For the normal functioning of all organs and systems, it is necessary to eat a balanced diet. Carbohydrates, both complex and fast, are irreplaceable and mandatory in the diet. It is complex carbohydrates that bring maximum benefits to the body. Fast carbohydrates are quickly absorbed by the body, and saturation from eating disappears. Consequently, the body begins to require more food. Simple carbohydrates include baked goods, fast foods, and sweets. What are complex carbohydrates? What are these foods with complex carbohydrates?
Simple and complex (fast and slow) carbohydrates
According to their chemical structure, types of carbohydrates are simple (mono- and disaccharides) and complex (polysaccharides). The energy value of 1 gram is equal to 4 kilocalories.
Recently, for instant satiation, people have been using products containing simple carbohydrates - they are high in calories, but very tasty. Consequently, preference is given to fast and refined carbohydrates. This is of great interest among scientists who are actively studying human performance in accordance with the food consumed.
First you need to understand what simple and complex carbohydrates are in order to come to the right conclusion.
Simple (fast) carbohydrates
Based on their chemical composition, simple carbohydrates are divided into two types.
| Monosaccharides (simple sugars, one molecule) | Disaccharides (contains 2 monosaccharide molecules) |
|
Why You Shouldn't Be Totally Afraid of Simple Sugars
There is no doubt that sugar can be harmful to your health when consumed in excess.
However, sugar is only one component of your diet. It is naive to hold it entirely responsible for obesity and other diseases and conditions in modern society (31).
Research shows that sugar only causes health problems when it's present in excess in your diet or if you're getting more calories than you need from sugar (10, 32, 33, 34).
Limiting your intake of sugar-sweetened drinks, sweets and desserts is important for good health, but completely cutting out a slice of pie or a scoop of your favorite ice cream is the wrong approach. It's not sustainable, enjoyable, or good for your health.
In addition, simple sugars occur naturally in a wide range of healthy foods, such as fruits, vegetables and dairy products. These foods add a variety of other important nutrients to your diet, such as vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber.
Sugar is bad for your health when it makes up too much of your diet or you get extra calories from sugar. Therefore, limiting, but not completely avoiding, sugar—especially added sugar—makes sense for your health.
Carbohydrates in foods can be simple (glucose, fructose, galactose) and complex (fiber, pectin, starch). Carbohydrates are sugars and are the most common organic compounds on Earth. And in human metabolism, the importance of sugars is enormous; it cannot be overestimated.
The main functions of sugars are:
Energy . In order to live and work normally, our body must constantly receive energy. The breakdown of carbohydrates occurs instantly. At the same time, a lot of energy is released, which is consumed by the body. Foods that are enriched with sugars quickly give you a feeling of fullness without feeling drowsy or lethargic. For this reason, in cases where it is necessary to quickly restore performance, it is recommended to eat chocolate or something similar.
Plastic . She is also a construction role. In the human body, glucose is involved in the synthesis of certain amino acids and takes part in the construction of nucleotides. Sugars also play a role in building cell walls.
Saving (saving) . Sugars have the ability to cumulate (accumulate). In the human body, this occurs in the form of glycogen, which is stored in reserve in muscles, liver and other tissues. When the body begins active work, these reserves begin to quickly be used up. When the body enters a state of rest, reserves begin to be replenished again due to food entering the body. If the muscular work of the body is constant and regular, then glycogen reserves will increase, which will result in increased endurance of the body.
Protective. Complex sugars (polysaccharides - fiber, starch, pectin) are responsible for this function. These compounds play a role in the immune system of our body and are part of the protective mucous coating of the vessels of the bronchi, nose, digestive system, and genitourinary tract. Therefore, many pathogenic microorganisms do not manage to penetrate the body.

Regulatory . Fiber plays a major role here. The fiber that enters the body with food is not digested in the intestines. Its role is to activate intestinal contractions, improve its functioning and increase the amount of nutrients absorbed.
Sources of simple and complex carbohydrates
Carbohydrates in foods can be found in the form of simple sugars and complex sugars.
Simple sugars - their main representatives are glucose, fructose, galactose.
Glucose is the main fuel for cells and, as a result of complex multi-stage transformations, is converted into carbon dioxide and water. Sources of glucose are fruits and vegetables. Among fruits, the most of this type of sugar is found in our garden berries and fruits, plums, strawberries, and watermelon. Among the vegetables that can boast of glucose content are pumpkin, white cabbage, and carrots.
Fructose - as the name suggests, it is found most abundantly in fruits. It is more preferable for patients with diabetes because it enters the tissues without including insulin in the metabolic chain. Grapes, apples, pears, watermelons, currants, raspberries, melons are rich in fructose - that is, almost all the fruits we eat.
Galactose itself is not contained in products. Combining with glucose, it forms lactose, the sugar in milk. Milk contains the most lactose; fermented milk products are somewhat less rich in this sugar.
Sucrose is a symbiosis of glucose and fructose. This compound is called empty sugar (a carrier of empty calories). Contained in beets, peaches, melons, plums, tangerines. In food products, there is a lot of sucrose in jams, honey, various sweets and drinks.
Complex sugars - the vast majority are glucose compounds - starch, inulin, glycogen.
Starch - occupies 80% of all carbohydrates consumed in food. Starch is found in bread, flour, cereals, potatoes, corn, pasta, and legumes.
Inulin is a fructose compound. This polysaccharide is found in Jerusalem artichoke and bananas, chicory (root), onions and garlic.

Glycogen is made up of glucose molecules. Contained in small doses in meat products (liver, etc.), honey, refined sugar, raisins, dates, chocolate, persimmons, figs, bananas, gingerbread.
Types of complex carbohydrates
Polysaccharides or long carbohydrates are large chains of compounds that, when broken down, can provide much more energy than simple ones. Complex carbohydrates are digested slowly and for a long time, without sudden spikes in insulin. After taking them, a person remains full for a long time, full of strength and vigor.
Fiber, starch and glycogen are complex carbohydrates. Each of them is an important component for building a harmonious diet, and ideally it should be a combination of all three types. Let's take a closer look at the features of each.
Starch is considered unique and the most valuable; about 80% comes from healthy carbohydrates from starchy foods. Compared to simple compounds, the product has longer chains consisting of glucose molecules. Similar polysaccharides are found in foods such as cereals, pasta and baked goods, rice and cereals, green beans and potatoes. There are also processed forms - these are short polymers of glucose and maltodextrin. They dissolve perfectly in water, which facilitates immediate entry into the bloodstream after administration.

This product has another big advantage - the absence of a side effect in the form of bloating. Complex compounds are recognized as the best sources of energy, so every athlete should add them to their diet.
Fiber – This substance is usually very neglected by many people. There is a lot of it in fruits and vegetables, legumes and grains, as well as nuts. Its structure is not a starchy polysaccharide, but in common parlance it is dietary fiber.
Has a number of features:
- there is no possibility of digesting fiber due to its resistance to digestive enzymes;
- reduces the risk of oncological pathologies of the colon, diabetes mellitus and diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- lowers levels of “bad” cholesterol;
- promotes the excretion of bile acid.

Fibers can be soluble or insoluble. Agree, not many people know which carbohydrates are insoluble in water and why they are needed. In the meantime, there are a number of advantages for athletes:
- The insoluble group helps improve the digestion process by slowing down the hydrolysis of starch, and also helps remove breakdown products and slow down the absorption of glucose.
- A group of soluble fibers slow down digestive activity and lower cholesterol levels. Like insoluble fiber, it slows down the absorption of glucose.
Glycogen - the chain contains several glucose molecules. Immediately after eating, glucose enters the bloodstream, the excess of which is stored in the form of glycogen. For example, during physical activity, glucose levels drop, the body begins to break down glycogen with the help of enzymes, returning glucose levels to normal. Even during the training process, all organs can produce energy in sufficient quantities.
The main places where glycogen accumulates are muscles and liver. The total amount varies in the range of 300-400 g. In the process of building the body, glycogen from muscle fibers is extremely important.
Under the influence of physical activity, fatigue occurs due to the depletion of stored glycogen. In this regard, one and a half to two hours before the start of training, you need to consume foods high in carbohydrates in order to replenish glycogen reserves.
The table provides specific examples of each type of long connection.
| Polysaccharides | ||
Starch:
| Soluble Fiber:
| Insoluble fiber:
|
What are simple sugars?
Carbohydrates are molecules that contain one, two, or more sugar molecules called saccharides (1).
They supply four calories per gram and are your body's preferred source of energy.
There are two main types of carbohydrates: simple and complex. The difference between them is the number of sugar molecules they contain.
Simple carbohydrates - also known as simple sugars - contain one or two sugar molecules, while complex carbohydrates have three or more molecules.
Simple sugar can be a mono- or disaccharide.
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates because your body cannot break them down any further.
This allows your body to absorb them quickly and easily, with the exception of fructose.
There are three types of monosaccharides (1):
- Glucose : Fruits and vegetables are natural sources of glucose. It is also often found in syrups, candies, honey, sports drinks and desserts.
- Fructose : The main natural dietary source of fructose is fruits and berries, which is why fructose is commonly called fruit sugar.
- Galactose : The main dietary source of galactose is lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products such as cheese, butter and yogurt.
Disaccharides
Disaccharides consist of two sugar molecules or two monosaccharides linked together.
Your body must break down bound monosaccharides before they can be absorbed.
There are three types of disaccharides (1):
- Sucrose (glucose + fructose) : Sucrose – most commonly called table sugar – is a natural sweetener derived from sugar beets or sugar cane. It is added to food during processing and occurs naturally in fruits and vegetables.
- Lactose (glucose + galactose) : Also known as milk sugar, lactose is found in milk and dairy products.
- Maltose (glucose + glucose) : Maltose is found in malt beverages such as beer and malt beverages.
Simple sugars contain one or two sugar molecules. A carbohydrate with one sugar molecule is called a monosaccharide, while a carbohydrate with two sugar molecules linked together is a disaccharide.
How does carbohydrate metabolism occur?
Food containing complex carbohydrates in the gastrointestinal tract can be broken down into simple compounds, namely glucose, after which it is absorbed into the blood. A hormone (insulin) is synthesized, which converts the product into glycogen. The process lasts until blood glucose levels stabilize.
Glycogen reserves are located in muscle fibers and liver cells. During training, reserves in the muscles are depleted, and reserves in the liver are aimed at maintaining the required level of glucose in the blood. The norm is considered to be from 80 to 120 mg/dl.
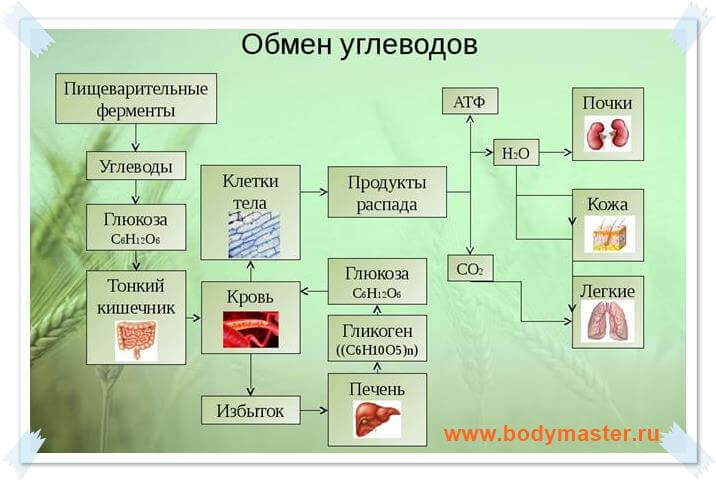
In case of a lack of nutrients, glycogen from the liver is converted back into glucose and enters the blood - all this is necessary to maintain the normal functioning of the body.
What happens when you have too many carbohydrates?
If complex carbohydrates enter the body in excess, this helps to increase insulin production, no matter what foods are consumed. Overload of the pancreas leads to depletion of its cells, which, if there is a tendency, can cause diabetes mellitus. A completely unpleasant bonus to everything will be the deposition of fat with an excessive concentration of glycogen.
When complex carbohydrates are consumed in excessive amounts and are poorly chewed, fermentation processes are started in the intestines. This is not only bloating and discomfort during training, but also poisoning the body with toxins from the intestines. In medicine this is called fermentative dyspepsia.
What happens when there is a lack of carbohydrates
If, when planning your diet, you strictly cut carbohydrates for a long time, this can lead to irreversible metabolic disorders. The body will not receive important energy from food, so it begins to waste glycogen from the liver, which provokes a disruption in its activity.
When there are no food sources of carbohydrates, the process of protein breakdown is activated to obtain the necessary energy. As a result, the destruction of muscle mass begins, which was built so long and diligently in the gym. It should be noted that the process also affects the heart muscle. All these factors make a long-term and grueling low-carb diet extremely detrimental to a person.

Low levels of glucose in the blood provoke exacerbation of hunger, and prolonged deficiency leads to weakness and lack of energy, nausea and sweating, headaches and systematic dizziness, tremors and tachycardia. This is called hypoglycemia, which is made worse by insulin resistance (metabolic syndrome).
Expert opinion
Smirnov Viktor Petrovich Dietitian, Samara
All slow polysaccharides and their representatives are truly “long-range artillery” and lead to long-term saturation of the body. Of these, the table shows not only exogenous, but also endogenous carbohydrates, which are practically not found in products; they cannot be found on sale in their pure form. This is animal starch - glycogen. After eating, it is formed in our liver, into which glucose enters under the influence of insulin. In glycogen, sugar is stored in the form of condensed glucose residues. Glycogen in our body is the first “accumulator” of energy and, gradually breaking down again into glucose under the influence of the counter-insular hormone glucagon, ensures its concentration in the blood plasma. It is on the first and even the second day of complete fasting that all adequate carbohydrate consumption, including for the functioning of the brain and myocardium, is ensured due to the slow breakdown of glycogen. And only on the third or fourth day of fasting does an acidotic crisis begin, when the body begins to look for other metabolic pathways, activating lipolysis, or the breakdown of fats. Other types of slow carbohydrates are also irreplaceable, and especially pectins and fiber. Fiber differs from all carbohydrates in that at first glance it is a ballast substance: it is not nutritious, since it is not absorbed by the body. But it is fiber that binds various exotoxins and radionuclides, prevents dysbiosis, stimulates peristalsis and is very useful in the fight against atonic constipation.
Clinical picture
Excessive consumption or deficiency of carbohydrates can be harmful to health. To maintain normal metabolism, you need to include at least 60% of a macronutrient in your diet every day.
What doctors say about losing weight
Nutritionists and trainers very often in practice are faced with the stereotype that in order to lose weight it is necessary to either critically reduce the amount of carbohydrates or give them up altogether. The root of the evil is the lack of information and a large number of false facts that can be read in popular communities. Such actions will not only weaken the immune system, but will also seriously undermine your health.
Experts also believe that in the process of losing excess weight, slow carbohydrates improve peristalsis and intestinal microflora. The component is also indispensable during muscle mass gain. Recipes for each purpose can be found at the end of the article.
The role of carbohydrates in the body
The main role of carbohydrates is to provide the body with energy for the normal functioning of all life processes. Among the secondary, but no less important, functions are:
- protective - the formation of certain types of immune cells, as well as mucopolysaccharides that protect the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract from the penetration of bacteria, is impossible without a sufficient supply of complex carbohydrates;
- plastic - carbohydrates are part of cell membranes, a number of enzymes, and participate in the construction of nucleotides and nucleic acids necessary for the release of energy in cells and the construction of cartilage tissue;
- prebiotic - some types of complex carbohydrates (for example, fiber) are not broken down, but play a significant role in regulating the work of the small and large intestines, the formation of chyme and are a breeding ground for beneficial bacteria in the intestines;
- osmotic - carbohydrates participate in the regulation of osmotic pressure, which ensures the normal flow of blood plasma in the vessels;
- strategic - when carbohydrates are supplied, part of the energy is stored in the body in the form of glycogen and fat deposits for later use.
Where are complex (slow) carbohydrates found - list of products
We have already figured out what long-term carbohydrates are, and now let’s talk about which foods contain them the most.
The key rule of proper nutrition is that it is better to consume slow carbohydrates in the first half of the day, and this is due to the most successful time for their absorption. However, if the workout is planned for the evening, then there is nothing critical in eating foods that contain these macroelements for dinner. In the case when the main goal is weight loss, it is best to give preference to fiber, which quickly saturates and is not absorbed by the body. At the stage of gaining muscle mass, it is better to switch to ingredients rich in starch and glycogen, but you should not forget about protein foods either.

To make it easier for you to choose complex carbohydrates to achieve your goals, we have provided a table with the most popular ingredients in descending order of macronutrient amount.
| Product groups | Name | Amount of carbohydrates per 100 g |
| Whole grains | corn grits | 75 |
| Brown rice | 72,9 | |
| barley | 71,7 | |
| wheat | 69,3 | |
| buckwheat | 68 | |
| oats | 66,2 | |
| spelled | 61,2 | |
| quinoa | 57,2 | |
| Whole grain bread and pasta | durum pasta | 71,5 |
| wheat bread | 53,4 | |
| Rye bread | 49,8 | |
| Legumes | chickpeas | 61 |
| lentils | 60 | |
| beans | 52,7 | |
| green beans | 3,6 | |
| Nuts | cedar | 28,4 |
| cashew | 22,5 | |
| almond | 21,7 | |
| hazelnut | 9,4 | |
| walnut | 7 | |
| Milk products | yogurt 1.5% | 7,4 |
| milk 2.5% | 4,7 | |
| cottage cheese 1.8% | 3,3 | |
| Fruits and berries | banana | 21 |
| grape | 15,4 | |
| apple | 13,8 | |
| raspberries | 11,9 | |
| plum | 11,4 | |
| pear | 10,3 | |
| orange | 8,1 | |
| strawberry | 7,5 | |
| currant | 7,3 | |
| Vegetables | potato | 18,1 |
| carrot | 6,9 | |
| broccoli | 6,6 | |
| pumpkin | 6,5 | |
| cauliflower | 5,4 | |
| tomato | 3,7 | |
| cucumber | 2,8 |
Contents by groups, differences
As you have seen, complex carbohydrates are synthesized in various ingredients, and the following list of generalized foods reveals their main characteristics.
Vegetables and fruits are an indispensable and key component of a healthy diet for any person, regardless of the specifics of training. Vegetables and fruits contain complex compounds. To obtain the maximum amount of useful substances, it is recommended to consume them raw, because any method of heat treatment suppresses their numbers.

Greens - experts highly recommend including this ingredient in your menu, because... it can not only enrich it with useful substances, but also normalizes the processes of digestion and the excretory system.
It’s not for nothing that they say that porridge If they are prepared on the basis of whole grain cereals, which are classified as complex compounds, then this is the best option for daily nutrition. It is recommended to avoid highly processed products because... they have a high glycemic index and negatively affect the weight loss process. Displays the glycemic index, the level of blood glucose response to any product.
Dairy products contain lactose, which classifies these products as simple carbohydrates. But this does not mean that you need to abandon this source, because low-fat products still contain slow chains and are rich in calcium and phosphorus.
Legumes and grains are another great source of energy. You can significantly increase your intake of this macronutrient by replacing processed grains with legumes. Replacing wheat bread with a whole grain product can significantly increase your fiber intake.

Freshly squeezed juices are a liquid form of complex carbohydrates from fruits and vegetables, consumed in the form of drinks.
How to increase your polysaccharide intake
Supermarket products now have all grain alternatives, so it's not that difficult to make them a big part of your diet:
- Switch from white bread to whole/low-grade/multi-grain flour bread. You can also easily find wholemeal white bread that is better for you;
- make it a habit to eat high-fiber foods and low-calorie grains in the morning, the best choice being oatmeal;
- Try eating brown rice and wholemeal pasta more often than white rice and pasta.
- increase your daily intake of vegetables and fruits.
Video
However, the GI does not take into account the different ways the body processes polysaccharides from starches such as brown rice or oatmeal versus a simple carbohydrate such as an apple. Therefore, we cannot use the GI as the sole measure to determine whether the carbohydrate we choose will help us lose weight or not. In other words, most foods classified as polysaccharides will have low GI values, but there are exceptions, such as some fruits.
The benefits of complex carbohydrates
Excessive macronutrient content in the diet can negatively affect the health and fitness of an athlete, but its role is extremely important in the life of the body:
- The main source of energy - carbohydrate provides fuel for a full, productive workout. The daily requirement is calculated individually;
- after the reserves of glucose and glycogen are depleted, thanks to the slow chains of the macroelement, the consumption of protein as an energy source does not turn on. This phenomenon is called glycogenesis and occurs when blood glucose levels are low. Accompanied by the release of glucagon;
- prevents the process of catabolism and muscle atrophy, which leads to loss of muscle mass as a result of the process of glucogenesis;
- Another huge benefit from consuming healthy carbohydrates is that they can improve brain function and maintain the central nervous system in a normal state. Glycogen does not accumulate in the brain, therefore, on a low-carbohydrate diet, athletes often observe a decrease in mental activity, especially concentration;
- Eating nutritious meals with enough carbohydrates prevents hypoglycemia, the symptoms of which are: hunger, loss of energy, migraines and dizziness. To avoid experiencing such feelings during training, it is important to make sure that your diet meets the standards.

1 - Slow Carbs Are Less Likely to Cause Blood Sugar Spikes
Bad carbohydrates can significantly increase blood sugar levels, which forces the pancreas to produce a large dose of insulin. This not only returns the feeling of hunger, but also provokes you to eat another portion of sweet food. Complex types of carbohydrates take much longer to digest than simple carbohydrates, which helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, providing a boost of energy throughout the day and during the training process.
2 - Complex carbohydrates may reduce the risk of some chronic diseases
For a healthy and nutritious diet, it is important to eat foods containing complex carbohydrates, which will not only significantly reduce the risk of gaining excess weight, but will also help prevent the development of chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular pathologies. All sources of slow carbohydrates are rich in dietary fiber, vitamins and minerals, as well as antioxidants and plant compounds - this complex provides excellent prevention of diseases of various types.
It should be noted that many studies support the positive association between low levels of “bad” cholesterol and blood sugar with a diet that includes fiber from whole foods.
3 – Long-lasting carbohydrates promote a healthy digestive system
The human intestine contains a huge variety of “good” bacteria – these are microbiota. They promote healthy digestion, better absorption of minerals, neutralize inflammatory processes in the intestines, and also fight constipation. All foods containing complex carbohydrates contain large amounts of soluble fiber, which promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria by feeding them. The bacteria in turn produce short-chain fatty acids, which are extremely beneficial for the digestive system. If you feed them with the right macronutrients, you can forget about the craving for overeating, which is very important on a diet.
4 – Long Carbohydrates May Reduce Inflammation
Inflammation is the human body’s response to internal stimuli. A prolonged nature contributes to the development of chronic forms of diseases of the cardiovascular system, hypertension and diabetes, metabolic syndrome and even cancer.
Sweet products and refined flour provoke inflammation, and complex types of carbohydrates help counteract its occurrence. Fiber, found in whole grains, fruits and legumes, has anti-inflammatory effects.
How to start eating more complex carbohydrates
In order for healthy carbohydrates to bring the most positive results both in the training process and for health in general, you may need to adjust your eating habits and choose foods that contain slow carbohydrates. For example, buy pasta and bread from whole wheat, and not from premium varieties. Give preference to vegetable snacks rather than fatty chips. Replace polished white rice with other sources of complex carbohydrates - legumes or unprocessed cereals.

Polysaccharides for weight loss
Many nutritionists don't use the word "bad" when describing foods because, as the saying goes, "there are no good or bad foods, only good or bad diets." With that said, carbohydrates that have a rapid rise in blood sugar levels are generally considered fast or light, while those that are absorbed slowly and have little effect on blood sugar are considered slow or heavy.
Please note: The glycemic index was created to measure the rate at which carbohydrates are converted into glucose. Fast-digesting foods have a high index, which ranges from 0 to 100, while “slow” foods have a lower index.
This is important because large spikes in insulin levels affect your hunger (can make you even hungrier), can negatively impact weight loss, and can even lead to diabetes if levels are chronically elevated from eating too much fast carbohydrates.
Advice from nutritionists

Replace sweets with fruits
- Nutritionists advise eating more plant foods and replacing sweets with fruits. After all, fruits are sweet enough to satisfy your “sweet hunger.”
- If you want to lose weight, you need to do this gradually and systematically, without strict diets, fasting and pills.
- Do not make strict restrictions on food. With very strong restrictions, the likelihood of breaking the diet increases. With such measures, appetite increases even more.
- Anyone who wants to lose weight cannot do without physical activity. It is advisable to walk in the fresh air, moving at an active pace.
- Don't try to lose weight quickly. In weight loss, the main thing is not the speed, but the duration of maintaining the achieved weight. With gradual weight loss, the skin will have time to tighten, and health will be maintained.
- Proper nutrition should become permanent. You need to eat 5-6 times a day, eat more plant foods.
- When choosing fruits, it is worth considering that large ones with an impeccable appearance may contain harmful substances.
By adding low-carb fruits to your diet, losing weight will still not be very easy. Only by consuming them in combination with moderate physical activity and proper nutrition can you achieve good results. Fruits should be included in the diet throughout the year. If some cannot be kept fresh, you can prepare them for the winter by drying or freezing.
Let me introduce myself!
We know from the school chemistry curriculum that carbohydrates, being organic compounds, are included in absolutely any living organism.
The name says it all: carbohydrate = carbon + water.
From a nutritional point of view (from which we will consider them), carbohydrates are an indispensable catalyst for the process of converting proteins and fats into other useful substances.
In other words, without them it is not at all possible for our body to function without problems.

The most common type of carbohydrate in the body is glucose.
It is in this “guise” that they take root in human organs and systems.
Glucose belongs to the group of so-called “simple” carbohydrates (also called “fast”), because they have a simple chemical structure.
In contrast to simple ones, there are also “complex” carbohydrates (the second name, accordingly, is “slow”).
We will focus your attention on them in more detail.
Fruits in human nutrition
Fast and slow carbohydrates
The main sources of carbohydrates are plant products. Fruit carbohydrates are of great importance in nutrition. They are well absorbed by the body and have a good effect on liver activity. Fruits are an excellent source of vitamins and minerals. They are usually consumed fresh, separately from main meals. Half an hour before any meal, it is good to eat some fruit. This promotes weight loss and maximum absorption of all vitamins and microelements contained in the fruits.

Fruits are an excellent source of vitamins and minerals
Helpful information! Nuts, vegetables, fruits are ideal food for humans. For example, hazelnuts stimulate metabolism in the body and increase metabolic rate.











