What are fats
Fats or lipids are organic substances that are the main component of the membrane and nucleus of cells.
It is one of the main sources of energy in the body.
We must remember that the fat cell is the most energy-intensive!
1 gram of fat contains as many as 9 kcal, while 1 gram of protein or carbohydrates contains 4 kcal.
Fat (or, to be more precise, fatty acids) is an extremely unprofitable source of energy for the body; these are precious reserve reserves that are reserved for a “special occasion” when energy is really needed for survival, for example.
Therefore, the body is extremely reluctant to part with its reserve energy sources, but prefers to use a cheaper source - carbohydrates.
It’s as if you heat the stove in your house not with wood (carbohydrates), but with expensive photo paper or money.
It’s the same for the body; it stores the most energy-intensive source of energy, and uses the cheapest one more readily.
So, to summarize the above, fat cells serve to store energy reserves, as well as to prevent heat loss from the body.
Fats include:
- triglycerides;
- sterols;
- phospholipids;
All of them perform many important functions in the body, which we will talk about a little further.
In the intestine, lipids are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids, which take part in metabolism and other biological processes.
By the way, I already mentioned fatty acids above, it is this part of the fat cell that circulates in the blood to get into the muscles, where they will be used as energy during your physical activity.
Among fatty acids there are essential ones, which are not produced in the body, but come from food.
These include arachidonic, linoleic, gamma-linolenic, docosahexaenoic and other fatty acids.
We all really need them for the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system and brain, participate in the production of testosterone and other hormones, and improve the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
By the way, I once already wrote an article about vitamins for sports. Be sure to read it.
Yogurt
Natural yogurt is incredibly healthy. It contains all the same important nutrients as other dairy products, but in addition, it also contains probiotic bacteria that can have powerful positive effects on your health.
Research shows that eating yogurt can lead to significant improvements in digestive health and may even help fight cardiovascular disease and obesity (29, 30, 31).
Unfortunately, many of the yogurts sold in grocery stores are low in fat and contain sugar. It is better to avoid eating store-bought yoghurts and use homemade ones whenever possible.
You can learn more about the beneficial properties of yogurt and possible side effects from consuming it on this page - Yogurt: benefits and harm to the body.
Summary:
Natural yogurt contains fats that are beneficial for cardiovascular health, and also contains probiotic bacteria that improve gastrointestinal health.
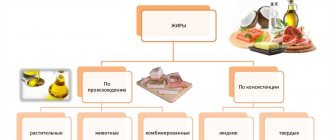
Types of fats
Fats are of vegetable and animal origin.
By consistency - solid and liquid.
Also, all fats that enter the body with food are divided into 3 groups:
- Saturated.
- Unsaturated.
- Trans fats.
Saturated
Saturated fats are so called because they have a simple structure and single bonds between atoms.
These are mainly animal lipids that have a solid consistency at room temperature.
They are quickly absorbed and, with a lack of physical activity, are deposited in adipose tissue.
Saturated fats are involved in the production of cholesterol, sex hormones, and regulate heat exchange.
The products in which they are present are nutritious and contain vitamins A, D, and lecithin.
Therefore, they should be consumed, but in limited quantities.
With an excess of saturated fats, cholesterol levels increase and excess weight accumulates.
They increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
I will definitely tell you today about the most rational proportion of fats of animal and vegetable origin.
Unsaturated
Unsaturated fats are found mainly in plant foods and fish.
According to their structure, they have double and triple bonds between atoms.
Therefore, such lipids are easily oxidized in air and destroyed during heat treatment.
Unsaturated fatty acids are called Omega 3, Omega 6 and Omega 9.
Remember I wrote a cool and detailed article about flaxseed oil and fish oil?
These fats are divided into monounsaturated and polyunsaturated.
- Monounsaturated are Omega 9. They can be produced in the body, so they are not essential. These acids strengthen the immune system, normalize the absorption of glucose, reduce cholesterol levels, and accelerate metabolic processes. But if consumed in excess with food, they can accumulate.
- Polyunsaturated Omega 6s have more bonds between atoms. They are considered essential because they are not produced in the body. They perform important functions: improve skin condition, relieve inflammation, normalize blood clotting.
- Omega 3 polyunsaturated acids enter the body only with food. They are the most useful and necessary for the normal functioning of all organs. These acids strengthen cell membranes, accelerate regeneration processes, and improve the functioning of the nervous, reproductive and immune systems.
Trans fats
It is a type of saturated fat that has been artificially modified and processed. I gave you a link to an article about this type of fat above. Be sure to read it.
You can't use them!
They are very harmful to health, as they increase cholesterol levels (specifically, “bad cholesterol” LDL), worsen metabolism, and increase the risk of obesity and cardiovascular pathologies.
It is not recommended to consume products containing them. They lead to increased insulin synthesis and accumulation of fat cells.
Cheese
Cheese is incredibly nutritious. This makes sense considering that an entire glass of milk is used to produce one dense piece of cheese. Cheese is an excellent source of calcium, vitamin B12, phosphorus and selenium, and contains all sorts of other nutrients (41).
It is also very rich in protein - 100 grams of cheese can contain between 20 and 40 grams of high-quality protein. Cheese, like other high-fat dairy products, also contains powerful fatty acids that have been linked to a variety of health benefits, including a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes (42).
You can learn more about the beneficial properties of cheese and the possible harm from consuming it on this page - Cheese: benefits and harm for the human body.
Summary:
Cheese is incredibly nutritious. Just one piece contains as many nutrients as a glass of milk. It is an excellent source of vitamins, minerals, quality proteins and healthy fats.
Positive properties of fats
All lipids, except trans fats, are necessary for the normal functioning of the body. Trans fats, I repeat once again, should not be consumed!
Lipids perform the following useful functions:
- strengthen cell membranes;
- participate in the synthesis of sex hormones;
- regulates heat exchange;
- protect internal organs from damage;
- serve as a strategic reserve of energy;
- participate in the absorption of vitamins A, D, E, K;
- normalize heart function;
- improve brain function, memory, concentration and mood;
- necessary for the normal functioning of the nervous system, as they are part of the nerve sheaths and participate in the passage of nerve impulses;
- stimulate the production of bile and participate in digestion;
- improve potency in men and the functioning of the reproductive system;
- reduce cholesterol levels;
- relieve pain and inflammation in joints;
- accelerate regeneration processes, promote rejuvenation;
- normalize hormonal levels;
- improve the condition of skin, hair, nails;
- prevent the development of cancer, strokes, arthritis.
As you can see, eliminating all fats from the diet is the stupidest idea that can come to the mind of a person who wants to know how to lose weight quickly.
How much fat does a person need?
To meet the body's needs for fats, their amount should be about 30% of the total calorie intake.
On average, for an adult male it is about 100 g. For girls it is about 50-70 g.
Older people need less fat - about 70-80 g.
The ratio of different types of fats is important.
I promised to tell you about the correct proportion of fats in the diet, I keep my promise)
It is recommended to consume 70% vegetable fats and 30% animal fats.
In more detail, the types of lipids should be distributed as follows:
- saturated fats – 10%;
- Omega 9 monounsaturated fatty acids – about 50%;
- Omega 6 polyunsaturated acids – 30%;
- polyunsaturated acids Omega 3 – 10%.
The need for fats is individual and depends on age, physical activity, and the presence of chronic diseases.
Also, their amount depends on the total caloric intake of the diet and the consumption of carbohydrates. When entering the body, fats are broken down in the intestines and enter the tissues through the blood. There they are used to build cell membranes and as an energy source.
If a lot of glucose is consumed (and as we know, any carbohydrates that enter your body are eventually broken down into glucose), insulin is intensively synthesized.
Under the influence of this hormone, lipids are deposited in adipose tissue.
They are released and broken down under the influence of somatotropic hormone (“growth hormone”), adrenaline, and also during intense physical activity.
During fasting, fats become the main source of energy and are converted into carbohydrates.
If you consume more fat than necessary, the volume of fat deposits increases.
In general, it’s not just about fats, it’s about the total daily caloric content of the diet!
If you consume more calories per day than you expend, it does not matter whether you consume them from carbohydrates, proteins or fats. You will still gain excess fat mass.
Because of this, the condition of blood vessels and skin worsens, an increased load on the liver is created, and blood pressure rises. Excess weight has never made anyone prettier.
It is recommended to consume less fatty foods than normal for overweight people who lead an inactive lifestyle.
But sometimes the amount of fat can be increased. The need for them increases in the following cases:
- with atherosclerosis, decreased elasticity of blood vessels;
- when playing sports;
- increased physical activity;
- for diabetes mellitus;
- hormonal imbalances;
- in adolescence;
- during pregnancy and lactation;
- in the cold season.
Chia seeds
Chia seeds are not typically thought of as a "fatty" food. However, 100 grams of chia seeds contain 31 grams of healthy fats. Considering that almost all of the carbohydrates in chia seeds are fiber, the majority of their calories (80%) actually come from fat. This makes them an excellent fatty plant food.
And it's not just any fat—most of the fat in chia seeds is a healthy omega-3 fatty acid called alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).
Chia seeds also have numerous beneficial properties that help lower blood pressure and reduce inflammation in the body (39, 40).
They are also incredibly nutritious. In addition to being rich in dietary fiber and omega-3 fatty acids, chia seeds are also rich in minerals.
Summary:
Chia seeds are very rich in healthy fats, especially an omega-3 fatty acid called ALA. They are also high in fiber and minerals and have numerous health benefits.
What happens if there is not enough fat?
Since fats are necessary for the normal functioning of all organs and systems, I do not recommend excluding them from the diet.
Low-fat foods and diets are not a panacea, just control the proportion of fat entering the body and you will be happy.
Even when losing weight, you cannot reduce their amount below normal.
This will lead to a deterioration in metabolism and slow down the weight loss process.
Due to a lack of fat in the diet, health problems may arise:
- hormonal imbalances, decreased libido;
- deterioration in performance, lack of energy, increased fatigue;
- decreased skin elasticity, dryness, hair loss and fragility;
- acceleration of aging processes, appearance of wrinkles;
- exhaustion of the nervous system, depression;
- decreased immunity;
- avitaminosis;
- deterioration of mental activity, decreased concentration;
- blurred vision;
- joint pathologies;
- development of gallstone disease.
Is it possible to completely avoid saturated fats?
Lipids are an important component of food and the main source of energy.
Therefore, even saturated fats are essential for health.
You cannot completely abandon them, you just need not to exceed the recommended norms (10% of all fats in the diet). They are especially important for people involved in sports or intense mental work.
Low-fat food does not help you lose weight if the main rule of losing weight is not followed:
Consume less calories than you burn.
Low-fat food is less tasty, less satiating and leads to a decrease in physical activity if you do not plan your diet correctly.
A lack of saturated fats can cause hormonal imbalances, deterioration of immunity, and decreased vascular elasticity. And in low-fat dairy products, calcium absorption deteriorates.
Therefore, saturated fats are also useful, foods containing them should be included in the diet daily.
I will say for the third time that you should only avoid trans fats, which do nothing but harm the body.
Is switching to unsaturated fats necessary for health?
Various researchers in the field of healthy eating and dietetics argue that consuming significant amounts of saturated fat is unsafe and leads to increased cholesterol in the blood, which in turn contributes to the formation of sclerotic plaques and significantly increases the risk of stroke and heart attack.
This occurs because saturated fats lack double bonds and are difficult for the human body to absorb and digest. Unsaturated acids (both poly- and mono-) contain such carbon double bonds, which facilitates their breakdown and not only prevents the deposition of bad cholesterol, but also reduces its level.

In addition, consuming unsaturated fats cannot make you fat - they are not stored as fat deposits and, moreover, help break down existing fat. However, completely avoiding saturated fats is also harmful. Their consumption should be reasonable and limited, and the majority of the diet should still be unsaturated fats.
Fats in food: table

To consume the required amount of fat, you need to know how much is contained in different foods.
I advise you to use natural foods, since semi-finished and ready-made foods are high in carbohydrates and processed saturated fats.
In this case, it is difficult to determine how many grams entered the body.
In order not to exceed the daily norm, you need to know which foods contain the most fat:
- saturated ones are found in fatty dairy products, meat, coconut oil;
- monounsaturated – in nuts, olive oil, mustard oil, avocado;
- polyunsaturated – in fatty fish, vegetable oils, eggs, sesame.
A table with foods containing the maximum amount of fatty acids will help you correctly create a diet:
| amount of fat per 100 g of product | products |
| 80-100 g | lard, butter, vegetable oils, margarine |
| 40-80 g | nuts, seeds |
| 20-40 g | sausages, cheese, sour cream, pork, duck meat, halva, chocolate |
| 10-20 g | cottage cheese, ice cream, cream, lamb, beef, chicken meat, turkey, eggs, fish |
There are foods that are low in fat. These are flour products, cereals, pasta, fruits, vegetables, lean meat.
With their help, it is difficult to reach the daily requirement of fatty acids, as there will be an excess of carbohydrates. But when choosing a diet, their composition also needs to be taken into account.
| amount of fat per 100 g | products |
| 3-9 g | medium-fat dairy products, lean meat, baked goods, sweets, pink salmon, tuna |
| 1-3 g | cereals, hake, cod, chicken breast, bread |
| less than 1 g | vegetables and fruits except avocados |
To study in detail the dietary fat and calorie content of all food products, you can use this table on my blog:
Bad fats
Saturated fatty acids of animal origin, it is recommended to consume no more than 10% of all fats in the diet per day.
List of foods with unhealthy fats:
- butter;
- cream, cheese (refractory fat), sour cream;
- margarine;
- chicken skin;
- salo;
- pork, lamb and other meat fats;
- chocolate, confectionery;
- palm and coconut oils.
Multi-ingredient dishes are especially harmful: fried meat, potatoes, products with mayonnaise, baked goods, sausages.
Trans fats
Modified saturated fats, even in small doses, can harm the body.
They lead to a slowdown in metabolic processes, the development of atherosclerosis, and obesity.
The following foods contain trans fats:
- margarine;
- confectionery fat;
- spread;
- fast food;
- French fries;
- chips;
- crackers;
- pizza;
- semi-finished meat products;
- confectionery and baked goods with cream;
- mayonnaise.
Above, give a link to your article about trans fats, be sure to read it.
Healthy foods rich in fats

90% of your daily fat intake should come from healthy foods.
They contain polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acids.
It can be plant or animal food:
- eggs;
- avocado;
- walnuts, almonds, pistachios;
- pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds;
- fatty fish;
- olive, flaxseed, rapeseed, sunflower or corn oil;
- olives;
- soya beans.