Chromium is a biogenic element that is constantly present in the structure of tissues of plants, animals and humans. Chromium is a vital microelement, necessary for every cell of any living organism, organ and tissue. It is mainly concentrated in parts of our body such as muscles, adrenal glands and brain.
Chromium enters the human body through proper food, water, and even through the air. But this microelement is also consumed quickly, especially during severe stressful situations, physical activity, various infections, injuries, diets, pregnancy and aging.
It is important to promptly and correctly compensate for the spent chromium in the body, since its insufficient level or excess affects a person’s health.
Biological role of chromium
Chrome features:
• Improves the uptake of glucose by cells and tissues, increasing the efficiency of insulin. This helps prevent the development of diabetes mellitus, and also improves the condition of people with already developed disease. • Reduces hunger by regulating appetite. On this basis, organic chromium compounds are often recommended as weight loss agents and added to dietary supplements for weight loss. • Is a component of enzymes that regulate tissue respiration. • Takes part in the synthesis of amino acids and protein in the body. • Plays an important role in fat metabolism. • Stabilizes blood pressure levels. • Improves the functioning of the nervous system. Helps improve mood, eliminate depressive and anxiety disorders. • Increases performance. • Participates in the formation of DNA and RNA molecules. • Reduces cholesterol levels in the blood, which protects blood vessels and the heart from atherosclerosis (formation of fatty plaques in the walls of the arteries). • Reduces the harmful effects of negative external factors on the body.
Body tissues - bone tissue, muscles contain only 6-12 mg of chromium! But these magic milligrams can do a lot:
- regulate the formation of fats, including converting excess carbohydrates into fats, which reduces cholesterol levels;
- increase muscle and bone mass, which is important for speeding up metabolism and reduce the amount of fat in the body;
- provide glucose tolerance, which maintains stable glucose levels in the body. Chromium ensures insulin activity and together with it regulates glucose levels; protect nucleic acids from destruction;
- support the functioning of cardiac tissue and blood vessels;
- participate in the elimination of toxins, heavy metal salts, and radionuclides.
I see symptoms of chromium deficiency in tests all the time, and they affect different areas of our body. Complaints of fatigue and anxiety, insomnia, headaches, inability to lose a couple of kilos or, conversely, gain weight
.
Isn’t it true that one of these occurs in every second person? A little less often I encounter complaints of numbness in the hands combined with tremors in the muscles.
And this is also a disadvantage of chromium. Excessive consumption of carbohydrates - flour and sweets, as well as physical activity, pregnancy lead to increased excretion of chromium in the urine and its deficiency. Deficiency also occurs due to insufficient absorption, since chromium is usually found in inorganic form in foods. Therefore, no more than 25% is absorbed from the intestines.
!
Chromium is found in foods such as broccoli, green beans, berries, fruits, fish, shrimp, crabs, chicken eggs, brewer's yeast, and black pepper.
Without chromium, insulin is not able to regulate the amount of triglycerides and cholesterol, which threatens the development of atherosclerosis. Chromium enhances the action of insulin and prevents insulin resistance, which reduces the risk of developing metabolic syndrome
. By adjusting this point, you can solve many problems from lowering cholesterol levels to lowering blood pressure.
Chromium supplementation
has been shown in studies B compared to placebo.
Chromium reduces insulin resistance, which regulates cellular and blood sugar levels. Studies have shown that patients with type 2 diabetes have 20-40% less chromium in their blood than people without this diagnosis! At the same time, diabetes itself leads to a decrease in the amount of chromium in the body, since chromium is intensively excreted in the urine.
A review of studies using chromium picolinate shows that chromium reduces glycated hemoglobin by 0.95%
, which may be enough to
keep a person from developing diabetes
if they already have the condition of prediabetes!
Chromium helps to better break down molecules of protein, carbohydrates, fats and reduces appetite, food cravings and the amount of food consumed, which leads to weight loss
.
Study participants who took chromium picolinate daily for 24 weeks experienced a 1 kg weight loss compared to participants who took placebo. Yes, this is not much, but if combined with physical activity, it is a good and safe strategy for weight loss.
Chromium affects the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine in the brain, which helps block feedback and regulate appetite. Chromium helps fight depression
, as this condition is often accompanied by strong cravings for carbohydrates and increased appetite. Research shows that 600 mg of chromium picolinate per day reduces carbohydrate cravings and symptoms of depression by affecting insulin levels and regulating appetite.
Chromium relieves headaches
,
improves the condition of the skin with acne
, as it improves sensitivity to insulin.
Increases levels of the hormone DHEA, which helps strengthen bones
.
During pregnancy, the level of chromium decreases physiologically, which causes the development of diabetes mellitus in pregnant women and high fetal weight. Studies have shown a decrease in the levels of chromium, zinc and magnesium in women who gave birth to overweight children. I have not found a single study that chromium is harmful, but this does not mean that you should be overly involved in replenishment. In the 2nd trimester, you can use brewer's yeast to replenish chromium deficiency.
How to replenish chromium if it is difficult to obtain from food?
Research shows that the absorption of chromium with picolinic acid is higher than other compounds. In supplements, this compound is called chromium picolinate. It is more stable than other compounds and can resist stomach acidity in order to be absorbed into the small intestine. Chromium accumulates in the tissues of the body, so it is advisable to take it not constantly, but for 3-6 months and take a break. Daily dose from 200 to 1000 mcg. Toxic dose for humans: 200 mg. Lethal dose for humans: more than 3.0 g.
An indicator of a sufficient amount of chromium in the body is daily excretion in urine of 5-10 mcg/day; if more, this means increased excretion and the creation of a deficiency in the body, which needs to be corrected in time. Chromium picolinate dosages
:
- 1000 mcg for 3-6 months if you are diagnosed with metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes.
- To reduce appetite, 400 mcg per day for 3-6 months, or according to the presence of a symptom.
- For weight loss 400 mcg per day, combined with physical activity
- For depression, 200-600 mcg until symptoms subside.
After researching articles and literature on micronutrients and completing PreventAge training, I can confidently say about the importance of each mineral. Replenishing minerals is a fine-tuning of our body, since minerals are used and found in the body in small dosages, but these dosages can work wonders and remove not just the symptoms of diseases, but the causes
. It has long been known that deficiency and disease can be equated. Let there be less of these equalities and more health in your life.
Source: https://organicwoman.ru/41183-2/ © organicwoman.ru
Signs of chromium deficiency
With a lack of chromium in the body, disorders of a variety of organs may occur. In children, the first thing that becomes noticeable is a slowdown in growth.
People of any age experience memory impairment. Depressive disorders, increased blood sugar and cholesterol, increased body weight, headache, sleep disturbances, anxiety, weakness, sensitivity disorders.
In people with chronic chromium deficiency, heart disease progresses faster and there is a risk of infertility.
Chromium and its importance for the human body
The benefits of chromium for the body include performing many functions, including:
- support for the structural integrity of nucleic acids, because the mineral is included in RNA and DNA;
- regulation of cholesterol concentration in the circulatory system (the substance improves fat metabolism, stimulates the breakdown of lipids and removes excess cholesterol from the blood);
- improving the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- normalization of blood glucose concentration;
- improvement of muscle tone;
- neutralization of toxic substances and salts;
- improving the immune system;
- activation of metabolic processes in the body;
- restoration of tissues and cells;
- improvement of intestinal microflora;
- normalization of blood pressure, blood purification;
- preventing blood clots;
- strengthening bones, hair, nail plates;
- improvement of the hormonal system;
- prevention of premature aging;
- prevention of diabetes mellitus;
- increasing stress resistance, etc.

When taking drugs containing chromium, you must strictly follow the instructions
Recommended Daily Allowance for Chromium
The effect of chromium on the human body depends on compliance with the permitted dosage of the mineral. It is recommended to consume about 25-160 mcg of chromium per day. An adult needs up to 50 mcg of the substance daily. The standard serving for children is 11-35 mcg daily.
If there are special indications, the dosage may be increased taking into account the state of health and the available limit of the substance for the body. Teenagers are recommended to consume from 0.02 to 0.03 mg of the microelement. During lactation, up to 0.05-0.2 mg of the substance is required daily.
The body needs the mineral during intense sports. Chromium for a person who regularly trains in the gym should be included in the daily diet at the rate of 0.15-0.2 mg.
Harm of chromium
An excess of a microelement can cause harm to the body. The disadvantage of chromium is the toxic effect on the body if the daily dosage is not followed and artificial supplements are used. With an excessive amount of the mineral, inflammatory processes in the body are possible.
Signs of excess chromium
Toxic doses of chromium vary. This depends on the valence of the element in the substance entering the body. Trivalent chromium is less harmful when in excess, hexavalent chromium is more harmful.
With a moderate excess of chromium in the body, there is a tendency to allergic reactions, disorders of the liver and kidneys. In addition, there are also features depending on the valence of the element. Trivalent chromium primarily irritates the stomach, hence the likelihood of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Hexavalent chromium is more dangerous; it penetrates the body and has a negative effect on metabolism. It is also a carcinogen; prolonged contact with such chromium increases the risk of lung cancer.
With a serious overdose of 6-valent chromium, the following symptoms occur: immunity “falls”, the action of tissue enzymes is disrupted, the liver and heart suffer seriously, ulcers can form in the stomach and intestines, areas of compaction appear in the lungs, which impairs breathing.
Of course, such serious health problems cannot arise as a result of the use of chromium in dietary supplements or its consumption in food. This happens when inhaling polluted air, ingesting toxic substances containing chromium, or coming into contact with toxic compounds at work.
Sometimes, in rare cases, an excess of the mineral is due to a diet that lacks iron and zinc. In such cases, chromium is intensively absorbed from food, which can hypothetically create the preconditions for its “overdose.”
Products containing chromium
A person receives the main and largest dose of chromium from food, so it is important to eat, including foods rich in it in your daily diet.
These include:
- black tea, cocoa;
- sea fish - tuna, mackerel, herring, capelin, salmon, etc.;
- various seafood - crab meat, lobster, oysters, lobsters, shrimp;
- Brewer's yeast;
- various cereals, such as pearl barley, wheat bran, rye flour, oats, barley, millet;
- legumes – beans, peas, beans;
- nuts – hazelnuts, walnuts, in particular almonds;
- mushrooms;
- chicken, turkey, duck meat;
- meat by-products – pork and beef liver, heart, kidneys;
- vegetables - tomatoes, cucumbers, cabbage, radishes, carrots, beets, corn, garlic;
- fruits - grapes, apples, apricots, plums, bananas;
- berries – sea buckthorn, bird cherry, cherry, cranberry, blueberry;
- eggs;
- milk;
- cheese.

It is recommended to drink herbal teas - lemon balm, hops, marsh grass, juices - grape, orange.
Additional sources of chromium.
Chromium is a widely used additive. Estimated sales to consumers in 2002 were $85 million, representing 5.6% of the total mineral supplement sales market. Chromium supplements can be in the form of chromium-only products or in combination with other substances, especially those forms marketed for weight loss. Additional doses usually range from 50 to 200 mcg. The safety and effectiveness of chromium supplements requires further study. Never start taking any medications without getting the approval of qualified professionals. Chromium supplements are available in the form of chromium chloride, chromium nicotinate, chromium picolinate, high chromium yeast, and chromium citrate. In particular, chromium chloride has poor bioavailability. However, given the limited data on chromium absorption in humans, it is unclear which forms are best to take.
Who might need extra chrome?
There is evidence of age-related declines in chromium concentrations in hair, sweat and blood, suggesting that older people are more susceptible to chromium depletion than younger people. However, one cannot be sure, since chromium status is difficult to determine. This is because levels in the blood, urine or hair do not necessarily reflect the body's reserves as a whole. In addition, no chromium-specific enzyme has been found that could reliably assess a person's chromium status. There is considerable interest in the possibility that supplemental chromium may help treat impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. However, research at the moment is not enough, but it is constantly being conducted in this area.
Using chromium for weight loss
Information about the miraculous effect of chromium on weight loss has become widespread - especially in weight loss techniques.
Indeed, by regulating blood sugar levels, it significantly reduces the need for sweets and attacks of ravenous appetite.
It is also capable of speeding up metabolism, so it can be an excellent ally in the fight against excess weight, but not a “magic pill” that will solve the problem for a person.
The use of chromium for weight loss should be accompanied by constant strength loads: then the useful microelement will help build muscle mass and break down fat.
In addition, chromium-containing preparations, without the use of special diets, help prevent harmful fat deposits and remove dangerous carcinogens.
Another beneficial property of the microelement for metabolism is the normalization and restoration of thyroid function.
Chromium also acts in favor of stimulating reproductive function in a woman's body.
Daily requirement for chromium
The microelement enters the body through the air and through food. The amount of chromium absorbed in its pure form after passing through the digestive tract is about 0.5–1%.
It is recommended to calculate a safe daily dose of substance consumption for humans according to the following criteria:
- for men of reproductive age - 30 mcg, for the elderly and elderly - 18–20 mcg;
- for women under 50 years of age, including lactation - from 50 mcg. During menopause and postmenopause - 18 mcg;
- for people leading an inactive, sedentary lifestyle - no more than 25–35 mcg;
- The recommended amount of the substance for pregnant women, as well as for athletes, is approximately 150–200 mcg.
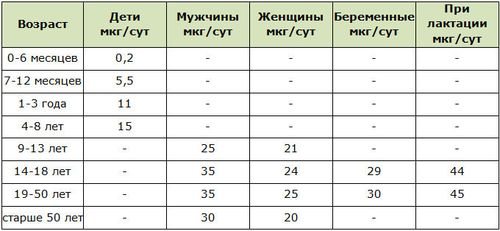
Standards for chromium intake for children:
- from 1 year to 3 years - 11 mcg;
- from 3 to 11 years - 15 mcg;
- from 11 to 14 years - 25 mcg;
- for young men aged 14 to 18 years - up to 35 mcg;
- girls between 14 and 18 years old - about 50 mcg.
There are no clearly established values for these indicators of daily mineral consumption, therefore average data are given, taking into account which the consumption of a microelement is unable to cause even minimal harm to the health of an adult or child.
Basic nutritional recommendations include:
- Eating a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, low-fat or fat-free dairy products, and oils.
- Whole grains and some fruits and vegetables (broccoli, potatoes, grape juice and oranges) are sources of chromium. Ready-to-eat cereal bran can also be a relatively good source of chromium.
- Eating a variety of protein foods, including seafood, lean meat and poultry, eggs, legumes, nuts, seeds, and soy products.
- Lean beef, oysters, eggs and turkey are good sources of chromium.
- Limiting saturated and trans fats, added sugars and salt
- Stay within your daily calorie needs.
This article cannot be a guide to any action. It is for informational purposes only. Any treatment, including taking medications, especially treatment with folk remedies, requires mandatory consultation with a specialist.
764, today 1










