Most nutritionists believe that to lose weight, you need to increase your protein intake and limit carbohydrates. But there is another approach, according to which you can lose weight on complex carbohydrates. This diet is suitable for those people who cannot consume large amounts of protein due to health problems (for example, kidney disease).
The carbohydrate diet for weight loss is considered one of the simplest. Its essence comes down to the fact that you need to consume complex carbohydrates, and in addition to them - a small amount of fats and proteins. A proper nutrition system is built on these principles.
- Chicken and pea soup
General rules
A carbohydrate diet for weight loss is based on a sharp limitation or complete exclusion of simple carbohydrates from the diet and an increase in foods and dishes from them high in complex carbohydrates with a reduced intake of fat. This dietary program, which seems like a paradox to many, is based on accelerating metabolic , which is due to the relatively rapid absorption of carbohydrates in the body.
The importance of carbohydrates in human nutrition is extremely high. First of all, it is the main source of recycled energy that ensures life. The energy function is performed mainly by glucose, fructose, glycogen, sucrose and starch. An important role is played by “indigestible” carbohydrates (hemicellulose, cellulose, pectin), which stimulate the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract, adsorb cholesterol and toxic compounds, and create conditions for the normal functioning of the natural intestinal microflora.
Carbohydrates are represented by a large class of compounds and include both simple - monosaccharides and complex - polysaccharides . The effect of different types of carbohydrates on metabolism varies significantly.
Simple (quickly digestible) carbohydrates - in the body they are broken down into monosaccharides (glucose and fructose), which are quickly absorbed, and if there is an excess of them in the body and there is no immediate need for them, a complex mechanism of their conversion into subcutaneous and intra-abdominal fat is triggered. This type of carbohydrate quickly increases blood sugar levels, which leads to a feeling of fullness, which goes away just as quickly. These include honey, sugar, confectionery, sweet fruits. Such sources of carbohydrates in the diet must be limited.
Complex (slowly digestible) carbohydrates - starch, pectin, glycogen, inulin, fiber. The structure of the molecule is complex and includes dozens of monosaccharides . The process of their breakdown occurs in the small intestine quite slowly (the duration is 2-5 times longer), and the process of their absorption is slowed down by fiber. They slowly increase blood sugar levels and the body is evenly saturated with energy. It is these carbohydrates in food that should be the main source of energy and account for 95% of the daily value. These include various products containing a lot of fiber, pectin, starch (cereals and cereals made from them, white rice, whole grain bread, bananas, pineapple, grapes, dried fruits and others).
A general idea of the carbohydrate content of certain foods can be obtained from the table below.
Table of carbohydrate content in food:
| Product name | Carbohydrate content (per 100 g of product) |
| White bread | 50 |
| Boiled pasta | 25 |
| Cornflakes | 75 |
| Boiled rice | 30 |
| Armenian lavash | 56 |
| Bagels | 58 |
| Bread Borodinsky | 40 |
| Wheat porridge | 26 |
| Buckwheat | 29 |
| White sugar | 105 |
| Marmalade | 70 |
| Honey | 77 |
| Milk chocolate | 60 |
| Walnuts | 12 |
| Peanut | 15 |
| Cashew | 25 |
| Hazelnut | 15 |
| Sunflower seeds | 18 |
| Sesame seeds | 20 |
| Dates | 68 |
| Watermelon | 9 |
| Eggplant | 5 |
| Green peas | 12 |
| Parsley | 8 |
| Tomatoes | 4 |
| Carrot | 5 |
| Sweet pepper | 5 |
| Boiled potatoes | 16 |
| Boiled beets | 7 |
| Fruit kefir | 5 |
| Whole milk | 12 |
| Sour cream | 3 |
| Milk ice cream | 25 |
| Shortbread cookies | 68 |
| Banana | 20 |
| Grape | 15 |
| Raspberries, strawberries | 5 |
| Tangerines, oranges | 7 |
| Apricot compote | 21 |
| Pear compote | 18 |
| Dried rose hips | 22 |
| Red/black currant | 7 |
| Cherry | 12 |
| Apples | 10 |
This list of products will allow you to create your individual dietary menu for the week every day.
The basic principles of dietary nutrition are:
- Follow your individual “norm” of carbohydrate consumption for weight loss, calculated according to the formula: 3.0 g x 1 kg of weight, proteins are not limited, fats are reduced to 75-80 g/day, mainly due to solid animal fats. The total calorie content is about 1600 - 1800 Kcal/day.
- Eliminate or sharply limit foods containing simple carbohydrates from your diet by increasing complex carbohydrates in your menu. The ratio of complex and simple carbohydrates should be approximately 95 to 5 percent.
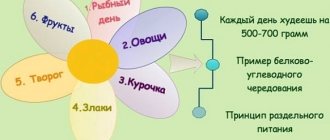
- Practice split meals.
- The main intake of foods containing complex carbohydrates should be 1 meal in the first half of the day. At other meals it is necessary to combine proteins with carbohydrates. For dinner, it is recommended to avoid eating carbohydrates, giving preference to protein foods.
- Limit salt intake in your diet.
- Avoid snacking between meals, and if this is difficult for you, exclude flour/confectionery products from the snack menu.
- Prepare dishes using dietary methods - steam, boil, bake, stew.
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of free fluid.
Do you need carbohydrates to survive?
Carbohydrates are nutrients that are in high demand. According to scientific research, 45%-65% of calories should come from carbohydrates, as this is the main source of fuel for the body. The nutrient is easily converted into energy that tissues use.
Carbohydrates are stored in the muscles and liver, and then used to obtain the energy necessary for the full functioning of the central nervous system, kidneys, brain, muscles (including the heart). A lack of glycogen (a fuel source) forces the body to use muscle protein as an alternative source of energy.
Conversion of glucose to glycogen
The pancreas is the first to increase blood glucose levels after a meal by secreting insulin. The hormone signals the body's tissues to absorb excess glucose, some of which is converted into glycogen by the muscles and liver. The glycogen content in the muscles makes up two-thirds of the reserves and is used only during physical activity. The remaining third remains available in the liver to nourish the brain and other organs in case glucose supplies run low.
Glycogen is needed to release glucose. When blood glucose levels drop, cells require energy. The supply of the pancreatic hormone glucagon is activated. Thousands of liver cell enzymes respond by releasing glucose into the blood for use by other cells in the body. Adrenaline works the same way, as a form of the body's defense mechanism when danger arises.
Converting excess glucose into fat
Systematic increased glucose consumption leads to increased fat synthesis. When the supply of glucose continues after the muscles and liver are filled with glycogen, the glucose is not excreted and left idle. There is a transformation into a form of fuel storage with unlimited potential, i.e. Triglycerides accumulate in adipose tissue.
During glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate, which is converted to acetyl-CoA, the starting material for fatty acid synthesis. The process takes place in the liver after converting fatty acids into triglycerides (also in the liver), then transporting them to adipose tissue for storage. Triglycerides (fats) form the main energy reserve in the body.
Authorized Products
The basis of carbohydrate foods is buckwheat, oatmeal, wheat and rice porridge cooked in water. Be sure to include in your diet all legumes (beans, lentils, peas, chickpeas), whole grain baked goods (whole wheat pasta, whole grain bread). A good source of complex carbohydrates is boiled or baked potatoes.
Do not limit proteins in your diet - eat chicken, rabbit, veal, and low-fat cheese. It is imperative to eat fresh vegetables and fruits rich in fiber: cabbage, zucchini, carrots, eggplants, cucumbers, tomatoes, melons. As for fats, it is recommended to consume refined vegetable oils and, in smaller quantities, butter.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| boiled peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
| buckwheat | 4,5 | 2,3 | 25,0 | 132 |
| oatmeal | 3,2 | 4,1 | 14,2 | 102 |
| millet porridge | 4,7 | 1,1 | 26,1 | 135 |
| white boiled rice | 2,2 | 0,5 | 24,9 | 116 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
| veal | 19,7 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 90 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Recipes

Special recipes for salads, first and second courses will help you fill the menu of a protein-carbohydrate diet.
Salads
Recipe No. 1. Protein egg salad
Ingredients:
- bulb;
- breast 200 gr;
- squid 200 gr;
- eggs 4 pcs;
- powder mustard 10 gr.
Preparation:
- Boil the eggs soft-boiled.
- Boil the breast. Cut into strips.
- Boil the squid. Cut into strips.
- Mix onion, eggs, mustard in a blender.
- Dress the salad.
- Mix everything.
Recipe No. 2. Carbohydrate honey-cabbage salad
Ingredients:
- fresh cabbage 300 gr;
- sugar 10 g;
- lemon juice 15 ml;
- rhubarb juice 40 ml;
- honey to taste.
Preparation:
- Shred the cabbage.
- Grind it until the juice comes out.
- Add all other components.
Recipe No. 3. Protein-carbohydrate salad
Ingredients:
- squid 150 gr;
- cucumber;
- chicken breast 100 g;
- lettuce 2 leaves;
- dill sprig.
Preparation:
- Boil squid and chicken breast until cooked.
- Chop them with chopsticks.
- Cut the cucumber in the same way and add to them. Mix.
- Place lettuce leaves on a plate.
- Decorate the salad beautifully.
- Top with chopped dill.
First courses (soups)

Recipe No. 1. Protein soup with spinach
Ingredients:
- turkey 400 gr;
- spinach 100 gr;
- garlic 2 cloves;
- milk 100 ml;
- seasonings to taste.
Preparation:
- Boil the meat, remove from the water, cool, remove the bones, chop, return to the broth.
- Chop the spinach and cook with the meat for 10 minutes.
- Puree the mixture using a blender, adding milk in small portions.
- Sprinkle with spices.
- Serve hot.
Recipe No. 2. Carbohydrate potato and sour cream soup
Ingredients:
- green onions, dill;
- potatoes 400 gr;
- carrot;
- petiole celery 1 stalk;
- celery root 100 gr;
- vegetable broth 3 l;
- sour cream 250 gr;
- lemon juice 50 ml;
- seasonings
Preparation:
- Peel the vegetables, chop and boil.
- Add sour cream.
- Cook until creamy consistency.
- Season with juice, chopped herbs, and seasonings.
- Serve hot.
Recipe No. 3. For a mixed day. Lentil and chicken soup.
Ingredients:
- lentils 250 gr;
- bulb;
- water 5 l;
- chicken fillet 400 gr;
- celery root 100 gr;
- carrot.
Preparation:
- Boil the fillet.
- Add lentils to the broth.
- After 10 minutes, add chopped vegetables.
- After 20 minutes - chicken, cut into strips.
Second courses

Recipe No. 1. Protein chicken nuggets.
Ingredients:
- oat flour 25 gr;
- chicken fillet 500 gr;
- eggs 2 pcs;
- seasoning to taste.
Preparation:
- Make nuggets from the fillet. Hit it with a hammer.
- Beat eggs, mix with flour and seasonings.
- Roll the nuggets in breading.
- Bake in the oven until done.
Recipe No. 2. Carbohydrate nutrition. Vareniki.
Ingredients:
- potatoes 500 gr;
- cabbage 200 gr;
- bulb;
- flour 250 gr.
Preparation:
- Knead the dough.
- Finely chop the cabbage.
- Put it out.
- Fry chopped onion.
- Boil mashed potatoes.
- Mix cabbage, mashed potatoes, onions.
- Make, fill, boil dumplings.
Recipe No. 3. Mixed nutrition. Curry.
Ingredients:
- brown rice 250 gr;
- chickpeas 100 gr;
- beef 400 gr;
- curry to taste;
- carrot.
Preparation:
- Soak the chickpeas for 12 hours.
- Boil rice and chickpeas separately from each other.
- Cut the beef into strips.
- Grate the carrots.
- Stew carrots and beef until half cooked.
- Add everything else to them. To fill with water. Stew.
With such recipes, a protein-carbohydrate diet will not be like a hunger strike and will help you get through the weight loss period easily and tasty.
Fully or partially limited products
Completely eliminate the consumption of sugar, halva, chocolate, sweets, honey, cookies, jam, dried fruits (raisins, figs, dates, pineapple, etc.), and condensed milk from your diet. You should not eat white bread, gingerbread, rolls, pasta, waffles, crackers, cakes, or semolina from cereals. Fatty meats, lard, bacon, smoked meats, whole milk, cream, fried potatoes, sweet carbonated and alcoholic drinks are excluded.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| fried potato | 2,8 | 9,5 | 23,4 | 192 |
Fruits | ||||
| figs | 0,7 | 0,2 | 13,7 | 49 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dates | 2,5 | 0,5 | 69,2 | 274 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| pancakes | 6,1 | 12,3 | 26,0 | 233 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,2 | 6,2 | 51,0 | 317 |
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| cake | 3,8 | 22,6 | 47,0 | 397 |
| jam | 0,4 | 0,2 | 58,6 | 233 |
| halva | 11,6 | 29,7 | 54,0 | 523 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 28,2 | 27,5 | 0,0 | 360 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fried fish | 19,5 | 11,7 | 6,2 | 206 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| white dessert wine 16% | 0,5 | 0,0 | 16,0 | 153 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Menu (Power Mode)
Here is an example of several menu options.
Option 1
| Breakfast |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Option 2
| Breakfast |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Option 3
| Breakfast |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
How to get out of a diet correctly
It is important to get out of the carbohydrate diet wisely. In the first 15-20 days, you need to eat low-calorie foods. It is important to exclude sweets and fatty foods.
New products are introduced gradually and in minimal quantities. This is the only way to consolidate the results of the diet. On the first day of release, the menu may look like this:

- breakfast – porridge with lentils, applesauce;
- snack – citrus juice;
- lunch - vegetable stew, salad with tomatoes, chicken and beans;
- dinner - boiled rice and a slice of fish;
- before bed – a glass of kefir.
This diet will allow you to maintain weight for a long time.
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
Adviсe
- For more effective control, keep a special diary. In it you will create your menu with a breakdown of calories and biological value of the diet (amount of proteins/fats/carbohydrates), describe your well-being and psychological state. This is good discipline.
- Don't go on a diet suddenly. It is recommended to prepare the body in advance, which consists of a fasting day (kefir, apple). To improve the cleansing of the body, you should do a full cleansing enema. The same applies to leaving a diet. Expand your diet and increase the volume of portions gradually, over 7 days.
Comments from nutritionists
In addition to a carbohydrate diet for weight loss, there is a high-carbohydrate diet for weight gain, and many people confuse the principles of nutrition on them. Weight gain is achieved through a combination of high protein and carbohydrate content in the diet (protein-carbohydrate diet), with very limited fat intake. It has its own specifics for carbohydrate intake, both during the day and immediately after training during the open “carbohydrate-protein window”.
For those who find it difficult to tolerate a carbohydrate diet, it is recommended to make snacks and use raw, boiled and stewed vegetables and fruits for this.
During the diet, be sure to take vitamin and mineral complexes.
How many carbohydrates do we need?
Formula for the energy value of carbohydrates:
1 g carbohydrates = 4 calories
If a carbohydrate diet or other type of specific nutrition is not implied, then normally 40 to 60% of calories are required to come from carbohydrates. Glucose is oxidized better than fatty acids with the same carbon chain length and is used under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Conclusion: at least 50% of energy must be obtained from carbohydrates. An increase in muscle activity implies an adequate supply of fuel for ATP synthesis by the muscles. When physical activity is expected, the adrenal glands release adrenaline.
The hormone reduces the level of glycogen in muscles (the breakdown of enzymes is activated, synthesis is deactivated). After the action stops, the production of adrenaline stops.
The intake of glucose after a meal replenishes glycogen stores in the muscles. Glucose enters muscle cells in two ways:
- use of glycogen reserves in muscles;
- from the liver through the bloodstream.
Dietary fiber, indigestible carbohydrates, provide minimal energy after intestinal fermentation, unlike digestible carbohydrates. Metabolism of fermentable fibers, absorbed in the colon, produces short chains of fatty acids that are transported to the muscles and liver. The energy supply in this case is about 2 kcal/g energy. The indigestible components of fiber are beneficial to the gastrointestinal tract, facilitating the transport of nutrients and waste.
The absolute minimum carbohydrate required per day for healthy brain function is 150 g.
The amount of carbohydrates recommended for men, recreational athletes, and non-pregnant women is 50% of energy intake. Athletes who train for endurance and strength - 6-10g of carbohydrates per kilogram of weight (up to 60% of the nutrient).
When using a carbohydrate diet for weight loss, it is necessary to eliminate processed (refined) carbohydrates from the diet, since processing removes nutrients and turns the product into empty calories, which is not beneficial for cellular functions. The amount of carbohydrates is reduced by up to 30%.
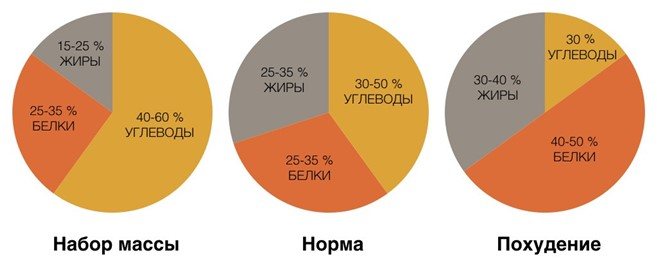
The proportion changes up or down depending on the success of weight loss and well-being. A carbohydrate alternation diet is also used (changing the proportion of nutrients according to the scheme).
Carbohydrate diet: reviews and results
Reviews of the carbohydrate diet for weight loss among those who were on it vary significantly:
- “... The carbohydrate diet turned out to be not effective enough for me - only 3 kg in two weeks. But she helped me balance my diet correctly, since my problem was eating a lot of bread and flour products. I managed to rethink my diet, make it better and healthier”;
- “... I don’t know if you can really lose weight by 5-6 kg in two weeks on a carbohydrate diet or if this is just an advertisement. At least I couldn't achieve this. Although I complied with all the basic requirements”;
- “... I really liked the diet. For me it turned out to be easy. Probably because I have always preferred plant-based foods and even tried to switch to a vegetarian diet. Result: I lost 4.5 kg. I will practice this diet more often, and I recommend it to everyone.”
Advantages and disadvantages of a popular method of weight loss
With a carbohydrate diet you can lose from five to ten kilograms. At the same time, the fair sex, as a rule, feels great. Her performance does not decrease.
The diet can be called balanced, as a result of which the traditional carbohydrate diet does not have a negative impact on the health of the fair sex.
This weight loss technique also has a small drawback. It involves eating foods that are low in calories. You should not often resort to this method of losing weight. Women with chronic diseases are advised to consult a doctor before going on a diet.