The benefits of salt
Content:
- The benefits of salt
- The essence and rules of a salt-free diet
- Prohibited Products
- Authorized Products
- Japanese salt-free diet
- Salt-free diet for 15 days
- Salt-free diet for 4 days
- Salt-free diet for pregnant women
- Salt-free rice diet
- Results and harm of a salt-free diet
- Salt-free diet recipes
- conclusions
Salt is vital for the normal functioning of the body, the stable functioning of all its important organs and systems. Therefore, complete abstinence from salt is simply impossible. Otherwise, this can lead to unpleasant consequences, because salt is necessary for the proper production of insulin, as it is capable of breaking down glucose. It helps to relax the muscles, which is necessary for their constant work. Salt promotes the rapid digestion of food and the breakdown of food, since thanks to it, hydrochloric acid is produced in the human body. That is, it is with the help of salt that all useful substances, vitamins, macro- and microelements enter the blood. Thus, it turns out that salt is really good for the body, but only in small quantities.
Eating food without salt for a long time can lead to serious diseases such as anorexia and osteoporosis. It will cause metabolic disorders and nervous system disorders, which can result in depression or other mental illnesses.
What is a salt-free diet?
The term “salt-free diet” should not be understood as a complete abstinence from salt, but its limitation. A salt-free diet involves a complete rejection of smoked meats, canned foods, sausages, processed foods, flour products, fast food, and mayonnaise.
In people suffering from heart disease and hypertension, a salt-free diet helps get rid of edema and high blood pressure, and improves the quality of life. For people with excess body weight, such a diet will help get rid of the hated extra pounds, especially if you combine salt restriction with reducing the calorie content of the food you eat and cleansing the body with Enterosgel.
The essence and rules of a salt-free diet
In fact, it is impossible to completely give up salt even because it is present in various foods: meat, bread, vegetables and even various fruits. The salt-free diet is based precisely on this principle - the use of salt, which is contained only in foods, completely excluding other types. This strict regime is suitable for people with exacerbation of chronic diseases or with advanced disease states. If the goal of such a diet is only to get rid of puffiness, then it is quite possible to get by with a gentle option. In this case, adding salt to the food is allowed, but table salt should be used only in a minimal amount.
A salt-free diet can last from 4 to 15 days, depending on the results you want to achieve. And to really please these results, you should follow a few simple rules, thanks to which a salt-free diet will not cause serious discomfort:
- the daily diet should be divided into several small portions, eaten at least five times a day, but not much;
- It is better to eat steamed dishes, completely eliminating frying;
- salt dishes either at the very end of cooking, or already cooked foods;
- add oil only to prepared dishes;
- Garlic, onion or herbs can be used as a salt substitute; the addition of soy sauce is allowed, but only without salt content;
- It is strictly prohibited to consume alcoholic beverages;
- Every day you need to drink more than two liters of water;
- do not overeat and always get up from the table with a slight feeling of hunger.
Low salt diets: eating out
For many people, eating out is a way to relax and socialize. You don't have to give this up if you're on a sodium-restricted diet, but you do need to be more careful about what you order at restaurants. Sodium is not just table salt. It can also be found in sodium citrate, sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and monosodium glutamate (MSG). Asian foods often contain MSG, as well as soy sauce, which is very salty. But with some helpful tips, you can enjoy your restaurant experience while limiting the amount of sodium in your diet.
Key points
- Restaurant foods tend to be high in sodium.
- Most restaurants will prepare food with little or no sodium if you ask.
- Food can be both tasty and low in sodium.
What is a low sodium diet?
If you are following a low-sodium diet, you should limit your intake of salt and other forms of sodium in the foods you eat. Depending on your condition, your doctor will likely limit your sodium intake to less than 2,000 milligrams (mg) per day. This can pose a problem for people who like to eat out because processed foods, including restaurant food, are often the biggest source of sodium in our diets.
Test your knowledge
The biggest source of sodium in most people's diets is added salt to their food.
Correct answer.
Prepared foods, including restaurant foods, are often the biggest source of sodium in our diets.
Why is it important to limit sodium when eating out?
Sodium causes fluid retention in your body. It may worsen some conditions, such as heart failure or kidney disease. For example, if you have heart failure, too much sodium increases the load on your already weakened heart, which can lead to the development of acute heart failure. Fluid may accumulate in your lungs (making it difficult for you to breathe), feet, ankles, legs, and abdomen. Limiting sodium in your diet can improve your well-being.
Test your knowledge
Too much sodium can cause fluid retention in your body.
Correct answer.
Too much sodium can cause fluid to accumulate in your body. It may worsen some conditions, such as heart failure or kidney disease.
How can you avoid sodium when eating out?
Limiting sodium requires extra effort when eating out because you can't always tell which foods are high in sodium by looking at the menu. It often depends on how the restaurant prepares the dish, what ingredients are used and how much sodium is added. Here are some ways to avoid sodium when dining out.
- Try to choose restaurants where dishes are prepared to your order, instead of fast foods or cafeterias. Before you order, ask how the food is prepared and if there are low-sodium items on the menu. Often you can ask that your order be prepared without adding salt.
- Most fast food restaurants have nutritional information available, including sodium content. If you eat fast food, ask for the information sheet and choose low-sodium items.
- Ethnic cuisines such as Asian or Mexican are often high in sodium. You don't have to skip them, but you can ask the waiter to help you choose low-sodium foods.
- When you eat out, try to eat low-sodium foods the rest of the day. This will help you maintain your daily sodium limit.
Find out what foods you can eat and which you should avoid. For example, 1 tablespoon of soy sauce contains more than 1,000 mg of sodium and 1 teaspoon of salt contains about 2,000 mg of sodium. You can use the list below and take it with you to the restaurant. You can replace low-salt or fresh foods with ones that are higher in sodium.
| Tips for eating out | |
| Dishes to Avoid | Instead, choose or ask... |
| Smoked, canned and salted meat, fish and poultry | Fresh, grilled, boiled, simmered or fried meat, fish and poultry |
| Ham, bacon, hot dogs, mixed meats and cheeses | Freshly roasted pork, turkey or chicken |
| Canned vegetables | Fresh, steamed vegetables without added salt. (Don't forget that salt is added to boiled vegetables unless you ask not to) |
| Condiments such as vinegar, olives, tartar sauce and ketchup | Sliced cucumbers, malt vinegar or low-sodium ketchup and mustard |
| Sauces, including soy, tomato, gravies and products in their own juice | Low sodium soy sauce, olive oil |
| Salad dressings | Vegetable oil, vinegar, lemon juice, or low-sodium dressings |
| Fast food items including French fries, pizza and tacos | Baked Tomato Grilled Chicken Sandwiches |
| Soups and broths | Salads without croutons, bacon, cheese or olives |
| Any drinks containing tomato juice, V-8 or Clamato. Including alcoholic drinks such as Bloody Mary | Orange juice, other citrus juices, or soft drinks |
| Fried or seasoned rice | Steamed rice. (Asian restaurants often add salt to this type of rice. Be sure to ask that no salt be added to steamed rice.) |
| Pasta dishes with tomato sauce | Pasta dishes seasoned with olive oil or fresh tomatoes |
For dessert, you can choose ice cream, sorbet, frozen yogurt and angel food cake, which are low in sodium.
Test your knowledge
If you are following a low-sodium diet, you cannot eat out because food prepared in restaurants is very high in sodium.
Correct answer.
You can eat out if you are on a low-sodium diet. But this will create additional difficulties for you, because you cannot always tell by looking at the menu which dish has a high sodium content. It often depends on how the restaurant prepares it, what ingredients they use, and how much sodium they add.
Grilled chicken, steamed vegetables and roasted tomatoes are good choices if you want to eat out without compromising your low-sodium diet.
Correct answer.
Grilled chicken, steamed vegetables and baked tomatoes can be selected if you eat out and are on a sodium-restricted diet.
Where can I go?
Now that you've read this information, you can choose low-sodium foods when you eat out. Discuss changes in your diet with your doctor. Your doctor can give you advice on how to avoid sodium if you eat out. You may also want to consult with a registered dietitian to get more ideas about your healthy diet.
Authorized Products
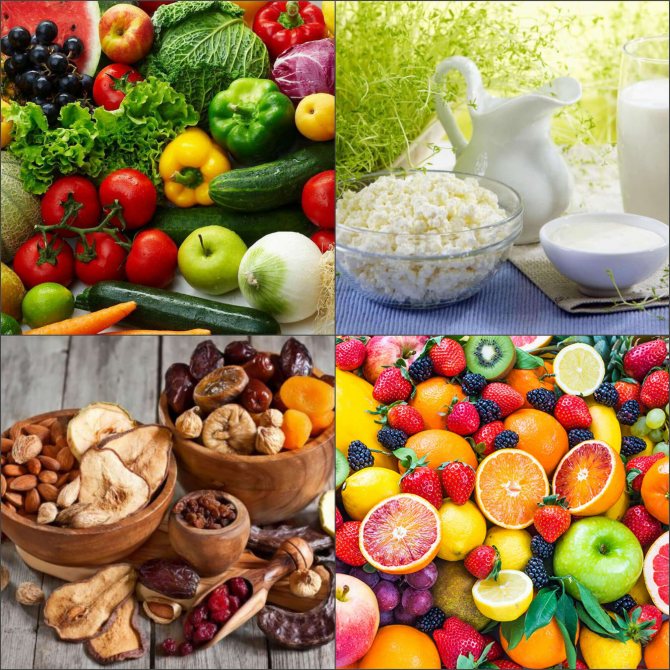

List of allowed foods on a salt-free diet:
- raw and boiled vegetables;
- skimmed milk;
- fermented milk products and cottage cheese;
- fruits and berries;
- dried fruits and jelly;
- low-fat types of fish and meat;
- vegetable broth;
- rye and wheat bread;
- porridge;
- tea.
Products on a salt-free diet
Can be consumed
- rye bread and crackers
- soups, only with vegetable or fruit broth
- lean beef, poultry and fish
- porridges of different grains
- raw and boiled vegetables (cabbage, potatoes, cucumbers, zucchini, radishes, beans, tomatoes)
- sweet fruits and berries
- eggs (no more than one per day)
- jelly, compotes, jelly
- milk, cottage cheese, mild cheese
- raisins, dried apricots, apricots, figs
- green tea
Cannot be consumed on a salt-free diet
- everything fried and fatty
- spicy and smoked
- pickles and marinades
- fish and meat broths
Japanese salt-free diet
The Japanese diet is a type of salt-free diet. This is not a quick, but very effective means for losing weight. It is balanced, and during the fasting process you can lose up to four kilograms of weight weekly, and for the entire course of the diet, about eight kilograms. This option requires a complete absence of salt in dishes. You can use a thirteen-day weight loss method, or you can limit yourself to a diet program for a week. You can use dishes for the first 7 days in your diet.
Japanese salt-free diet menu for 13 days
First day:
- breakfast – natural freshly brewed unsweetened coffee;
- lunch – boiled cabbage, flavored with vegetable oil, two boiled eggs, 250 grams of tomato juice;
- dinner - about two hundred grams of fish cooked in a double boiler or baked in the oven.
Second day:
- breakfast – natural freshly brewed unsweetened coffee, a slice of black rye bread;
- lunch - about two hundred grams of fish cooked in a steamer or baked in the oven, boiled cabbage, flavored with vegetable oil;
- dinner – 250 grams of fermented milk product, one hundred grams of boiled unsalted beef.

The third day:
- breakfast – natural freshly brewed unsweetened coffee, a slice of black rye bread;
- lunch – eggplants or zucchini fried with vegetable oil;
- dinner - about two hundred grams of unsalted beef cooked in a double boiler, two hard-boiled eggs, fresh cabbage flavored with vegetable oil.
Fourth day:
- breakfast – fresh small carrots and freshly squeezed lemon juice;
- lunch - about two hundred grams of fish cooked in a steamer or baked in the oven, 250 grams of tomato juice;
- dinner - about two hundred grams of various fruits.
Fifth day:
- breakfast – fresh small carrots and freshly squeezed lemon juice;
- lunch - about two hundred grams of fish cooked in a steamer or baked in the oven, 250 grams of tomato juice;
- dinner - about two hundred grams of various fruits.
Sixth day:
- breakfast – natural freshly brewed unsweetened coffee;
- lunch - about two hundred grams of unsalted boiled chicken, fresh cabbage with carrots, flavored with vegetable oil;
- dinner - two boiled eggs, one fresh carrot, flavored with vegetable oil.
Seventh day:
- breakfast – freshly brewed green tea;
- lunch – about two hundred grams of unsalted boiled beef;
- dinner - you should choose any of the above complexes, except for the diet from the third day.
Eighth day:
- breakfast – natural freshly brewed unsweetened coffee;
- lunch – half a kilogram of unsalted boiled chicken, fresh cabbage and carrots flavored with vegetable oil;
- dinner - one grated carrot, flavored with vegetable oil, two boiled eggs.

Ninth day:
- breakfast – fresh small carrots, freshly prepared lemon juice;
- lunch – about two hundred grams of fish cooked in a steamer or baked in the oven, 250 grams of tomato juice;
- dinner - about two hundred grams of various fruits.
Tenth day:
- breakfast – natural freshly brewed unsweetened coffee;
- lunch – fifty grams of hard cheese, one boiled egg, three medium carrots, flavored with vegetable oil;
- dinner - about two hundred grams of various fruits.
Eleventh day:
- breakfast – natural freshly brewed unsweetened coffee and a slice of black rye bread;
- lunch - eggplants or zucchini, fried with vegetable oil;
- dinner - fresh cabbage, seasoned with vegetable oil, two boiled eggs, about two hundred grams of unsalted boiled beef.
Twelfth day:
- breakfast – natural freshly brewed unsweetened coffee and a slice of black rye bread;
- lunch - baked or steamed fish, fresh cabbage flavored with vegetable oil;
- dinner – 250 grams of fermented milk product, one hundred grams of boiled unsalted beef.
Thirteenth day:
- breakfast – natural freshly brewed unsweetened coffee;
- lunch – boiled cabbage, flavored with vegetable oil, two boiled eggs, 250 grams of tomato juice;
- dinner - about two hundred grams of steamed or baked fish.
Popular types of salt-free diets
Salt-free weight loss methods have many varieties.
Japanese salt-free diet
The Japanese salt-free diet program, designed for 7 days, is very strict and tough. According to reviews, you can lose up to 7 kg of excess weight with it.
The menu is as follows:
| ☀ Day one: — breakfast - a cup of coffee without sugar; — dinner — fresh carrot salad, 2 boiled eggs; — dinner - the same salad and boiled or fried fish. | ☀ Day two: — breakfast - a cup of coffee without sugar, a slice of rye bread; — dinner - 200 g of boiled fish, cabbage salad, 1 raw egg;- — dinner - apples. |
| ☀ Day three: — breakfast - a cup of coffee without sugar; — dinner - fresh carrot salad, 1 raw egg; — dinner - apples. | ☀ Day four: — breakfast - a cup of coffee without sugar, a slice of rye bread; — dinner - zucchini fried in vegetable oil; — dinner - 2 boiled eggs, 200 g of lean beef, cabbage salad. |
| ☀ Day five: — breakfast - salad of grated raw carrots, seasoned with lemon juice; — dinner - boiled fish, tomato juice; — dinner - apples. | ☀ Day six: — breakfast - a cup of coffee without sugar, a slice of rye bread; — dinner - 0.5 boiled chicken, carrot and cabbage salad; — dinner — 2 boiled eggs, carrot salad. |
| ☀ Day seven: — breakfast - a cup of green tea; | |
There is also a two-week version of this weight loss program.
Salt-free diet for four days
During such a diet, you can lose five kilograms of excess weight.
☀ First day:
During the day, you need to eat only boiled potatoes without salt and seasonings, and drink drinks without sugar.
☀ Second day:
Throughout the day, you should only eat pasta without salt, oil or seasonings, and drink unsweetened drinks.
☀ Third day:
During the day, eat boiled chicken without skin and fat, salt and spices, and drink drinks without sugar.
☀ Day four:
We eat boiled potatoes all day and drink unsweetened drinks.
During this diet, consume the above foods in moderation.
Salt-free diet option for 15 days
☀ First 3 days
We eat chicken without skin and fat (preferably breast). You can eat 500 grams per day.
☀ Next three days
We eat non-fatty fish. We eat 500 grams per day.
☀ Three days
any porridge cooked in water. We eat 500g per day.
☀ Three days
vegetables, any except potatoes. Can be raw, boiled, baked, 1-2 kg per day.
☀ Three days
fruits other than bananas. 1-2 kg in 1 day.
Salt-free diet for 15 days
This diet is designed for five stages, each of which lasts three days.

The first stage involves eating chicken breast, or chicken meat without fat and skin, for three days. The recommended amount is 500 grams per day.
At the second stage, you are allowed to eat lean fish in the amount of 500 grams per day for all three days.
At the third stage - various porridges cooked in water. Not sweet and not salty. Quantity: 500 grams per day.
The fourth stage involves introducing vegetables into the diet. You are allowed to eat different vegetables, excluding only potatoes from the diet. You can eat fresh, boiled or baked foods in quantities of up to two kilograms per day.
The last fifth stage allows the consumption of fruits, with the exception of bananas, in an amount of about two kilograms per day.
Salt-free diet for 4 days
During such fasting you can lose about five kilograms of excess weight. Products recommended for consumption should be eaten in small quantities at several meals.
On the first day you need to eat only boiled potatoes and drink unsweetened drinks. The use of various seasonings, salt and sugar is prohibited.
On the second day, you should give preference to pasta, still without salt, seasonings and oil. You should also drink sugar-free drinks.
On the third day, it is recommended to eat lean boiled chicken without skin and sugar-free drinks.
The menu on the fourth day is exactly the same as on the first.
Salt-free diet for pregnant women
It is known that salt can retain water in the body, which invariably leads to edema. This can be noticed especially often during pregnancy. Of course, expectant mothers should never go on a diet, but following some rules of a salt-free diet can even be useful in some cases. It is best to start following this diet in the third trimester, when susceptibility to edema is highest.
Sample menu for a salt-free diet during pregnancy

Breakfast:
- semolina porridge;
- milk tea or coffee with milk.
Dinner:
- borscht or soup;
- stewed or steamed meat;
- pasta or stewed vegetables;
- baked potato;
- fruits.
Afternoon snack:
- bun with fermented baked milk or milk;
Dinner:
- steamed fish or meat cutlets;
- boiled potatoes;
- milk;
- Apple pie.
Salt-free diet for pregnant women

During pregnancy, the diet should be carried out on the advice of a doctor. If a pregnant woman suffers from edema syndrome , following a diet based on a salt-free method helps get rid of excess fluid.
You can achieve the effect by removing marinades, pickles, and seasonings containing salt from your diet.
The salt restriction is compensated by an increase in dairy and plant products in the menu. Fruits, vegetables, and cereals will bring benefits. According to the rules of the diet, cheese must be excluded. Steam cooking is encouraged.
When using a diet using the salt-free method, a pregnant woman should monitor the calorie content of her meals . The daily intake must correspond to the caloric intake required in a particular trimester.
Salt-free rice diet
One of the popular types of salt-free diet is the rice diet. Her diet is quite balanced and includes the consumption of boiled rice without salt, herbs and fresh unsalted vegetables. You can eat rice porridge as much as you like, but it is better in moderation. At the same time, the amount of vegetables on the menu should not exceed the amount of rice. The recommended duration of such a diet is 7 days. Throughout the entire period of such fasting, you can lose from three to five kilograms of excess weight. In addition, the rice diet is not only a way to get rid of unnecessary pounds, but also a way to quickly and effectively cleanse the body. After all, rice is able to remove dangerous toxins and harmful waste, and also has a significant rejuvenating and healing effect.
Results and harm of a salt-free diet
With proper and moderate consumption of salt in food, the results of a salt-free diet will undoubtedly please you, since such a diet will not only allow you to get rid of a few extra pounds, but also restore and normalize the water-salt balance of the body. However, you should remember that you need to exit any type of fasting with caution, gradually introducing other foods into your diet. It is advisable, of course, to try to use salt in fairly small quantities, and perhaps even replace it with spices and seasonings.

Harm from a salt-free diet is only possible if you use it for a long time, since prolonged consumption of food without salt can cause metabolic disorders. In this case, dehydration, cramps in the calf muscles, and poor absorption of vitamins and minerals necessary for the normal functioning of the organs and systems of the human body may occur. Also, a lack of sodium, which is contained in table salt, can lead to heart disease. Therefore, it is better to listen to the recommendations of nutritionists and not to sit on a strict salt-free diet for a long time.
Salt-free diets: useful, but not for long...
Salt has existed with humanity throughout its history. At first, people used sea water and rock salt deposits, then they learned to process it - saltworks appeared, one of them, the largest, was opened on the territory of Bulgaria several thousand years ago. In Russia, salt became available to the entire population from the 15th century, when the great salt route, the Chumatsky Tract, stretched from the Crimean lakes to Muscovy and Ukraine. Salt was a fairly expensive product and was worth its weight in gold. Lack of salt in Ancient Rus' was considered a real disaster. If for some reason there were interruptions in the supply of salt, people became weaker and, according to the chronicle, “were in great sadness” and could neither work nor eat. Since salt became a cheap and widely available product, its consumption has been steadily increasing. Thus, from 1940 to 1985, its consumption increased by an average of 2.4 times.
However, in 1979, at an international symposium in Germany, it was first recognized that salt was a harmful product, which led to a craze for salt-free diets. People once again experimented on themselves. The “white death” was published in magazines, talked about on television, and to this day a huge number of weight loss diets are based on a complete abstinence from sodium chloride in the diet.
Why is salt needed?
Salt (sodium chloride) is vital for every living organism: it is part of the intercellular fluid, lymph, soft tissues of the body, as well as bones. Sodium ions are necessary for the penetration into cells of energy sources and substances that will be used as structural components of cells. Sodium chloride ensures fluid balance between blood plasma and plasma inside cells, transmission of intracellular and nerve impulses. In addition, sodium chloride is needed for the secretion of hydrochloric acid, which is part of the gastric juice. In a word, life is simply not possible without salt! Therefore, both excess and deficiency of this substance are harmful. Thus, a lack of sodium chloride causes dehydration of the body, which, even in mild forms, can cause a decrease in skin turgor (flabbiness), dizziness and headaches.
It is clear that the body has substantial reserves of such a strategic product as sodium chloride, and several days of a salt-free diet will not do any harm. But, no matter how large the internal reserves of salt are, they are depleted if sodium chloride is not supplied for a long enough time.
Excess sodium chloride leads to an increase in blood viscosity, to the formation of stones in the liver and kidneys, provokes heartburn and increased blood pressure, and also leads to disruption of the kidneys, liver and heart. Excess salt in the diet leads to edema, arterial hypertension and many other pathological conditions. The least harm that is familiar to each of us is swelling. But an excess of this macroelement is also accompanied by a lack of potassium, since these substances are interconnected in the body, therefore both a complete refusal of salt and its excess are harmful for cardiac activity. After all, potassium regulates the activity of the heart muscle.
That is, salt is necessary for the body, but in large quantities it can cause serious harm. Therefore, for starters, it would be nice to think about how much salt we consume in regular food?
The adult human body contains about 250 grams of sodium chloride. Every day, every adult needs from 5 to 7 grams of salt per day; in the summer, due to increased sweating, this need increases to 10–15 grams. For children, the daily need for sodium chloride is much less: children under one year old need 1-2 grams of NaCl per day, children aged 4-6 years need 3 grams per day, children 7-10 years old - 7 grams, children over 11 years old - 6 grams per day.
Modern food is oversaturated with salt. People who do not monitor the amount of salt in their diet can unnoticed increase their daily salt intake to 30–40 grams per day. Why can we, without even noticing it, significantly exceed our daily salt intake by eating the most ordinary foods? Because many of them contain salt in fairly large quantities, which may not be obvious at first glance. Here is a list of foods that are surprisingly high in salt and should always be taken into account when planning your diet:
- Cheese . One hundred grams of cheese contains about 1.5 grams of salt - and this is already a quarter of its daily requirement.
- Nuts . Prepared nut mixtures contain a high amount of salt due to the way they are prepared: manufacturers add salt to them to increase shelf life and enhance flavor. PER 100 grams of mixture there is at least 0.5 grams of salt.
- Soy products. Soy sauce contains 6 grams of salt in 100 grams. Soy meat substitutes (included in sausages, sausages or dietary products for vegetarians) contain at least 2 grams of salt per 100 grams of product.
- Corn flakes . 100 grams of flakes contain 0.7 grams of salt.
- Bread . Rye varieties of bread contain 0.5 grams of salt per hundred grams of product, white varieties - half as much.
- Semi-finished products . Ready-made cutlets, steaks, sausages and dumplings contain a very large amount of salt - 1 gram of salt per hundred grams of product.
- Sauces . All sauces (not just soy sauce) contain at least 1 gram of salt per hundred grams of food.
- Canned vegetables contain at least 1–2 grams of salt per hundred grams of product. Salted or canned fish can contain up to 5 grams of salt per 100 grams of product.
- Olives . The technology for preparing canned olives also uses a strong salt solution. 100 grams of olives contain at least 1.5 grams of salt.
This is how it turns out that, even if we do not consume salt in dry form, the quantities we absorb through many foods can be represented in the form of teaspoons and tablespoons of NaCl.
In normal health, you simply need to limit your salt intake to at least the daily requirement. But in some cases, it is recommended to reduce the salt content in the diet to a minimum.
Salt-free diets are recommended for certain diseases and metabolic disorders:
- acute inflammation of the kidneys with edema;
- heart failure accompanied by edema;
- ascites;
- myocardiosclerosis and hypertension;
- obesity;
- dysfunction of the pancreas;
- allergic inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eyes and nose;
- chronic inflammation of the intestinal mucosa;
- peptic ulcer;
- chronic and acute gastritis with high acidity;
- acute articular rheumatism.
Diets for such conditions should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor, and the body’s reaction to them should be monitored using tests.
Salt-free diets involve control and limitation (or complete exclusion) of table salt from the diet.
They are very popular among people trying to lose weight as quickly as possible. Indeed, salt-free diets show us the miracles of weight loss on the scale in the very first 2-3 days of their use. Only the rapid decrease in weight when giving up salt and salty foods has nothing to do with fat. Water is removed from the body, which will certainly return when you return to normal nutrition. Therefore, losing 3–5 kg (depending on initial body weight) in the first days of a salt-free diet can rather be called a dietary trick than a result. Of course, it is very tempting to get such almost instant and impressive results from a diet, but the harm from depriving yourself of sodium chloride is no less impressive.
In 1998, Michael Elderman, a cardiologist at the A. Einstein College of Medicine in New York, first published the results of his 20-year follow-up of 11,348 people who restricted their salt intake to varying degrees. According to the study, participants who reduced their average daily salt intake from 8.75 to 6 g began to feel better. Moreover, statistical regression analysis demonstrated that there was a clear pattern between severe sodium restriction in the diet and an increase in the number of heart attacks and strokes over long-term follow-up. The scientist was convinced of a pathological increase in the activity of nerve cells, of an increased risk of heart attack due to narrowing and spasms of blood vessels and thickening of the blood due to a lack of salt in the body. Since then, many studies have been presented confirming Michael Elderman's conclusions, which has led professional nutritionists to warn people against excess salt in their diet rather than to urge them to avoid it completely.
When are salt-free diets not recommended?
- For pregnant and nursing mothers. During pregnancy and during breastfeeding, the mother's body consumes a large amount of sodium chloride, and limiting its supply can cause health problems for both mother and child. In some cases (problems with the kidneys, heart, severe edema), it is recommended to limit the intake of sodium chloride into the body, but such restrictions should only be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
- When playing sports. During active physical exercise, the body excretes up to 30–40 grams of salt per day through sweat. Sodium is found in every cell of our body and is involved in the processes of muscle contraction, so sodium restriction in the diet is contraindicated for people with heavy physical labor or athletes, especially since this element is very actively lost through sweat.
- People taking diuretics should absolutely not completely avoid salt.
- In hot countries. If you live in a country with a hot climate, or are on vacation in a southern country, salt-free diets are not recommended. In countries with a temperate climate in the summer, it is also better not to adhere to salt-free diets, postponing them for the cold season.
- For workers of heavy physical labor. Salt-free diets are not recommended for those employed in jobs with heavy physical exertion.
conclusions
A salt-free diet can be recommended for many conditions and diseases. Limiting salt in your daily diet to at least the daily requirement is very useful. However, the duration of salt-free diets, which exclude salt almost completely, should not exceed 2 weeks. Strict salt-free diets can be recommended exclusively as a short-term measure to relieve swelling and normalize the electrolyte balance of the body. Even completely healthy people are strictly prohibited from adhering to a strict salt-free diet for a long time! When limiting the intake of sodium chloride into the body, even for short periods, you should ensure that its amount is not less than 5 grams per day.
Thus, when it comes to salt, a middle ground is needed. In no case should you be persuaded to completely give up sodium chloride, but be sure to take a closer look at your diet to find out if there is an excess of it.
During a salt-free diet, you must follow the following rules .
- The following products should be completely excluded: pickles and marinades; chips and nuts; smoked meats; fast food; fat meat; sausages and smoked meats.
- Only spicy, fatty, sweet, salty and flour foods are excluded from the diet. The menu includes protein and plant foods; among dairy products, preference is given to kefir.
- During the salt-free diet, introduce foods such as seaweed and citrus fruits into your diet. To enhance the taste, you can add onions, garlic and herbs to your food.
- Split meals are recommended: 4–5 times a day in small portions.
- Meat and vegetables must be steamed or boiled without salt.
- It is better to have dinner no earlier than 3 hours before going to bed.
- You should stick to a non-strict salt-free diet for no longer than two weeks.
- A strict salt-free diet should only be carried out under the supervision of a doctor solely for medical reasons.
- Author - Polukhina Anastasia Aleksandrovna
- 01.11.2017
- All consultations by the author
Salt-free diet recipes
In order to make it easier to endure the period of salt-free fasting, various recipes are proposed below. Cooking such tasty and healthy dishes will distract you and allow you to enjoy food without salt without causing discomfort.
Vegetable okroshka
To prepare this easy soup you will need:
- radishes – 10 pieces;
- cucumber – 2 pieces;
- potatoes - 2 pieces;
- celery stalk – 2 pieces;
- garlic – 2 cloves.
Finely chop the vegetables and place on plates. Pour the contents of the plates with kefir or whey.
Chicken pancakes
To prepare chicken and vegetable pancakes you will need:
- chicken fillet – 1 piece;
- onions – 2 pieces;
- potatoes - 2 pieces;
- carrots – 2 pieces;
- greenery;
- soda;
- lemon juice.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Finely chop the fillet, grate the onion, add to the meat and leave for half an hour. Then add grated vegetables, soda, herbs and a little lemon juice to the minced meat. Mix everything thoroughly and cook like regular pancakes. They will be especially useful in a double boiler. You can serve this dish with unsweetened yogurt or sour cream.
conclusions
A salt-free diet is effective and useful if you have chronic diseases for which salt consumption is contraindicated. You can also use a more gentle option for losing weight and getting rid of puffiness. In this case, a small amount of salt per day and the use of a variety of spices and spices are allowed. It is extremely important to drink enough water during this period. A salt-free diet helps not only to get rid of extra pounds of weight, but also to normalize the water-salt balance of the body. It is also useful for pregnant women, especially in the last trimester, when swelling appears. But it should be remembered that a lack of salt in the body is just as destructive as its excess. Therefore, when on a salt-free diet, the main thing is not to overdo it, because everything is good in moderation.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons: