What is this nutrient? Its distinctive features, what it contains, when it should be consumed. No matter what type of diet you eat, adding legumes, nuts and seeds will improve your diet. Beans, peas, nuts, seeds, soybeans and lentils are extremely healthy natural foods. They're high in energy, a good source of plant-based protein, high in phytonutrients and fiber, and low in cholesterol and sodium. A diet that focuses on plant sources of protein may be beneficial in preventing diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Advantages
Protein-rich plant foods include primarily legumes, grains, nuts, soy and seeds . The element is also present in vegetables and fruits, but in significantly smaller quantities.
Eating plant protein has numerous health benefits. Numerous evidence in favor of its importance gives reason for many nutritionists to recommend:
- Increase the presence of such compounds in the diet.
- Increase your consumption of seafood and low-fat dairy products.
- When consuming animal and poultry meat, try to choose the leanest options.
Plant protein in a vegan diet: where to get it and what to replace it with
Protein in a vegan diet
Not only those interested in the topic of ethical nutrition, but also people with other views on human nature are often interested in the question of where vegans get their protein.
This is precisely the question that is one of the arguments of opponents of eating without animal products, when they assume that it is impossible to obtain a sufficient dosage of protein in a daily diet on veganism. The inevitable deficiency of protein in a vegan diet, as well as its importance in human nutrition in general, is a big misconception. For those who are interested in what vegans replace protein with, they do not replace it, but get it fully in their daily diet, since plant foods are a good source of protein. Taking into account the recommended daily protein intake by the World Health Organization, a person needs to receive 0.8 g of protein per kilogram of weight every day. Given the difference between plant and animal protein—certain types of plant protein are processed in the gastrointestinal tract somewhat differently than animal protein—for people following a plant-based diet, it is advisable to increase the daily dose of protein to 1g per kilogram of weight.
An important factor in the correct calculation of the dosage of microelements is the percentage of protein and the total number of calories consumed by a person. A significantly lower level of calorie intake for a plant-based dieter is common in the absence of control over calorie intake to a certain standard. A sixty-kilogram vegan will consume 60 grams of plant protein per day, which is a larger percentage of his caloric intake than a meat eater who will consume the same amount of protein. Average statistical estimates suggest that the level of protein consumed by a meat eater is 10-13% of the total daily calorie intake, while vegetarians and vegans most often consume 14-18% protein. This means that the ratio of CBJU, which is one of the most important factors in balanced and proper nutrition, is normal among those who adhere to abstaining from animal products (ASF).
Most often, in the absence of strict control of BPJU, a meat-eating person tends to go over the recommended daily protein intake, especially if he is fond of visiting fast food restaurants and ready-made foods. The danger of too much protein should not be underestimated: it fuels the development of many diseases. Animal protein, not to mention too much of it, tends to provoke the development of cancer cells, obesity, problems with the cardiovascular system and other serious abnormalities.
Therefore, obtaining vegan protein is not at all difficult. For greater specificity, we will combine sources containing essential amino acids and proteins of plant origin into the list of products. So where is the most plant-based protein?
Seitan
Seitan is one of the most common protein sources for vegans.
The product is made from gluten, the main type of protein in wheat. Many note its similarity to meat in appearance and consistency of the product. 100g of pure seitan without additives contains 25g of protein, making it one of the richest sources of protein.
Seitan is not very easy to find on Russian store shelves, but it is very common abroad. You can only buy it in specialized plant food stores. But seitan is quite easy to prepare at home, because there are many different variations of its preparation online. Seitan is consumed fried in a pan or grilled, as well as boiled, so it can be used in countless dishes. Contraindicated for people with celiac disease.
Tofu, tempe and edamame
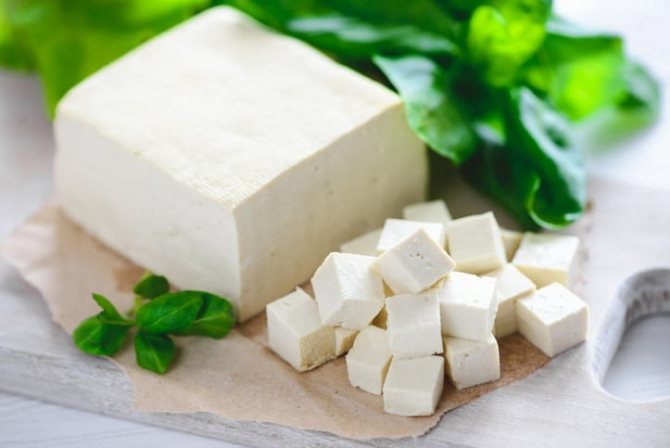

These products are soy derivatives. Soybeans are a complete source of protein that saturates the body with the amino acids it needs.
Edamame is an unripe soybean with a sweet and slightly grassy flavor. They can be cooked in a double boiler or boiled to serve as an independent side dish or added to hot and main courses.
Tofu, or “vegan cheese” as it is often called, is made from pressed minced beans using a technology similar to making cheese. Recently, it can be found not only in specialized stores, but also in almost every hypermarket throughout Russia. It costs no more than cheese, and is served in many variations with different additives, such as herbs, spices or even fruits.
Tempe soy product is made by boiling and pressing ripe soybeans. It has a slightly nutty flavor and contains an impressive amount of probiotics and vitamins.
These soy products contain 10-19 grams of protein, depending on preparation, for every 100 grams of product.
Lentils
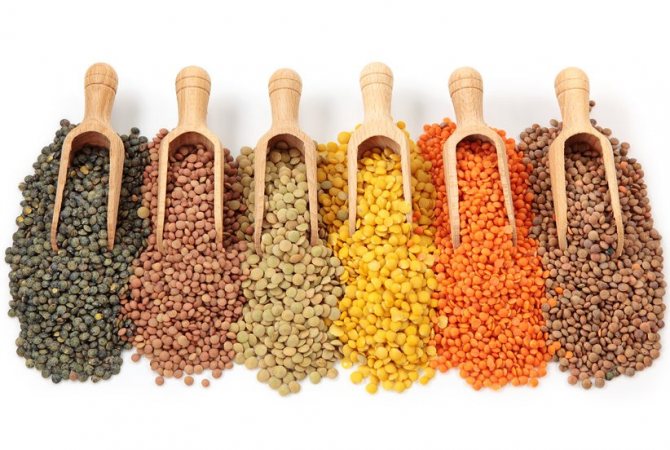

All varieties of lentils (red, green, brown) contain 25g of plant-based protein. It is one of the record holders in protein value. Of course, you need to take into account its quantity in dry form.
Chickpeas and most legumes
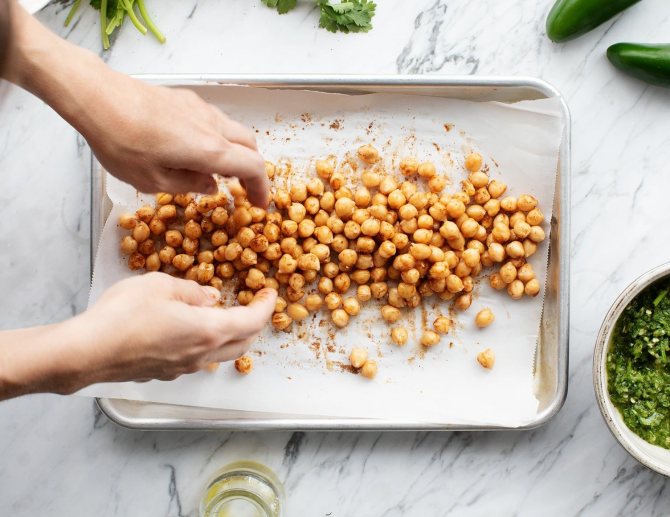

As a rule, all legumes are famous for their high protein content. For example, popular chickpea beans (most often eaten with minced meat - falafel) contain 19 grams of protein per 100 grams of product.
The beneficial properties of legumes can be listed for a long time: they are valuable sources of long-digesting complex carbohydrates, fiber, iron, folic acid, and a diet whose main product is legumes helps control cholesterol and blood sugar, regulate blood pressure in hypertension and help normalize weight in obesity .
Spirulina
Just two scoops (14g) of nutritious spirulina algae will provide you with 8 grams of pure protein, plus 22% of your daily iron and thiamine needs. Spirulina has a lot of unique medicinal properties.
Spirulina in its various forms can be purchased in specialized stores and some hypermarkets at a price that will seem too low to you compared to the storehouse of useful microelements and properties that you will receive. Most often, spirulina is produced in dried form. You can order it in almost every online health food store.
Amaranth and quinoa
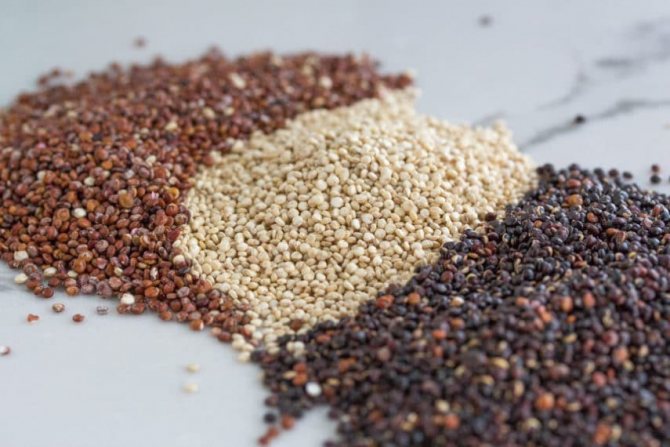

Nutritious cereals, which are completely gluten-free, contain 14 g of protein per hundred grams of product. They are prepared as individual dishes or ground into flour for use in cooking.
Crispbreads and bread products made from sprouted grains
Any bread products made from natural sprouted grains or legumes contain approximately 8 g of protein per serving of product, equal to two slices of regular bread (which has several times less protein).
In addition, sprouted grains and legumes increase their nutritional properties and the number of amino acids, and reduce the amount of anti-nutrients. The amino acid lysine, which opens during germination, helps improve the quality of the resulting protein. And the combination of grains and legumes in the preparation of bread will improve the quality of bread to the limit.
Plant milk
Soy, almond, coconut and other plant milks contain approximately 3-4 grams of protein. Accordingly, drinking an average glass of this milk (250 milliliters) will provide you with approximately 9 grams of protein.
All pasteurized plant milks are pre-fortified with additional calcium and essential vitamin B12.
Nuts and products made from them (peanut butter, peanut butter, etc.)
Nuts and vegan protein-rich products made from them are another great source of protein.
100g of each type of nut contains about 20g of protein. They also contain a treasure trove of fiber, healthy fats and a variety of vitamins.
When purchasing nuts, you should keep in mind that roasting and heat treatment can reduce their nutritional value and the amount of useful substances. To get the most benefit from your nuts, consume them pre-soaked (two to twelve hours, depending on the nut).
When choosing nut butters and pastes, give preference to products that are as simple in composition as possible and do not contain excess oil, sugar and salt. This way the protein and other micronutrients contained in them are absorbed best.
Table of protein content in nuts, dried fruits and seeds
| Dried fruits, nuts, seeds | Name | Proteins per 100 gr. product |
| Dried apricots | 4.8 gr. | |
| Prunes | 2.3 gr. | |
| Dates | 2.5 gr. | |
| Raisin | 1.8 g | |
| Dried figs | 3.1 gr. | |
| Dried apple | 3.2 gr. | |
| Dried apricots | 5.1 gr. | |
| Peanut | 26.3 gr. | |
| Walnut | 16.2 gr. | |
| Pine nut | 11.6 gr. | |
| Cashew | 17.5 gr. | |
| Almond | 21.2 gr. | |
| Pistachios | 20.1 gr. | |
| Hazelnut | 16.1 gr. | |
| Sunflower seeds | 23.1 gr. | |
| Pumpkin seeds | 24.5 gr. | |
| Hemp seeds | 35.3 gr. | |
| Chia seeds | 16.6 gr. | |
| Sesame seeds | 18.4 gr. | |
| Flax seeds | 18.1 g |
Protein-rich fresh vegetables and fruits
Vegetables and fruits, which often make up the majority of the diet of plant-based dieters, are usually underestimated in their benefits. Yes, the amount of protein in vegetables and fruits is usually small, but some of them contain enough.
Where to get protein for vegans: fruit and vegetable products.
Table of protein content in vegetables and mushrooms
| Vegetables, mushrooms | Titles | Proteins in 100 gr. product |
| Potato | 2 gr. | |
| Beet | 2.5 gr. | |
| Cauliflower | 2.5 gr. | |
| Garlic | 6.5 gr. | |
| White cabbage | 1.8 gr. | |
| Eggplant | 1.2 gr. | |
| Zucchini | 1.2 gr. | |
| Carrot | 1.4 gr. | |
| Pepper | 1.3 gr. | |
| Radish | 1.9 g | |
| Asparagus | 2.2 gr. | |
| Artichoke | 1.2 gr. | |
| Corn | 3.3 gr. | |
| Green pea | 5.4 gr. | |
| Chilli | 2 gr. | |
| Pumpkin | 1 gr. | |
| White onion | 1.4 gr. | |
| Broccoli | 2.8 gr. | |
| Tomatoes | 1.1 gr. | |
| cucumbers | 0.8 gr. | |
| Porcini mushrooms | 3.7 gr. | |
| Champignon | 4.3 gr. |
Fresh fruits are somewhat inferior to vegetables in terms of protein amino acid content. Together with the microelements in their composition, they bring undeniable benefits.
Table of protein content in fruits
| Fruits | Name | Proteins in 100 gr. product |
| Apricot | 1.4 gr. | |
| A pineapple | 0.5 gr. | |
| Orange | 0.9 gr. | |
| Watermelon | 0.6 gr. | |
| Banana | 3.9 gr. | |
| Grape | 0.6 gr. | |
| Cherry | 1.1 gr. | |
| Pomegranate | 0.9 gr. | |
| Grapefruit | 0.7 gr. | |
| Pear | 0.5 gr. | |
| Melon | 0.8 gr. | |
| Figs | 0.7 gr. | |
| Kiwi | 0.8 gr. | |
| Coconut | 3.3 gr. | |
| Lemon | 0.9 gr. | |
| Mango | 0.5 gr. | |
| Mandarin | 0.6 gr. | |
| Apple | 0.3 gr. | |
| Pomelo | 0.8 gr. | |
| Papaya | 0.6 gr. | |
| Peach | 0.9 gr. | |
| Plum | 0.7 gr. | |
| Cherries | 1.1 gr. |
Although nuts are one of the leading plant foods in terms of protein content, some plants also contain decent amounts.
Here are 18 healthy leafy greens that contain enough protein.
Table of protein content in greens
| Greenery | Name | Proteins in 100 gr. product |
| Basil | 3.2 gr. | |
| Green onions | 1.1 gr. | |
| Ivan-tea angustifolia | 4.7 gr. | |
| Keil | 4.3 gr. | |
| Cilantro | 2.1 gr. | |
| Watercress | 2.6 gr. | |
| Leaf lettuce | 1.5 gr. | |
| Dandelion leaves | 2.7 gr. | |
| Chard | 1.8 gr. | |
| White pigweed | 4.2 gr. | |
| Mint | 3.7 gr. | |
| Oregano | 9.9 gr. | |
| Parsley | 3.7 gr. | |
| Romano | 1.5 gr. | |
| Arugula | 2.6 gr. | |
| Dill | 2.5 gr. | |
| Spinach | 2.9 gr. | |
| Sorrel | 1.5 gr. |
Contrary to myths, protein deficiency in plant-based diets is not common. One of the main rules for any diet, plant-based or with ALP, is to control the ratio of nutrients to maintain optimal balance.
Tags: plant-based protein nutrition plant protein
Posted by Vegan Ray October 25, 2021
Comparison of plant and animal sources
What is plant protein? This is the same chemical compound as the animal, consisting of the same amino acids. Most residents of developed countries consume protein in sufficient quantities, and sometimes even in excess. Some experts recommend increased levels of its consumption, for example, this is practiced in a number of low-carb diets or to reduce the consumption of refined carbohydrates. Studies have shown that replacing these carbohydrates with plant protein has a beneficial effect on body weight and reducing the risk of CVD.
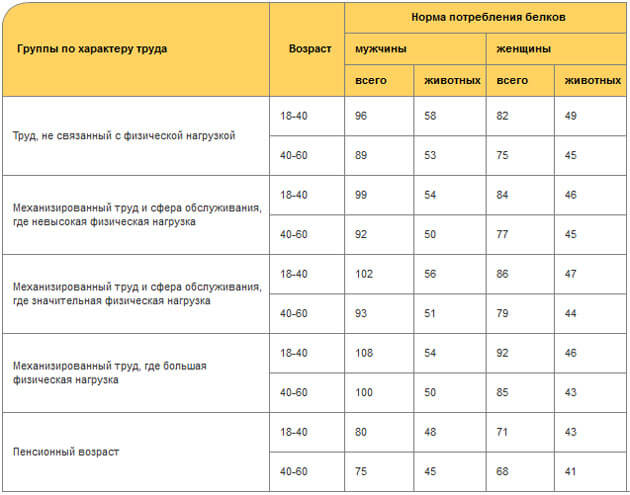
Adults need
60 to 110 grams of protein , which equates to approximately 20-40% of calories. In developed countries, 70% of protein consumed comes from animal sources and only 30% from plant sources.
To form a complete diet, the correct combination of them is important. All complete types of proteins contain 9 essential amino acids. The problem is that plant sources are usually deficient in one or more essential amino acids . Animals provide all 9 in adequate quantities and are considered complete proteins. Accordingly, proteins of plant origin are called incomplete.
People on low-calorie, vegan or vegetarian diets are at increased risk of lacking essential amino acids. To minimize such risks, you can combine different types of plant foods. For example, rice can be eaten with legumes, and vegetables can be eaten with whole grains.
How much protein does a person need?
It is generally accepted that for full health a person needs at least 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of weight. If you weigh 75 kg, then your minimum protein intake should be 60 grams per day.
With active physical activity, this amount quickly increases by 2-3 times. A person involved in sports or heavy physical work must take at least 1.5-2.5 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight to maintain health.
To comply with these standards, it is worth taking some protein product in sufficient quantity with each meal.
Contents in products
- Nuts are rich in plant proteins and also contain healthy fats. They serve as an excellent source of fiber and phytonutrients. For example, walnuts are rich in healthy fatty acids, peanuts are rich in plant protein, and almonds contain high amounts of calcium and fiber. Nuts can improve your nutrient intake and overall diet. Taking them with food helps reduce the risk of CVD.
- Legume products are so beneficial that a number of nutritionists recommend increasing their weekly dose to 3 cups. They're filling, high in protein, and rich in fiber, calcium and potassium, nutrients that are often lacking in the diets of developed countries. For example, most US residents consume only 15 grams of fiber daily, while the daily value is 25-38 grams. Just one cup of cooked legumes contains 12 grams.
- Gluten is a well-known plant protein found in many grains. Many experts associate it with digestion problems, as well as a number of diseases of the digestive system and allergenic reactions. Gluten intolerance is usually diagnosed by a number of signs, which are important to listen for in order to adjust your diet appropriately in consultation with a nutritionist.
- Where else is plant protein found? Pea protein and chickpea flour are excellent sources. Chickpea flour can be a great substitute for other flours in cooking. Pea protein is often used by athletes following a plant-based diet to supply the body with easily digestible and high-quality elements in order to build muscle mass.
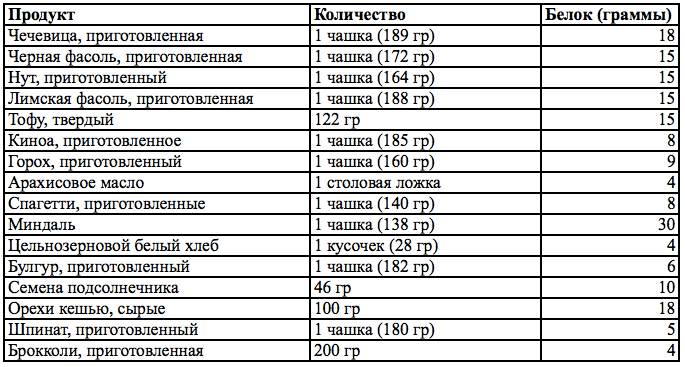
What is vegetable protein
These are proteins that are found exclusively in plant foods. Although many people prefer animal proteins, plant proteins are considered healthier. What advantages do they have?
They do not contain polyunsaturated fatty acids and sterols, which increase cholesterol levels. Easily absorbed by the body without overloading the liver. As an alternative, suitable for vegetarians and those who do not eat meat for other reasons.

Use on diet
When reducing your calorie intake, it is important to base your diet on healthy foods. Including plant protein in your menu can be a beneficial strategy in the fight against excess weight. By replacing foods with saturated fats and fast carbohydrates with this type of protein, you achieve a reduction in calories and also enrich your diet with fiber and a variety of nutrients.
The peculiarity of these proteins is that they require more energy to digest and assimilate compared to carbohydrates and fats. Digestion occurs quite slowly, which helps create a feeling of fullness and satiety.
Legumes are good to include in your diet. They can be included in salads, soups, stews, pastas, side dishes, meatloaves and other dishes. Nuts are great for snacks; they can also be added to a variety of salads, desserts, breakfast cereals, yogurts, and so on.
Plant proteins have many benefits for human metabolism. However, for their effect to be beneficial, it is necessary to correctly dose and select the types of such food.
Why do we need proteins at all?
The human body needs 20 amino acids: they are involved in the process of cell division.
The adult human body produces 12 of them itself, the remaining eight must come from food. These important elements are found in proteins, which are most abundant in animal products. Our muscles are built from proteins. Proteins ensure the development of immunity, transmission of nerve impulses, growth, development and restoration of cells All about PROTEIN. In addition, they satisfy hunger well. In general, there is no way to do without them.
On average, every woman needs a day. How much protein do you need every day? from 46 g of proteins, and for a man - from 56 g, depending on weight.
Plant-based foods high in protein

The following foods contain the most proteins:
- Legumes , especially soybean, its hydrolyzed protein and flour from it.
- Nuts, nut butters. Peanuts contain large quantities of protein, followed by pistachios, almonds, hazelnuts and walnuts.
- Seeds. Sunflower and sesame grains, pumpkin, quinoa, amaranth, and chia are useful. There are also many important substances in halva, kozinaki and other products with grains.
- Cereals. Of the cereals, buckwheat and millet contain the most valuable compounds, while rice contains the least. Wheat is in the middle, its protein is called gluten. Whole grain flour contains more amino acids than premium products. A good source of proteins is bran and baked goods with their addition.
- Vegetables. In this group, only spinach, potatoes and Brussels sprouts, and porcini mushrooms can be noted.
- Plant milk and products made from it. Soy milk and tofu nut drinks are a tasty source of vital compounds that will help add variety to your menu.










