp | 19.9 g | Sea bass / Shrimp / Saberfish | 20 g |
| Whitefish | 19 g | Saira | 18.6 g |
| Crabs | 18.7 g | Horse mackerel | 18.5 g |
| Ide | 18.2 g | Pike / Mackerel / Salaka | 18 g |
| Squid | 18 g | Shrimps | 17.8 |
| Flounder | 16.1 g | capelin | 13.4 |
| Cod | 17.5 g | Herring | 17.3 |
| Blue whiting | 17.9 g | Pollock / Sterlet / Catfish | 17 |
| Icy | 17.4 g | Sturgeon | 16.5 |
| Salmon | 20.8 g | Hake | 16.6 |
| Trout | 15.5 g | Oysters | 14 |
| Lamprey | 15 g | Canned fish in tomato | 12.8-19.7 g |
| Canned fish in oil | 17.4-20.7 g | Canned fish in its own juice | 20.9-28.7 g |
Milk proteins
| Protein content in dairy products | |||
| Milk | 2.8 g | Yogurt | 5 g |
| Kefir | 2.8 – 3.0 g | Buttermilk | 2.5 – 2.7 g |
| Sour cream | 3.0 – 3.4 g | Cottage cheese 20% | 14 g |
| Ryazhenka | 3.5 g | Smoked sausage cheese | 23 g |
| Curdled milk | 2.2 g – 2.8 g | Powdered milk | 25.6 g |
| Hard cheese | 25-35 g | Skim cheese | 16 g |
| Processed cheese | 20 g | Cream | 3.0 – 3.2 g |
| Ice cream | 3.5 g | Condensed milk | 8 g |
| Ayran (tan) | 2 g | Cheese Brynza | 17.9 g |
| Adyghe cheese | 18.5 g | Goat cheese | 22 g |
| Cheese Tofu | 8.1 g | Sulguni cheese | 20 g |
| Baked milk | 2.9 g | Goat milk | 3.6 g |
| Kumis | 2.1 g | Matsoni | 2.8 g |
| Butter | 0.9 g | Goat curd | 16.7 g |
Cereals
Detailed table with protein content in products
| Protein content in cereals, porridges, cereals and legumes | |||
| Bulgur | 12.3 g | Chickpeas | 20.1 g |
| Peas | 21.5 g | Oat groats | 11.9 g |
| Buckwheat | 13.5 g | Cereals | 11.7 g |
| Buckwheat flakes | 9.0 g | Pearl barley | 9.3 g |
| Quinoa | 14.1 g | Spelled | 14.7 g |
| Porridge 7 grains | 12.0 g | Sprouted wheat | 7.5 g |
| Corn grits | 8.3 g | Wheat groats | 11.5 g |
| Cornflakes | 7.4 g | Soft wheat grains | 11.8 g |
| Dry couscous | 12.8 g | Durum wheat grains | 13.0 g |
| Flaxseed porridge | 32.3 g | Wheat flakes | 11.0 g |
| Semolina | 11.4 g | Millet porridge | 11.2 g |
| Rye flakes | 6.4 g | Millet cereal | 11.5 g |
| Raw white rice | 5.0-8.0 g | Rye (grains) | 9.9 g |
| Brown rice | 7.4 g | Sago | 1.0 g |
| Brown rice | 6.3 g | Grain sorghum | 11.8 g |
| Golden rice | 8.1 g | Wheat talkan | 11.5 g |
| Red rice | 10.5 g | Teff | 13.3 g |
| Polished short grain rice | 0.1 g | Oatmeal | 12.5 g |
| Rice flakes | 7.0 g | Triticale | 12.8 g |
| White beans | 21.0 g | Lentils | 27.3 g |
| Red beans | 23.0 g | Barley grits | 10.4 g |
| Barley groats | 10.0 g | Barley flakes | 9.8 g |
Protein Digestibility Chart
All protein - both animal and plant - has a different effect on the body, is perceived differently by it, and therefore is absorbed differently. It depends on the amino acid composition. More precisely, from the ratio of one type of amino acid to another. The body does not synthesize the necessary amino acids, but uses only what it comes with food. If one of the amino acids is missing for the assimilation of proteins, then the rest will not be used. Easily digestible protein includes animal protein; an exemplary example of digestibility is the chicken egg - its digestibility is close to 100%. It is difficult to obtain protein from plant foods due to the lack of diversity in the composition of amino acids; protein in cereals and fruits is absorbed worst of all, since there are not enough components for this.
| Digestibility of protein in various foods | |||
| Product Names | Amount of protein | Absorption rate squirrel (PDCAAS) | Protein absorption percentage |
| Egg | 12.7 g | 1.0 | 100% |
| Egg powder | 45.0 g | 1.0 | 100% |
| Serum | 2.9 g | 1.0 | 100% |
| Milk, kefir | 2.8 g | 1.0 | 100% |
| Cottage cheese | 16.7 g | 1.0 | 100% |
| Cheese | 25.0 g | 1.0 | 100% |
| Beef | 18.9 g | 0.92 | 92% |
| Pork (not fatty) | 16.4 g | 0.63 | 63% |
| Pink salmon | 21.0 g | 0.90 | 90% |
| Chicken (poultry) | 20.8 g | 0.92 | 92% |
| Wheat | 12.7 g | 0.54 | 54% |
| Oats | 11.9 g | 0.57 | 57% |
| Rice | 7.0 g | 0.55 | 55% |
| Buckwheat | 12.6 g | 0.66 | 66% |
| Beans | 22.3 g | 0.68 | 68% |
| Peanut | 26.3 g | 0.52 | 52% |
| Peas | 23 g | 0.67 | 67% |
| Soybeans | 34.9 g | 0.91 | 91% |
| Corn | 8.3 g | 0.60 | 60% |
| Rye | 10.7 g | 0.63 | 63% |
| Cottage cheese | 15.0 g | 0.84 | 84% |
| Beans | 21 g | 0.49 | 49% |
| White bread | 9.0 g | 0.97 | 97% |
| Whole wheat bread | 11.3 g | 0.92 | 92% |
| Lentils | 27.3 g | 0.84 | 84% |
| Red caviar | 31.6 g | 0.90 | 90% |
| Squid | 21.2 g | 0.90 | 90% |
| Mutton | 22.0 g | 0.90 | 90% |
| Salmon | 21.7 g | 0.90 | 90% |
| Rabbit meat | 24.0 g | 0.90 | 90% |
| Tuna | 23.0 g | 0.90 | 90% |
Protein
In scientific terminology, a protein is defined as a substance that contains a chain of amino acids that creates a polypeptide. By analyzing the protein as it enters the body, it is possible to identify 20 amino acids, assembled by combining in various ways, resulting in the creation of many compounds, varied in composition and function. If you want to gain muscle mass, you need to have a sufficient level of nitrogen, which is achieved by adding protein to your food. Of all those presented, the enzymatic functions of protein are considered the most significant. They are the catalyst in the reactions of the biochemical process and exchange. Structural and mechanical tasks are responsible for the formation of the cell cytoskeleton. It is worth noting the importance of proteins in the cell cycle, immune and signaling systems.
History of protein research
The famous chemist from France Antoine de Fucroy and a group of scientists studied the entire class of proteins, as a result of which they discovered the ability of proteins to coagulate (denature) under the influence of heat or acids. Considerable attention was paid to the study of albumin, fibrin, and gluten.
The composition of proteins continued to be studied, as a result of which it was found that amino acids are formed during the hydrolysis reaction of proteins. Amino acids such as glycine and leucine have received their own characteristics. The hypothesis about the existence of a similar empirical formula for proteins was put forward by Gerrit Mulder. After a short period of time, he already presented his model of the chemical structure of protein. Based on the theory of radicals, Mulder deduced the composition of the minimal structural unit of the protein C40H62N10O12, which was called “protein” (Pr), and the theory was called “protein theory”. The scientist believed that the components of each protein are phosphorus, protein units, and sulfur. It was he who wrote down the fibrin formula as follows: 10PrSP. While researching amino acids, Mulder determined the molecular mass (131 daltons), allowing for a small error. Much new information about proteins came to light, but despite criticism, the protein theory was generally accepted until the late 1850s.
Many research projects during this period were devoted to amino acids, which are part of proteins at the end of the 19th century. For example, A.Ya. Danilevsky, a scientist from Russia, identified the presence of peptide groups (CO-NH) in the protein molecule. A little later, in 1894. Albrecht Kossel, a German professor of physiology, argued in his theory that amino acids are the main structural elements of proteins. At the beginning of the 20th century, Emil Fischer experimentally proved that the components of proteins are amino acid residues located in a peptide bond. After analyzing the amino acid sequence of the protein, he explained the phenomenon of proteolysis.
In 1926 James Sumner, an American chemist, discovered that the enzyme urease is a protein.
The following easily purified polypeptides were used for research: blood proteins, chicken eggs, various toxins, metabolic, digestive enzymes that were released after the slaughter of livestock, since the extraction of pure proteins was not an easy task.
In the 1950s, one of the American scientists was able to purify a kilogram of bovine ribonuclease A, which subsequently became the object of experiments in many studies. William Astbury believed that the secondary structure of proteins is considered the result of the formation of hydrogen bonds between amino acid residues, but Linus Pauling was the first to prove the secondary structure of proteins. Building on the work of Kai Linderström-Lang, Walter Krausman made great strides in the laws of protein tertiary structure formation and hydrophobic interactions. Fredrik Sanger worked on the protein sequencing method. In his works, he defined the amino acid sequence of the two chains of insulin, convincing everyone that proteins are not considered branched chains, but linear polymers of amino acids. Aspartate aminotransferase is considered to be the first amino acid sequence of a protein determined by USSR scientists. Since 1950, X-ray diffraction has been used to obtain results of the original spatial structures of proteins. Later, the discovery structures were studied using nuclear magnetic resonance. In 2012, there were approximately 87,000 different protein structures known to be in the Protein Data Bank. Now the study of proteins is at a completely different level, including purified proteins, post-translational modifications of proteins of individual cells, tissues and entire organisms in general. This branch of biochemistry is called proteomics. Bioinformatics gives us a chance to process information from X-ray diffraction analysis and suggest the structure of a protein, taking its amino acid sequence as a basis. Cryoelectron microscopy of large protein complexes is approached to atomic precision, as is the use of computer programs in predicting the spatial structures of protein domains.
Protein products and their biological value
Amino acid composition and digestibility certainly affect the biological value of the protein. When exposed to enzymes in the stomach, intestines, and pancreas, food protein simply breaks down into what it consists of: amino acids that enter the blood to form proteins.
There are two functional groups: the carboxyl group, which is responsible for the acidic properties of molecules, and the amino group, which imparts fundamental properties to this compound. 8 out of 20 amino acids are not formed naturally; they can only be introduced into the body through food.
- Amino acids
- Replaceable
- Irreplaceable
- Alanin
- Valin
- Arginine
- Histidine
- Asparagine
- Isoleucine
- Aspartic acid
- Leucine
- Glycine (glycocol)
- Lysine
- Glutamine
- Methionine
- Glutamic acid
- Threonine
- Proline
- Tryptophan
- Serin
- Phenylalanine
- Tyrosine
- Cystine
Each amino acid has its own exclusive functions. Methionine has an auxiliary effect for the formation of choline and the regulation of fat metabolism, but also has negative indications. After completing physical activity, it is not advisable to take gelatin-containing products, because methionine does not allow the removal of fat from the liver, being suppressed by glycol and regulating fat metabolism.
Protein will be easily absorbed by the body with a full balance of amino acids. If one amino acid is missing, the construction of proteins will not be as functional. Proteins with a high level of biological value are quickly absorbed, maintain a balance in amino acids, and are easily digested. This can include proteins from dairy products, eggs, fish and meat, removing connective tissue.
Plant proteins do not have such qualities due to the lack of balance in the composition of amino acids. For example, if there is insufficient amount of lysine, the value of bread proteins will be greatly underestimated. When considering cereals and their content, only buckwheat has sufficient amounts of lysine and threonine. Most plant foods are difficult to digest. This happens due to the presence of a shell of fiber and other substances on them that block the action of splitting. Elements found in legumes interfere with the positive effects of digestive enzymes. A high percentage of amino acid absorption - more than 90% - can be obtained from animal proteins, and up to 80% from plant proteins. The highest rate of digestion is for proteins from dairy products, baked goods and various cereals, fish and meat, and the latter take longer to digest due to connective tissue.
Protein absorption rate
The digestibility coefficient of food proteins is of great help in determining their quality. Its calculation includes the amino acid composition and completeness of protein digestion. Products with a coefficient of 1.0 can be considered the most saturated sources of protein.
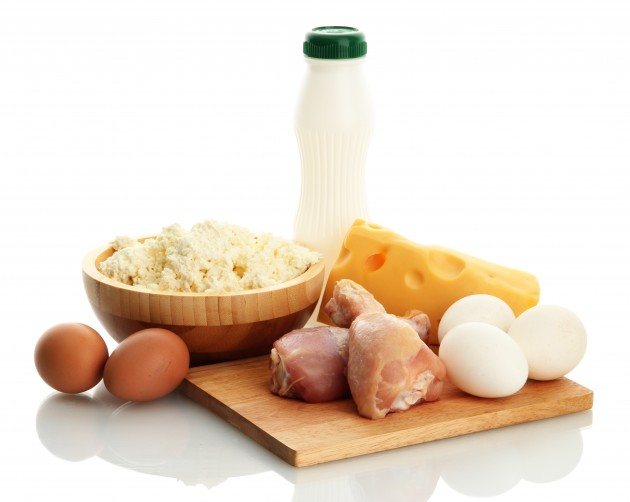

Protein in your diet
Our body constantly consumes and renews protein, which once again proves the necessity and importance of this substance. Proteolysis and replacement of proteins in the cytoplasm of cells occur non-stop. If you refuse to eat for a day, 23 g of protein will be destroyed and 3.7 g of nitrogen will be released. If you obtain protein by eating, a much larger amount of nitrogen will be released. To maintain the correct level of proteins, it is necessary to remember the pattern: the greater the amount of proteins introduced, the more of them will be destroyed. A distinctive feature of proteins from carbohydrates and fats is their ability not to be deposited in reserves. Proteins are an essential part of food because they cannot be formed from other nutrients. Protein is a minor source of energy and can be replaced by carbohydrates and fats. 1g of protein provides 16.7 kJ during the oxidative process.
The somatotropic hormone produced by the pituitary gland, the thyroid hormone thyroxine and the glucocortoid of the adrenal cortex influence protein metabolism. Proteins are the basis of our body, making up about 17% of the total body weight, 50% of which goes to muscle consumption, 20% to cartilage, bones, and 10% to skin.
Proteins and Protein Types by Origin
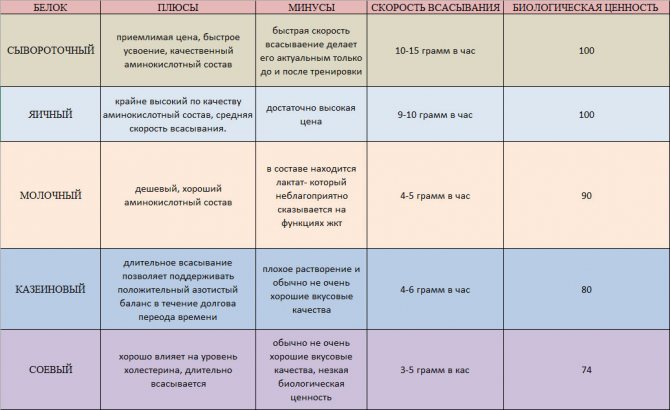
Animal proteins are most recommended for consumption because they are easily digestible and contain a lot of pure protein. But don’t forget that you shouldn’t focus on one protein product; your daily diet should be varied.
"Fast" and "slow" proteins
Let's focus our attention on the second category, since it is this that allows you to achieve results in the two most common actions: building muscle mass and losing weight. The second category of proteins is very popular, because it is “slow proteins” that will help you lose excess weight and build muscle mass. The calorie content of “slow” proteins is lower, they require more energy, and take longer to digest. Cottage cheese is one of the representatives of products belonging to this group. It takes the body up to 8 hours to absorb it. When consuming “slow” proteins, pay great attention to the timing of intake. If you want to gain muscle mass, it is recommended to consume it before bed, which will help you digest food without inconvenience, enriching your muscles with amino acids. Due to its ability to digest slowly, this product is also suitable if you are unable to eat for a long time, preventing you from feeling hungry. “Fast” protein, in turn, is absorbed by the body many times faster. It is perfect for people involved in sports. It is better to consume it before starting a workout or immediately after. At this time, the body needs restoration more than ever.
Products containing “fast” proteins are accordingly absorbed by the body at a fast pace. By consuming this type of protein before or after exercise, you will help your body recover. Therefore, this is an ideal product group for athletes.
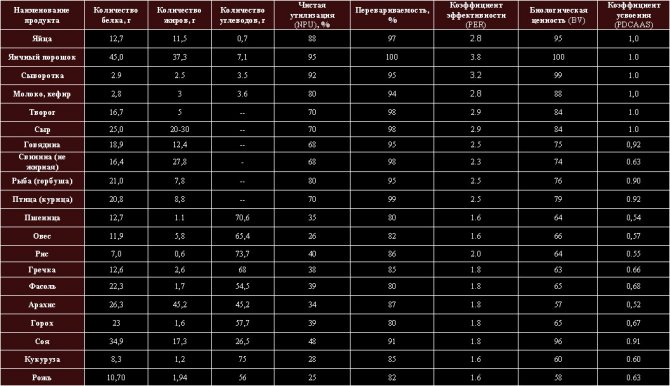
List of preferred protein foods : low-fat cheeses, low-fat cottage cheese, egg whites, most fresh fish and seafood, lean veal, young lamb, chicken, turkey, preferably skinless white meat, soy meat, soy milk or soy cheeses.
Less preferred foods: dark meat of chickens and turkeys, homemade cottage cheese, low-fat cold-smoked cuts, red meat (tenderloin), processed meats: bacon, salami, ham, milk and yoghurts with added sugar.
Choose protein-containing foods that are high in protein absorption, high in protein, and low in fat. When subjected to heat treatment, proteins have better digestibility and will become more accessible to enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract. But again, we must not forget that the biological value of the protein will be reduced because of this. Heat treatment will help in faster digestion of proteins, you can see this in the example of boiled or raw eggs. To increase the speed of digestion and absorption of proteins, products must be boiled more thoroughly, crushed in a blender, or rubbed through a sieve. Remember, overheating has a negative effect on amino acids. For example, with a temperature of 200 ° C, the biological value of casein milk protein will drop by 50%. To prevent the level of lysine from decreasing at high temperatures and prolonged heating, pre-soak the cereals, which will preserve all the beneficial properties. Combine animal and plant products, this will certainly have a positive effect on the balance of amino acids in your body. Include in your menu: dairy products with cereals, pasta, bakery products, cottage cheese, meat, fish, potatoes, vegetables with meat and don’t forget about legumes. The dominance of proteins with low biological value, insufficient amino acids and protein in the diet - all this inevitably leads to protein deficiency. Calorie content should be normal in order to prevent a lack of protein in the diet consumed and not to impair the absorption of already supplied protein.
There are no advantages in excess protein, this leads to an increased load on the kidneys and liver, a possible increase in the tension of the secretory function of digestion, nitrogen metabolism with a shift in the acid-base state to the acidic side, this naturally slows down the recovery process.
Daily protein requirement. Based on data from many sources, the human body is not able to synthesize more than 18 g of protein per day, so adding more than 500 g of pure muscle mass within a month is impossible, and total weight by 2-2.5 kg. Follow the general rules and do not exceed acceptable standards. For 1 kg of weight an athlete needs 2-3g. protein per day, and on days without training 1-2.5 g per 1 kg of body weight. If your main goal is to increase muscle mass, you will need 2.0-2.4 g per 1 kg of body weight; for relief - 1.4 - 2.4 g per 1 kg; in the transition period 1.0-1.2 g of protein per 1 kg; during the competitive cycle - 1.4-1.8 g per kg of your weight.
But there are also proponents of the “satiety” theory, who argue that additional amounts of protein can bring positive results. If the body is oversaturated, no complex reaction will result in stress, therefore, in order to achieve the fastest possible increase in muscle mass, some nutritionists take the above theory as a basis.
Table of protein requirements for athletes - bodybuilders based on
2.5 - 3 g per 1 kg of own weight.
| Body weight, kg | Required amount of protein, g |
| 60 | 150 |
| 65 | 162 |
| 70 | 175 |
| 80 | 200 |
| 85 | 212 |
| 90 | 225 |
| 95 | 237 |
| 100 | 250 |
Signs of protein deficiency
A lack of protein in the body manifests itself as follows:
- An irresistible desire to eat a certain product
It happens that you have a strong craving for sweet, salty or sour foods and it’s impossible to cope with it. Not always, but in frequent cases it is closely related to a lack of proteins.
- Sharp pain in muscles or joints
If your neck or knee suddenly hurts for no apparent reason and in the absence of diseases, you need to check whether there is enough protein in your diet. The body stores a little protein in reserve, which is closely related to the functioning of muscles and joints. With its constant shortage, this reserve is spent, which means health problems arise.
- Problems with sleep and fatigue
The body replaces the lack of proteins with an additional portion of carbohydrates and sugar, but they are quickly processed, energy is thrown away, and after a while it is not enough. If you have insomnia, you can try to reduce the amount of sweets and focus on protein.
- Moodiness, irritability, bad mood and constant stress
After a certain period of a protein-free regime, the body is completely exhausted, and even carbohydrate energy surges cannot save it. This leads to general malaise and irritability.
Protein diet for weight loss and health. Principles
The protein diet is a special and very effective type of diet, in which the diet of a losing weight person contains only those foods that contain a really large amount of proteins.

The main advantage of a protein diet is that proteins in the body help carbohydrates to be absorbed faster, thereby maintaining the necessary and stable sugar level in the blood.
At the same time, the body spends more energy for processing , protein is more difficult to digest than the same carbohydrates or fats. That is why this type of diet is considered the most effective for those who are struggling with excess weight.
Benefits of a Protein Diet
The main advantages and benefits of a protein diet are that it muffles the feeling of hunger, which usually always accompanies a person losing weight, and that weight loss is carried out by burning fat, and not by gaining muscle mass.
In addition, this diet is perfect for those who are intensely involved in any kind of sport or simply lead a very active and active lifestyle.
Weight decreases quickly; after finishing the diet, the kilograms do not return, as happens with other diets.
On average, in 2 weeks of such a diet you can lose from 4 to 9 kilograms!
Disadvantages of a protein diet
Despite a fair number of advantages, a protein diet (eating foods that contain protein) also has its disadvantages, of which there are also many.
The biggest disadvantage is that such a diet implies an unbalanced diet, which is not very good for the body. The lack of vitamins can negatively affect sleep and performance (a person will get tired and exhausted faster).
With such a diet there is a very large load on the kidneys.
High consumption of calcium in the body.
A protein diet can negatively affect the functioning and proper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
This diet is contraindicated for those who have heart or vascular problems.
List of products and how to create a menu
When creating a menu, it is recommended to choose natural products, preferably lactose-free.

Of the proteins, those proteins that have been subjected to heat treatment are most easily and quickly absorbed.
Grocery list:
- Chicken fillet.
- Veal.
- Rabbit meat.
- Fish with white meat.
- Shrimp, squid.
- Milk.
- Various eggs.
- Curds.
- Cheese.
- Soy cheese.
Sample menu for the week
Monday:
- Kefir, omelet (from 3-4 proteins), drinks – tea.
- The chicken is boiled, you can add spices to it. Apple.
- Fish baked in the oven, 150 g with spices and parsley, dill.
Tuesday:
- A tomato, two hard-boiled eggs, maybe yogurt.
- 100 g of meat, steamed exclusively, salad.
- 150 g of lettuce and cucumber salad.
Wednesday:
- Oatmeal (porridge) with dried fruits or nuts, tea, maybe coffee.
- Chicken breast, boiled, salad.
- Steamed fish, a glass of boiled beans, a glass of yogurt.
Thursday:
- 150 g of natural cottage cheese, tea (preferably green), nuts.
- Chicken broth, chicken breast, vegetables.
- Something meat, definitely baked, salad.
Friday:
- Fresh vegetable salad, yogurt, but only natural and without additives.
- Broccoli soup, boiled chicken breast. Bread.
- Fresh cabbage and pea salad, baked breast (can be topped with cheese).
Saturday:
- Omelet, a little ham, tea.
- 100 g steamed fish.
- Stew of meat and vegetables, yogurt. You can have kefir.
Sunday:
- 150 g of cottage cheese with dried apricots or prunes, green tea.
- Cooked buckwheat, some meat, maybe fish.
- 150 g meat with herbs (baked), kefir.
How to get off a protein diet correctly
In order for the body to experience less stress when leaving the diet, it must be done correctly and gradually.
It is recommended to regularly drink sugar-free drinks and try to eat less sweets and starchy foods.
It is better to have breakfast with porridge (for example, oatmeal) or cottage cheese.
It is recommended to eat more fresh vegetables and fruits.
Contraindications
A protein diet is contraindicated for people suffering from heart or vascular problems, as well as for people who have severe problems with the stomach and digestive process.
This diet is not recommended for those who have problems with the kidneys and liver.
Under no circumstances should anyone who has any type of cancer follow this diet.
It is also not recommended for older people to follow this type of diet, as it increases the risk of blood clots.
Protein content of available foods

In order to eat right and healthy, you don’t have to spend a lot of money on it. What inexpensive foods contain protein? List of available high protein foods:
- Buckwheat;
- Chicken;
- Peanut;
- Peas and beans;
- Chicken eggs;
- Hard, processed or any other cheese;
- Cottage cheese;
- Lentils;
- Canned fish and any other products.
In any case, one nutritious meal high in protein and fiber will not cost more than a fast food snack, which will give the body nothing but empty calories and unhealthy fat.
Animal protein. Grocery list
The following foods contain the largest amounts of animal protein:
- A variety of meat products.
- Fish.
- Milk.
- Curd products.
- Various eggs.
Meat products
List:
- Lean beef.
- Chicken fillet.
- Chicken breast.
- Turkey meat (fillet is best).
- Rabbit meat.
- Deer meat.
Seafood
List:
- Salmon.
- Tuna.
- Mackerel.
- Sardines.
- Shrimps.
- Lobsters.
- Squid.
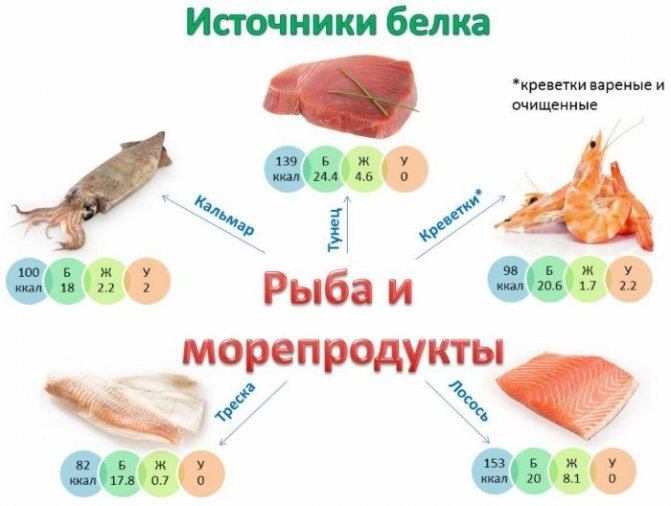
Dairy and fermented milk products
Milk proteins are special natural proteins - proteins of animal origin, which are more easily and quickly absorbed by the human body.
These dairy and fermented milk products include:
- milk,
- curdled milk,
- kefir,
- cheese,
- cottage cheese,
- sour cream.
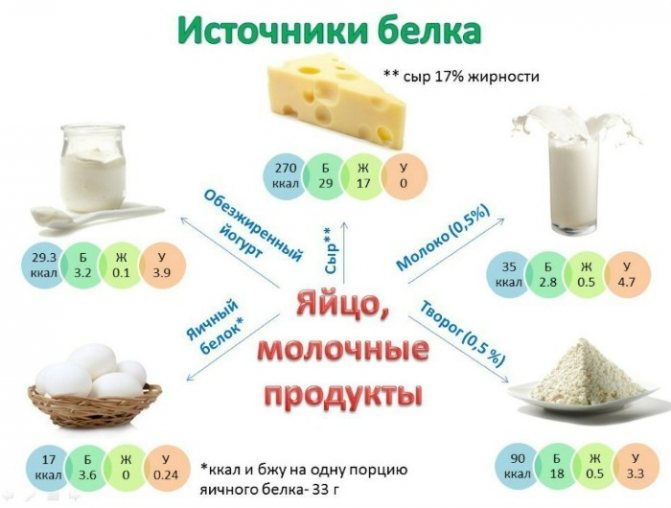
It is these products that should be present in the diet of every person, regardless of his desire to lose weight or build muscle mass.
Milk proteins increase the performance of the entire body, as well as its endurance.
In addition, such proteins are easily digestible due to the fact that they do not change the acid-forming function.
List of the healthiest protein foods
The most important thing in food is not only the protein content, but also the overall ratio of dietary fat, vitamins and nutrients. You cannot rely only on one positive point of a product; nutrition must be complete and varied.
Example of the most useful products:
- Cottage cheese – high calcium content
- Peanuts - healthy vegetable fats
- Tuna or any other fish - fish oil and omega
- Oatmeal or other porridge are slow carbohydrates that fill you up for a long time and provide a large supply of energy.
- Soy - a huge supply of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C and omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids
The importance of protein for the body
View this post on Instagram
The bamboo shoots that pandas eat contain 2.6 grams of protein for every 100 grams. We bet you that pandas would grow even bigger if they knew which foods contained a lot of protein. Find out what to include in your diet to safely call it “high-protein” (naturally, on our website











