One of the rules for losing weight and eating healthy is to exclude sugar and sugar-containing products from your daily diet. To replace it, you need to take cereals and grains, as well as add more fruits, berries and vegetables. Thus, it will be possible to shift the emphasis to complex carbohydrates, which take longer to digest and provide more energy. With calorie restrictions and diets, this becomes a real salvation - the craving for overeating is reduced, and a long-term feeling of satiety is maintained.
Simple and complex (fast and slow) carbohydrates
According to their chemical structure, types of carbohydrates are simple (mono- and disaccharides) and complex (polysaccharides). The energy value of 1 gram is equal to 4 kilocalories.
Recently, for instant satiation, people have been using products containing simple carbohydrates - they are high in calories, but very tasty. Consequently, preference is given to fast and refined carbohydrates. This is of great interest among scientists who are actively studying human performance in accordance with the food consumed.
First you need to understand what simple and complex carbohydrates are in order to come to the right conclusion.
Simple (fast) carbohydrates
Based on their chemical composition, simple carbohydrates are divided into two types.
| Monosaccharides (simple sugars, one molecule) | Disaccharides (contains 2 monosaccharide molecules) |
|
Types of complex carbohydrates
Polysaccharides or long carbohydrates are large chains of compounds that, when broken down, can provide much more energy than simple ones. Complex carbohydrates are digested slowly and for a long time, without sudden spikes in insulin. After taking them, a person remains full for a long time, full of strength and vigor.
Fiber, starch and glycogen are complex carbohydrates. Each of them is an important component for building a harmonious diet, and ideally it should be a combination of all three types. Let's take a closer look at the features of each.
Starch is considered unique and the most valuable; about 80% comes from healthy carbohydrates from starchy foods. Compared to simple compounds, the product has longer chains consisting of glucose molecules. Similar polysaccharides are found in foods such as cereals, pasta and baked goods, rice and cereals, green beans and potatoes. There are also processed forms - these are short polymers of glucose and maltodextrin. They dissolve perfectly in water, which facilitates immediate entry into the bloodstream after administration.
This product has another big advantage - the absence of a side effect in the form of bloating. Complex compounds are recognized as the best sources of energy, so every athlete should add them to their diet.
Fiber – This substance is usually very neglected by many people. There is a lot of it in fruits and vegetables, legumes and grains, as well as nuts. Its structure is not a starchy polysaccharide, but in common parlance it is dietary fiber.
Has a number of features:
- there is no possibility of digesting fiber due to its resistance to digestive enzymes;
- reduces the risk of oncological pathologies of the colon, diabetes mellitus and diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- lowers levels of “bad” cholesterol;
- promotes the excretion of bile acid.

Fibers can be soluble or insoluble. Agree, not many people know which carbohydrates are insoluble in water and why they are needed. In the meantime, there are a number of advantages for athletes:
- The insoluble group helps improve the digestion process by slowing down the hydrolysis of starch, and also helps remove breakdown products and slow down the absorption of glucose.
- A group of soluble fibers slow down digestive activity and lower cholesterol levels. Like insoluble fiber, it slows down the absorption of glucose.
Glycogen - the chain contains several glucose molecules. Immediately after eating, glucose enters the bloodstream, the excess of which is stored in the form of glycogen. For example, during physical activity, glucose levels drop, the body begins to break down glycogen with the help of enzymes, returning glucose levels to normal. Even during the training process, all organs can produce energy in sufficient quantities.
The main places where glycogen accumulates are muscles and liver. The total amount varies in the range of 300-400 g. In the process of building the body, glycogen from muscle fibers is extremely important.
Under the influence of physical activity, fatigue occurs due to the depletion of stored glycogen. In this regard, one and a half to two hours before the start of training, you need to consume foods high in carbohydrates in order to replenish glycogen reserves.
The table provides specific examples of each type of long connection.
| Polysaccharides | ||
Starch:
| Soluble Fiber:
| Insoluble fiber:
|
Too many added sugars can harm your health
For many people, the word "sugar" has a negative connotation.
Many nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits and vegetables, naturally contain sugar and should not be avoided for their health benefits.
On the other hand, added sugars—such as those found in sugary drinks, candy, baked goods, and desserts—can contribute to many health problems.
Added sugars have been linked to increased rates of obesity, cardiovascular disease and an increased risk of cancer.
Associated with obesity
Obesity affects almost 40% of adults living in many developed countries (2).
It is associated with serious health risks, including diabetes, heart disease and cancer.
In addition, obesity is very expensive to treat. Compared to people at a healthy weight, obese people spend thousands of dollars on healthcare annually (3).
This places a significant economic burden on individuals, families, and taxpayers (4).
The cause of obesity is widely debated and multifactorial, but excess intake of added sugars is thought to play a major role (5, 6).
Added sugars add extra calories to your diet, which can lead to weight gain over time.
Sweet taste and palatability may exacerbate excessive intake of added sugar relative to other nutrients, increasing the risk of weight gain (7, 8, 9, 10).
May contribute to the development of heart disease
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in many countries (11).
It is most often caused by atherosclerosis, a disease in which plaque (cholesterol plaques) on the inner walls of the blood vessels that lead to your heart causes them to narrow and harden. This reduces blood flow, which can lead to a heart attack (12, 13).
Several studies have shown that getting too many calories from added sugar can lead to elevated triglyceride levels, a known risk factor for heart disease (14, 15, 16, 17).
One study found that people who got 10-25% of their calories from added sugar had a 30% greater risk of dying from heart disease compared to those who got less than 10% of their calories from added sugar (18).
What's more, this risk nearly doubles for those who get more than 25% of their calories from added sugar.
May increase risk of cancer
Excess calories from added sugars can increase inflammation and oxidative stress.
Some inflammation and oxidative stress are essential for good health, but too much of it can lead to a number of diseases and conditions, including cancer (19, 20, 21).
Many studies have reported increased markers of inflammation—such as C-reactive protein and uric acid—with the consumption of added sugars (22, 23, 24).
Added sugar is thought to increase cancer risk by increasing levels of certain hormones, but these effects are not well understood (25, 26, 27).
Added sugars have been linked to obesity. Moreover, they may contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease and increase the risk of cancer.
How does carbohydrate metabolism occur?
Food containing complex carbohydrates in the gastrointestinal tract can be broken down into simple compounds, namely glucose, after which it is absorbed into the blood. A hormone (insulin) is synthesized, which converts the product into glycogen. The process lasts until blood glucose levels stabilize.
Glycogen reserves are located in muscle fibers and liver cells. During training, reserves in the muscles are depleted, and reserves in the liver are aimed at maintaining the required level of glucose in the blood. The norm is considered to be from 80 to 120 mg/dl.
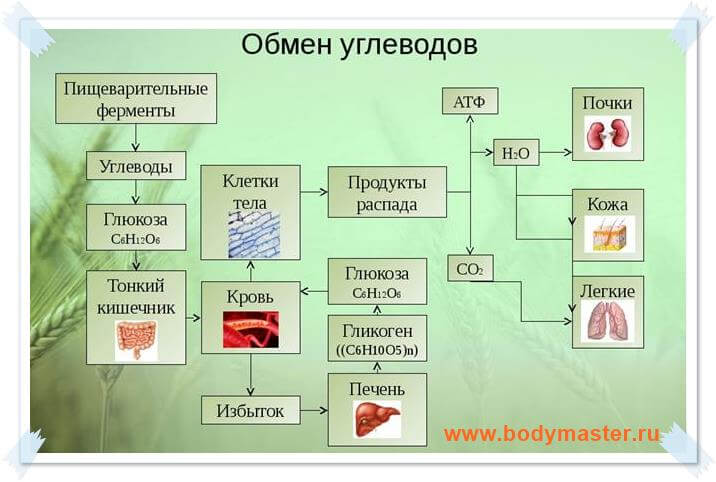
In case of a lack of nutrients, glycogen from the liver is converted back into glucose and enters the blood - all this is necessary to maintain the normal functioning of the body.
What happens when you have too many carbohydrates?
If complex carbohydrates enter the body in excess, this helps to increase insulin production, no matter what foods are consumed. Overload of the pancreas leads to depletion of its cells, which, if there is a tendency, can cause diabetes mellitus. A completely unpleasant bonus to everything will be the deposition of fat with an excessive concentration of glycogen.
When complex carbohydrates are consumed in excessive amounts and are poorly chewed, fermentation processes are started in the intestines. This is not only bloating and discomfort during training, but also poisoning the body with toxins from the intestines. In medicine this is called fermentative dyspepsia.
What happens when there is a lack of carbohydrates
If, when planning your diet, you strictly cut carbohydrates for a long time, this can lead to irreversible metabolic disorders. The body will not receive important energy from food, so it begins to waste glycogen from the liver, which provokes a disruption in its activity.
When there are no food sources of carbohydrates, the process of protein breakdown is activated to obtain the necessary energy. As a result, the destruction of muscle mass begins, which was built so long and diligently in the gym. It should be noted that the process also affects the heart muscle. All these factors make a long-term and grueling low-carb diet extremely detrimental to a person.

Low levels of glucose in the blood provoke exacerbation of hunger, and prolonged deficiency leads to weakness and lack of energy, nausea and sweating, headaches and systematic dizziness, tremors and tachycardia. This is called hypoglycemia, which is made worse by insulin resistance (metabolic syndrome).
How to Identify Added Sugars on Food Labels
You can find added sugars in many types of foods—even those you wouldn't consider sweet, like ketchup, bread, and canned beans.
However, the main sources of added sugars are sweetened drinks, candy, desserts, ice cream, and sugary cereals (28).
Check the food label to see how many grams of sugar it contains.
Historically, food labels have not differentiated between natural and added sugars. This makes it difficult to determine the amount of added sugar.
Clinical picture
Excessive consumption or deficiency of carbohydrates can be harmful to health. To maintain normal metabolism, you need to include at least 60% of a macronutrient in your diet every day.
What doctors say about losing weight
Nutritionists and trainers very often in practice are faced with the stereotype that in order to lose weight it is necessary to either critically reduce the amount of carbohydrates or give them up altogether. The root of the evil is the lack of information and a large number of false facts that can be read in popular communities. Such actions will not only weaken the immune system, but will also seriously undermine your health.
Experts also believe that in the process of losing excess weight, slow carbohydrates improve peristalsis and intestinal microflora. The component is also indispensable during muscle mass gain. Recipes for each purpose can be found at the end of the article.
Polysaccharides You Should Eat More of
If you are serious about eating a carbohydrate-heavy diet, then you need to know which foods contain complex carbohydrates. Be sure to include them as a regular part of your diet:
- Grains are good sources of fiber, as well as potassium, magnesium and selenium. Choose less processed whole grains, such as buckwheat and whole wheat pasta.
- Fiber-rich fruits such as apples, berries and bananas (avoid canned fruits as they usually contain added syrup).
- Vegetables rich in fiber. Eat more of any vegetables, including broccoli, leafy greens and carrots.
- Legumes. In addition to fiber, they are good sources of folic acid, iron and potassium.
Selecting slow polysaccharides can take some trial and error. But taking an inquisitive look at the labels of the foods you buy can help you start making healthier choices that will activate your body and protect it from long-term complications.
Where are complex (slow) carbohydrates found - list of products
We have already figured out what long-term carbohydrates are, and now let’s talk about which foods contain them the most.
The key rule of proper nutrition is that it is better to consume slow carbohydrates in the first half of the day, and this is due to the most successful time for their absorption. However, if the workout is planned for the evening, then there is nothing critical in eating foods that contain these macroelements for dinner. In the case when the main goal is weight loss, it is best to give preference to fiber, which quickly saturates and is not absorbed by the body. At the stage of gaining muscle mass, it is better to switch to ingredients rich in starch and glycogen, but you should not forget about protein foods either.

To make it easier for you to choose complex carbohydrates to achieve your goals, we have provided a table with the most popular ingredients in descending order of macronutrient amount.
| Product groups | Name | Amount of carbohydrates per 100 g |
| Whole grains | corn grits | 75 |
| Brown rice | 72,9 | |
| barley | 71,7 | |
| wheat | 69,3 | |
| buckwheat | 68 | |
| oats | 66,2 | |
| spelled | 61,2 | |
| quinoa | 57,2 | |
| Whole grain bread and pasta | durum pasta | 71,5 |
| wheat bread | 53,4 | |
| Rye bread | 49,8 | |
| Legumes | chickpeas | 61 |
| lentils | 60 | |
| beans | 52,7 | |
| green beans | 3,6 | |
| Nuts | cedar | 28,4 |
| cashew | 22,5 | |
| almond | 21,7 | |
| hazelnut | 9,4 | |
| walnut | 7 | |
| Milk products | yogurt 1.5% | 7,4 |
| milk 2.5% | 4,7 | |
| cottage cheese 1.8% | 3,3 | |
| Fruits and berries | banana | 21 |
| grape | 15,4 | |
| apple | 13,8 | |
| raspberries | 11,9 | |
| plum | 11,4 | |
| pear | 10,3 | |
| orange | 8,1 | |
| strawberry | 7,5 | |
| currant | 7,3 | |
| Vegetables | potato | 18,1 |
| carrot | 6,9 | |
| broccoli | 6,6 | |
| pumpkin | 6,5 | |
| cauliflower | 5,4 | |
| tomato | 3,7 | |
| cucumber | 2,8 |
Contents by groups, differences
As you have seen, complex carbohydrates are synthesized in various ingredients, and the following list of generalized foods reveals their main characteristics.
Vegetables and fruits are an indispensable and key component of a healthy diet for any person, regardless of the specifics of training. Vegetables and fruits contain complex compounds. To obtain the maximum amount of useful substances, it is recommended to consume them raw, because any method of heat treatment suppresses their numbers.

Greens - experts highly recommend including this ingredient in your menu, because... it can not only enrich it with useful substances, but also normalizes the processes of digestion and the excretory system.
It’s not for nothing that they say that porridge If they are prepared on the basis of whole grain cereals, which are classified as complex compounds, then this is the best option for daily nutrition. It is recommended to avoid highly processed products because... they have a high glycemic index and negatively affect the weight loss process. Displays the glycemic index, the level of blood glucose response to any product.
Dairy products contain lactose, which classifies these products as simple carbohydrates. But this does not mean that you need to abandon this source, because low-fat products still contain slow chains and are rich in calcium and phosphorus.
Legumes and grains are another great source of energy. You can significantly increase your intake of this macronutrient by replacing processed grains with legumes. Replacing wheat bread with a whole grain product can significantly increase your fiber intake.

Freshly squeezed juices are a liquid form of complex carbohydrates from fruits and vegetables, consumed in the form of drinks.
Diet

Complex carbohydrates form the basis of a healthy diet. For a healthy person, the ratio of simple and complex compounds is represented by a simple percentage:
- 65% should be complex carbohydrates.
- 25% are simple.
- The remaining 10% is the so-called ballast load, fiber, which vegetables and fruits are so rich in. It regulates the rate of absorption of substances, normalizes the evacuation of waste compounds, and the functioning of the digestive tract.
For diabetes, we are talking about eating only complex carbohydrates (90% are slow compounds and about 10% are fiber).
If a person is intensely involved in sports: 80% complex carbohydrates and about 15 simple ones.
This is very approximate. It all depends on the characteristics of the body, the speed and quality of metabolism, and health status. The issue should be discussed with a dietician or qualified nutritionist.
The benefits of complex carbohydrates
Excessive macronutrient content in the diet can negatively affect the health and fitness of an athlete, but its role is extremely important in the life of the body:
- The main source of energy - carbohydrate provides fuel for a full, productive workout. The daily requirement is calculated individually;
- after the reserves of glucose and glycogen are depleted, thanks to the slow chains of the macroelement, the consumption of protein as an energy source does not turn on. This phenomenon is called glycogenesis and occurs when blood glucose levels are low. Accompanied by the release of glucagon;
- prevents the process of catabolism and muscle atrophy, which leads to loss of muscle mass as a result of the process of glucogenesis;
- Another huge benefit from consuming healthy carbohydrates is that they can improve brain function and maintain the central nervous system in a normal state. Glycogen does not accumulate in the brain, therefore, on a low-carbohydrate diet, athletes often observe a decrease in mental activity, especially concentration;
- Eating nutritious meals with enough carbohydrates prevents hypoglycemia, the symptoms of which are: hunger, loss of energy, migraines and dizziness. To avoid experiencing such feelings during training, it is important to make sure that your diet meets the standards.

1 - Slow Carbs Are Less Likely to Cause Blood Sugar Spikes
Bad carbohydrates can significantly increase blood sugar levels, which forces the pancreas to produce a large dose of insulin. This not only returns the feeling of hunger, but also provokes you to eat another portion of sweet food. Complex types of carbohydrates take much longer to digest than simple carbohydrates, which helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, providing a boost of energy throughout the day and during the training process.
2 - Complex carbohydrates may reduce the risk of some chronic diseases
For a healthy and nutritious diet, it is important to eat foods containing complex carbohydrates, which will not only significantly reduce the risk of gaining excess weight, but will also help prevent the development of chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular pathologies. All sources of slow carbohydrates are rich in dietary fiber, vitamins and minerals, as well as antioxidants and plant compounds - this complex provides excellent prevention of diseases of various types.
It should be noted that many studies support the positive association between low levels of “bad” cholesterol and blood sugar with a diet that includes fiber from whole foods.
3 – Long-lasting carbohydrates promote a healthy digestive system
The human intestine contains a huge variety of “good” bacteria – these are microbiota. They promote healthy digestion, better absorption of minerals, neutralize inflammatory processes in the intestines, and also fight constipation. All foods containing complex carbohydrates contain large amounts of soluble fiber, which promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria by feeding them. The bacteria in turn produce short-chain fatty acids, which are extremely beneficial for the digestive system. If you feed them with the right macronutrients, you can forget about the craving for overeating, which is very important on a diet.
4 – Long Carbohydrates May Reduce Inflammation
Inflammation is the human body’s response to internal stimuli. A prolonged nature contributes to the development of chronic forms of diseases of the cardiovascular system, hypertension and diabetes, metabolic syndrome and even cancer.
Sweet products and refined flour provoke inflammation, and complex types of carbohydrates help counteract its occurrence. Fiber, found in whole grains, fruits and legumes, has anti-inflammatory effects.
How to start eating more complex carbohydrates
In order for healthy carbohydrates to bring the most positive results both in the training process and for health in general, you may need to adjust your eating habits and choose foods that contain slow carbohydrates. For example, buy pasta and bread from whole wheat, and not from premium varieties. Give preference to vegetable snacks rather than fatty chips. Replace polished white rice with other sources of complex carbohydrates - legumes or unprocessed cereals.

Summarize
- Complex carbohydrates are much more nutritious than simple carbohydrates.
- They are high in nutrients and fiber, and eating them regularly can be good for your health and waistline.
- On the other hand, simple carbohydrates have low nutritional value and should be avoided whenever possible.
Tags: carbohydrates
About the author: Anastasia Sheveleva
Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category, therapist, registered dietitian, nutrition consultant. More about the author.
- Related Posts
- 6 foods that cause inflammation in the human body
- Kosher and Halal Food: What's the Difference?
- Top 20 Foods Rich in Soluble Fiber
« Previous entry











