While there are many hotly debated nutrition topics, few generate as much passion and interest as carbohydrates. Diets based on them are unpopular, but what do we know about them? Carbohydrates are the main macronutrient and one of the main sources of energy for your body, they come in different types - simple and complex, or they are also called light and heavy, fast and slow. Simple or light carbohydrates are not good for health, as they quickly increase blood glucose levels and lead to obesity. Complex or heavy carbohydrates are beneficial because they have a slow effect on glucose levels and promote weight loss.
Complex carbohydrates are the familiar wheat, corn, rice, oats, barley, malt, rye, fruits, vegetables, legumes and much more. The difference from simple ones is that they consist of many glucose molecules joined together. Because the structure of these molecules is more complex than simple carbohydrates, these foods take much longer to digest. Carbohydrates are made up of three components: fiber, starch and sugar. Fiber and starch are heavy carbohydrates or polysaccharides, and sugar is a simple (monosaccharide). Depending on how many different components are found in a product, the quality of its nutritional properties is determined. Of great value for weight loss are low-glycemic heavy carbohydrates, which contain a minimal amount of sugar in their formula and, therefore, are much more beneficial for health and figure.
Types of heavy carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are found in foods including fruits, vegetables, grains, potatoes, baked goods and candy and are considered a preferred source of energy for the organs. Carbohydrates are sugar molecules that are a combination of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen (CHO). That is, in essence, it is one or more sugar molecules that are broken down by metabolism to be used for energy. Complex, or heavy, carbohydrates contain more nutrients than simple carbohydrates (monosaccharides) because they have more fiber and are digested more slowly. This also makes them more filling, which means they are a good option for weight loss. Carbohydrates are also ideal for people with type 2 diabetes because they help manage blood sugar levels after meals.
Complex carbohydrates: food list
Without thinking through your diet, it is impossible to organize proper nutrition. Complex carbohydrates must be included in the menu, a list of which, along with a description of the action, is presented in this article.
Starch is a complex carbohydrate
Starch is very different in structure from simple carbohydrates, as it is built from long lines of glucose molecules. The polysaccharides present in processed form are the glucose polymer, maltodextrin. These polysaccharides have shortened polymers, unlike the solid form such as potato starch. The latter are characterized by excellent dissolution in water.
That is why they are rapidly introduced into the blood. There is no bloating when consuming starch. It is strictly not recommended to replace complex carbohydrates with simple ones. Otherwise, obesity and diabetes may develop. In general, complex carbohydrates, including the plant-based substance starch, are positioned as the best source of energy.
Fiber and starch
These two components represent two types of difficult-to-digest carbohydrates. Fiber is especially important because it promotes bowel regulation and helps control cholesterol levels.
The main sources of dietary fiber are:
- fruits
- vegetables
- nuts
- beans
- whole grains
Starch is also found in some fiber foods. The difference is that some foods are considered more starchy than fibrous, such as potatoes.
Other foods high in starch:
- whole wheat bread
- wheat
- corn
- oats
- peas
- rice
What complex carbohydrates are is the key to long-term health and weight loss. They make it easier to maintain your weight and may even help protect against type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular problems in the future.
Slow carbohydrates - substances necessary for daily consumption
Carbohydrates, the list of products with which is replenished with flour, confectionery and plant foods, increase the functional activity of internal organs. Various types of polysaccharides are necessary for regulating metabolic processes in the body and normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Complex carbohydrates cleanse the digestive organs of toxins and excess fluid, and are involved in maintaining hormonal levels.
Starch
Required to regulate a number of protein compounds and enzymes responsible for the gradual absorption of glucose into the blood from the small intestine and the body's cells. By obtaining starch from food, the risk of developing sharp jumps in plasma sugar concentrations after eating foods with a high or medium GI value is reduced.
Glycogen
Formed from excess glucose in the liver and skeletal muscles. In a critical situation, it breaks down into sugar, which can be absorbed by the body's cells and processed into energy. This occurs when ATP and creatine are depleted.
Glycogen is often formed after eating large amounts of dried fruits, confectionery and starchy vegetables.
Cellulose
Plant fibers are found in fruits, berries, vegetables and nuts. They come in 2 types: soluble and insoluble. The former soften stool and speed up its elimination from the body, and are used as a preventive measure for constipation.
Insoluble or rough fiber is practically not digested by the body. It absorbs excess liquid in the gastrointestinal tract, swells and puts pressure on the walls of the stomach from the inside, making a person feel full.
Dietary fiber acts as an absorbent that absorbs toxins and, along with them, is eliminated from the body. Coarse fiber improves intestinal peristalsis, which results in rapid elimination of waste materials. The daily value of insoluble fiber is about 35-45 g.
Insulin
Insulin is formed by pancreatic cells from complex carbohydrate compounds. This hormone reduces the plasma concentration of glucose in the blood, preventing the risk of developing diabetes. Insulin increases the sensitivity of tissues to sugar, due to which cells begin to intensively absorb it and process it into energy.
What are monosaccharides and polysaccharides needed for?
Remember that carbohydrates are just sugar molecules, all of which are broken down into glucose by the body. Glucose is the only sugar molecule that is used as fuel by your body's cells from your brain to your muscles.
There are 3 types of carbohydrates, which are determined by the number of sugar molecules they contain:
- Monosaccharide - one sugar molecule, examples include glucose, galactose (in milk) and fructose (in fruit).
- Disaccharide - two sugar molecules, examples include sucrose, lactose (in milk) and maltose (in beer).
- Polysaccharides are several sugar molecules, examples include starchy foods such as pasta or potatoes, and fiber, which is an indigestible part of the plant but aids digestion.
When carbohydrates are "simple", they are mono and disaccharides that are easily absorbed into the bloodstream due to their simple molecular structure. We are talking about milk, fruit and table sugar. On the other hand, "complex" macronutrients are polysaccharides, and due to their more complex molecular structure, it may take longer for the body to break them down into sugar. This refers to grains, vegetables and potatoes.
Please note: Any excess glucose that is not used by the body for energy will be stored as fat. Therefore, to lose weight, combine heavy carbohydrate foods with active training.
Knowing how each of these molecules fits into your daily diet can help you get a mixture of polysaccharides in your diet for weight loss and healthy eating.
Complex carbohydrates
10.01.2020 08:00:00

What are complex carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates are organic compounds whose main sources are plant foods. This component is considered the main food element that carries energy. There is a list of foods with complex carbohydrates. Among them, mention should be made of potatoes and cereals, which contain the bulk of this substance. In various diets, the content of this element should reach fifty percent to ensure energy balance. The structure of complex carbohydrates is represented by at least two molecules of monosaccharides (simple sugars), which, in turn, are digestible and non-digestible (fiber). Their synthesis is carried out by plants during the process of photosynthesis. They may contain several or thousands of molecules of simple sugars connected by glycosidic bonds.
Types of complex carbohydrates
It is widely known that carbohydrates are the main source of energy needed by the human body.
Simple and complex carbohydrates differ in their structure. Simple ones are distinguished by their rapid digestibility and the achievement of an instant feeling of satiety. At the same time, they contribute to an increase in blood sugar levels, which leads to a slowdown in metabolic processes. After eating, they are transformed into sugar, which becomes fat deposits. The content of these chemical compounds is high in the following foods: from milk to fruits, from some vegetables and sweets. Due to the content of this element in sweets, they help to quickly but short-term satisfy hunger. The table of foods with slow carbohydrates contains food options with a complex structure. They are characterized by long-term absorption, which helps to provide the body with energy for a long time. They are recommended for use in diets, due to the guarantee of quick and long-lasting satiety in combination with proper digestion.
They are found in a variety of foods: from grains to legumes, from beets to potatoes, from carrots to nuts. Their use does not cause insulin spikes.
What are complex carbohydrates?
- Starch, represented by large quantities of glucose molecules. Starch is a substance that is soluble in water and normalizes digestion. Contained in various products: from rice to potatoes, from buckwheat to pasta.
- Fiber has an overly complex structure, which allows for only partial digestion. Fiber helps lower cholesterol levels and increase the efficiency of food absorption. Found in a variety of foods: from whole grains to apples, from kiwis to grapes, from nuts to vegetables.
- Glycogen is an energy reserve that accumulates in the body. Contained in fish, liver and other offal.
- Pectin is a polysaccharide that helps destroy toxins and other harmful substances. Found in cucumbers, root vegetables, cucumbers.
Why are they useful?
We can talk about the beneficial properties of slow carbohydrate sources for a long time.
They cope with the main function, being a source of energy. Due to the lack of elements characteristic of many diets, problems associated with starvation of brain cells may begin. This leads to loss of concentration, increased absent-mindedness and inattention. Thanks to their sufficient quantity, mental activity increases, which improves physical activity. When asked why complex carbohydrates are useful, you can spend a long time enumerating them. They help speed up metabolic processes. Due to their deficiency, prolactin and cortisol are formed, and the thyroid gland becomes less active. These problems lead to increased feelings of fatigue and worsening mood. Externally, these processes manifest themselves in the occurrence of edema. Glycogen, in combination with fiber, helps block the formation of harmful hormones and significantly improve overall mood. Let us also note the beneficial effects of these substances on digestion. Thanks to their use, the absorption of vitamins becomes more efficient. They help achieve a long-lasting and quick feeling of satiety.
Foods with complex carbohydrates
Nutritionists recommend consuming foods that contain complex carbohydrates to speed up metabolism, without wasting glucose, with its gradual accumulation, and without the formation of unnecessary fat reserves.
Let's move on to the list of products. There are several categories of sources of complex carbohydrates.
Vegetables, greens
Valuable sources include: from carrots to cucumbers, from beets to celery, from potatoes to pumpkin, from olives to tomatoes, from onions to garlic, from cabbage to exotic Brussels sprouts. Even seaweed is recommended to be included in the diet, in combination with lettuce and, of course, spinach.
Fruits, berries
There are examples of complex carbohydrates in this category. The choice of products should be made more carefully, guided by the lower sugar content. If it is in excess, insulin levels may rise, which will lead to active division of adipose tissue and an increase in your weight.
We recommend eating more apples and peaches, pears and pomegranates, all popular and not so popular citrus fruits. They belong to complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index. Don't forget to eat: from grapes to melon, from raspberries to plums, from blackcurrants to strawberries, from blackberries to gooseberries, from figs to quince. Cereals
The beneficial properties of cereals have long been known due to their rich content of vitamins and fiber.
Therefore, foods from wheat to buckwheat, from brown rye to oats, from brown rice to beans, from lentils to beans and peas should always be included in the diet. Porridge
Milk has a not very high glycogen index, reaching 32 units. It refers to foods rich in slow carbohydrates.
Pasta
, which include products made from wholemeal flour.
Dairy products.
In addition to porridges with milk, it is recommended to eat natural yoghurts, without flavorings, kefir, cottage cheese and low-fat cream (no more than 10%). These products, due to their calcium content, have an additional “building” effect and become the savior of our bones from fractures.
Sausages
, which are rich in fast and slow carbohydrates. They should be consumed in small quantities without harmful side dishes and accompanying dishes.
Red wine
, which has slow carbohydrates, although not with the lowest glycemic index.
Tomato juice
can be consumed in its natural form or used to make a sugar-free cocktail.
The main thing is to part with your favorite buns, waffles, cookies, sweets and other goodies. But you can pamper yourself with small amounts of marmalade, fructose-based ice cream, and sugar-free chocolate bars without harming your figure.
To lose weight, you need to take care of increasing the menu items rich in complex carbohydrates. By including these dishes in your diet, you can achieve not only weight loss, but also overall health of the body. We are talking, for example, about a vegetable cocktail or a glass of tomato juice.
Among the record holders for the content of this element, mention should be made of potatoes and olives, parsley root and beets, sweet peppers and white cabbage. Among fruits, figs are preferable. It is useful to have pomegranates and cherries, apricots, pears and oranges on the menu. For cereals, we recommend corn. Instead of bread, we recommend eating wheat crackers or bran bread. For legumes, choose beans and lentils, soybeans and pine nuts.
Complex carbohydrates for weight loss
Among the most important rules for losing weight, we mention the need to reduce the amount of simple substances in combination with an increase in the proportion of complex ones.
By consuming complex carbohydrates for weight loss, fats are effectively broken down, which is due to the large amount of energy required for their absorption. It is also important to remember to exercise regularly in order to achieve not only weight loss, but also weight stabilization. If you dream of a flat stomach, you should eliminate simple carbohydrates. An important factor in losing weight is the rate of saturation. By consuming complex carbohydrates for breakfast, you can achieve quick and long-lasting satiety. You don't have to supplement your diet with constant snacking. When calculating the ideal menu, you should remember the importance of taking into account the glycemic index. This indicator is a characteristic of the rate of splitting. It is this index that determines the possibility of using the product in diets.
Among the most useful, mention should be made of cabbage and lentils, cherries, broccoli, eggplants and green peppers. Products with a high glycemic index are dangerous for extra pounds on the sides. Therefore, do without semolina, pineapples, marmalade and other complications.
The required amount of complex carbohydrates for dinner is calculated in different ways. For athletes, the figure is five grams, for dieters – three grams per 1 kg of weight. The main portion for dietary nutrition should be consumed in the morning. In the evenings you need to eat other foods.
Complex carbohydrates for muscle gain
The formation of a balanced diet should be carried out in combination with protein foods and healthy fats, which are important for our body.
Eating complex carbohydrates to gain muscle mass helps:
- providing the body with the energy necessary for strength training;
- replenishment of glycogen reserves lost during training;
- production of growth hormone, lost due to physical activity, additional stimulation of muscle growth;
- ensuring the safety of muscles (if there is enough protein, they are not a source of energy).
To prevent the deposition of nutrients into fat, and use them to increase muscles, it is necessary to ensure the distribution of the daily intake as follows:
- in the first half of the day, to replenish glycogen reserves used up by the body during the night;
- after training to replenish energy balance.
Polysaccharides for weight loss
Many nutritionists don't use the word "bad" when describing foods because, as the saying goes, "there are no good or bad foods, only good or bad diets." With that said, carbohydrates that have a rapid rise in blood sugar levels are generally considered fast or light, while those that are absorbed slowly and have little effect on blood sugar are considered slow or heavy.
Please note: The glycemic index was created to measure the rate at which carbohydrates are converted into glucose. Fast-digesting foods have a high index, which ranges from 0 to 100, while “slow” foods have a lower index.
This is important because large spikes in insulin levels affect your hunger (can make you even hungrier), can negatively impact weight loss, and can even lead to diabetes if levels are chronically elevated from eating too much fast carbohydrates.
Is there starch in buckwheat? What foods contain starch?
It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that all food products contain proteins, fats, sugars and starch in varying quantities. The latter is a complex carbohydrate, very necessary for the normal development and functioning of the human body.
This carbohydrate can be of two types:
- Natural. Feel free to consume this type without worrying about your health. Cereals, root vegetables, potatoes, lentils and cereals contain such natural carbohydrates.
- Refined. Starch can be corn, wheat, potato, rye, rice and barley. Carbohydrates fill the body with unnecessary calories. If, for example, you dilute the refined powder with water, you will get a viscous mixture that is unpleasant to the touch. It is usually used to improve the taste, as well as to regulate the consistency of products. Therefore, starch is added to various sauces, yogurts, dairy drinks, confectionery, even baby food.
Almost all foods that are in the human diet contain starch in one form or another. Fans of proper nutrition insist not to combine large amounts of this carbohydrate with proteins in their menu. Mostly grains and legumes contain these two substances. There is no need to give them up. Cereals are essential for the normal functioning of the human body. Knowing where the most starch and protein are located, balance your diet as much as possible.
Find out more about types of legumes, recipes.

Starchy legumes and grains
In all these cereals, the level of heavy carbohydrate exceeds 70%, so when following a diet, it is better to eat light soups without cereals. Cereals containing a large percentage of starch include:
- rice (more than 80%);
- corn;
- oats;
- wheat.

Legumes such as lentils, soybeans, beans, and peas contain high levels of carbohydrates. If you need to lose excess weight, it is best to exclude them from your diet for a while. There is no need to completely forget about them; the human body still needs the mentioned products due to the content of a number of useful substances in legumes.
List of starchy vegetables
This carbohydrate is found in many vegetables. Root vegetables contain the most starch, that is, those vegetables that grow underground. The group with moderate starch content includes carrots, eggplants, beets and zucchini. They go well with each other, as well as with other non-starchy vegetables. Among them, a special place in terms of the presence of starch is occupied by:
- potato;
- corn
- sweet potato;
- pumpkin;
- Jerusalem artichoke;
- radish;
- squash.
This is a long list, because this carbohydrate is found in all edible roots, including celery root, parsley and horseradish. Not obvious for such a list is cauliflower. Starchy vegetables have a specific feature: they require the addition of “light” fats. These are considered vegetable oil, cream or sour cream. The combination of carbohydrates and fats in this form will ensure optimal absorption of the dish.
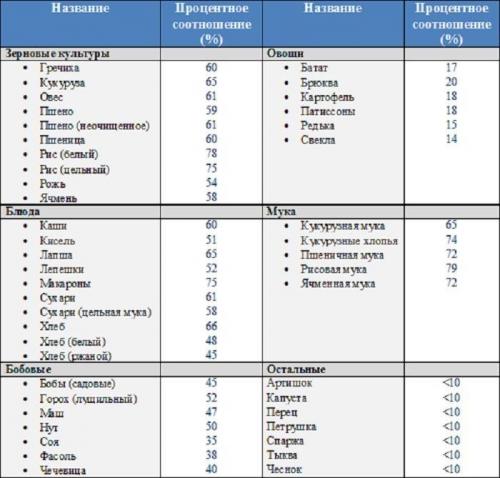
What foods contain polysaccharides?
To clearly understand what complex carbohydrates are, look at the table; it presents a list of weight loss products, where GI is the glycemic index.
| Product | GI |
| Yeast dough, beans | 50 |
| Peas, whole grain bread | 40 |
| Skim milk, apples | 35 |
| Dried beans, pasta, fresh fruit | 30 |
| Whole milk, prunes | 22 |
| Eggplant, green beans, cauliflower | 15 |
This table clearly shows that the glycemic index of the products is low, which means that these products are slow, that is, dietary. You can safely eat them and lose weight. But don't overdo it - remember that excess sugar that is not absorbed as energy is stored as fat. Print the table and hang it on the refrigerator so you don’t mix anything up.
Features of the metabolism of complex carbohydrates

Complex carbohydrates are broken down in several stages:
- Under the action of oral enzymes, the substance passes into an intermediate state.
- In the stomach, the transformation ends and gradual absorption begins.
- Part of the glucose is used to cover the current needs of the body: transmission of nerve impulses, brain function, contraction of skeletal muscles and smooth muscles of organs and blood vessels.
- The excess is transformed into glycogen, which is stored in tissues and organs.
- Whatever remains is converted into fatty acids and stored as fat.
This is a very simplified view of the process. The key feature of the metabolism of complex carbohydrates is its duration, which is precisely due to the need to decompose the substance in several stages. By comparison, it takes about 20-30 minutes to absorb simple substances. Difficult ones - about several hours. This is precisely where the beneficial properties of slow carbohydrates in organizing the diet and proper nutrition flow.
How to increase your polysaccharide intake
Supermarket products now have all grain alternatives, so it's not that difficult to make them a big part of your diet:
- Switch from white bread to whole/low-grade/multi-grain flour bread. You can also easily find wholemeal white bread that is better for you;
- make it a habit to eat high-fiber foods and low-calorie grains in the morning, the best choice being oatmeal;
- Try eating brown rice and wholemeal pasta more often than white rice and pasta.
- increase your daily intake of vegetables and fruits.
However, the GI does not take into account the different ways the body processes polysaccharides from starches such as brown rice or oatmeal versus a simple carbohydrate such as an apple. Therefore, we cannot use the GI as the sole measure to determine whether the carbohydrate we choose will help us lose weight or not. In other words, most foods classified as polysaccharides will have low GI values, but there are exceptions, such as some fruits.
Balanced diet for weight loss
To normalize your diet, you must follow the following rules:
- Maintain drinking regime. It is recommended to replace carbonated and sweet drinks with green, black tea, freshly squeezed juices and mineral water. It is necessary to drink up to 1.3-2 liters of fluid per day, depending on body weight and age.
- The diet should consist of 70% plant and 30% animal food. In this case, the ratio of fruits and vegetables is maintained at 2:3.
- It is recommended to take drinks 30 minutes before. before meals and after 45 minutes. after eating. This will speed up your metabolism.
- When preparing dishes, products must be subjected to gentle heat treatment. They need to be boiled, baked, steamed. It is advisable to fry in a dry frying pan or with the addition of no more than 1 tbsp. l. olive oils.
If you want to lose excess weight, in addition to changing the daily menu, it is important to reduce the daily amount of calories to 1300-1500 kcal for women, 1600-1800 kcal for men and introduce physical activity.
Product table
A balanced diet should contain both plant and animal products. They are necessary not only to obtain carbohydrates, but also to replenish proteins and fats.
A list of healthy foods necessary for proper nutrition can be found in the following table:
| Categories | Products |
| Vegetables, fruits, leafy greens |
|
| Nuts, seeds and dried fruits (no more than 30 g per day) |
|
| Protein food |
|
| Flour products |
|
If desired, you can include in your diet up to 50 g of bitter or dark chocolate, freshly prepared coffee without milk and sugar.
Menu for the week
When following a balanced diet, it is important to eat small meals, 5-6 times a day with a break of 2-3 hours. It is necessary to make 3 main meals with portions of food of 200-300 g, between which snacks with dried fruits, freshly squeezed juices, and fruits are made.
A balanced menu for the week can be found in the following table.
| Mode | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| 1 day | 200 g oatmeal with milk 1.5% fat, baked apple with cinnamon and honey, coffee or tea without sugar | Sweet and sour apple, glass of kefir | Meat cabbage soup, mashed potatoes with chicken cutlet | 50 g dark chocolate, tea | Fish fillet, cabbage or fruit salad |
| Day 2 | 200 g buckwheat porridge with 100 g chicken breast, green tea with honey | 100 g pineapple, natural yogurt | Vegetable soup, beef with a side dish of stewed cabbage, compote | Tea, oatmeal cookies | Cottage cheese casserole, fruit salad with yogurt dressing |
| Day 3 | Omelette of 2 chicken eggs, sandwich with whole grain bread and hard cheese | 150 g cottage cheese with 2 tsp. low-fat sour cream and raisins | Fish soup, vegetable salad | Fruit smoothie | Steamed broccoli, glass noodles with chicken |
| 4 day | Muesli with yogurt, sweet apple, coffee | Sandwich with cheese and tomatoes | Chicken soup, buckwheat porridge with minced beef, compote | Fruit salad with yogurt dressing | Stewed fish with a side dish of vegetables |
| 5 day | Rice porridge with milk, tea | Freshly squeezed citrus juice, 3 biscuits | Lenten borscht, potatoes with meat and stewed cabbage | Cocoa, 30 g nuts or dried fruits | Beef baked in tomato sauce |
| Day 6 | Curd cheesecakes, green tea with honey | 200 g fruit and berry salad | Seafood soup, fish stew with rice | Oatmeal cookies, freshly squeezed vegetable juice | Baked Chicken with Steamed Broccoli |
| Day 7 | Cottage cheese casserole, fruit salad | Dried fruits, tea with honey | Stewed meat with vegetables, cabbage salad, compote or berry juice | Crispy bread with cheese, tomato juice | Sauerkraut and meat stewed with brown rice |
If dizziness, acute abdominal pain and fainting develop, you must immediately stop following the diet and return to a normal diet.
Recipes
Carbohydrates, the list of products with which is represented mainly by plant foods, are used to prepare dishes to create a balanced diet. They can be consumed during weight loss due to their low calorie content. During the diet, it is recommended to select recipes with vegetables.
Seafood salad
To prepare a light snack you need the following ingredients:
- 300 g of shelled and gullet-cleaned shrimp;
- large tomato;
- lettuce leaves;
- 1 tbsp. l. lemon juice.
Shrimp meat is boiled in water with a pinch of salt added. Lettuce leaves are separated from the stem and divided into 2-3 parts. The tomato is washed, the stalk is removed and cut into slices. All ingredients are mixed, seasoned with citrus juice.
Vegetable pilaf
To create this dish you will need the following ingredients:
- 250 g long grain rice;
- 1 tbsp. l. olive oil;
- 3-4 tbsp. l. green peas;
- 2 onions;
- fresh herbs: parsley, dill or green onions;
- 2 medium sized carrots.

Onions and carrots are peeled, washed, chopped into cubes with a knife and grated. Heat olive oil in a frying pan, then fry vegetables in it for 5-7 minutes. over medium heat. The rice is thoroughly washed and then boiled until softened. The cereal is mixed with peas, fried vegetables and chopped herbs.
Curd casserole with fructose
If you want something sweet on your diet, it is recommended to prepare a cottage cheese casserole from the following products:
- 400 g low-fat cottage cheese;
- 1 tbsp. l. oatmeal;
- 4 egg whites;
- fructose to replace sugar;
- dried fruits of your choice: raisins, dried apricots.
Beat the egg whites with cottage cheese and flour until a fluffy white mass is obtained. Dried fruits and fructose are carefully added to it. The oven is preheated to +180°C. The curd mixture is placed in a baking dish, which is pre-wrapped in foil and greased with butter. Bake for 20 minutes.
Oatmeal with cinnamon powder and fruit
To prepare the dish you will need:
- 250 g oatmeal;
- 2 sweet and sour apples;
- 500 ml milk 1.5% fat;
- cinnamon powder.

You need to prepare oatmeal with milk. Peel the apples and remove the central part with the seeds. The fruit pulp is ground on a grater. Oatmeal is mixed with the resulting mass and ground cinnamon.
Vegetable cutlets
To create an unusual dish you will need:
- 2 zucchini;
- egg;
- bulbs;
- 1 tbsp. l. olive oil;
- large carrots;
- 250 g oat flour.
Vegetables are peeled, washed in water and grated. The resulting mass is mixed with flour and a chicken egg. Cutlets are formed from the preparation and fried in olive oil until a crust appears.
So, how many polysaccharides should you eat?
The amount of polysaccharides you should eat depends primarily on your genetics, weight, and activity level.
Important: If you are not actively exercising but want to maintain weight with several workouts per week, a good benchmark for polysaccharide intake is around 200g per day.
The more active you are, the more polysaccharides you can add. Endurance athletes can and should eat around 300-400g per day to help boost their training. The minimum RDA (recommended dietary allowance) for slow-release polysaccharides is 130 grams, with 55% of total calories coming from polysaccharides as a general recommendation.
From an evolutionary perspective, polysaccharides are not essential, meaning that we do not need to consume them to function. In fact, if you don't eat polysaccharides at all, your body will break down fat into small molecules called ketones.
Important: Ketosis is the process of creating ketones when our body uses primarily fat for energy, which involves consuming less than 25g of polysaccharides (less than 100g when ketones are present in the blood and urine). Our bodies not only use fat for energy during ketosis, but they can also convert protein (both plant and animal) into carbohydrates for use as fuel.
You might be thinking, “I need to get into ketosis immediately,” given the obvious fat-burning potential. While ketosis is a forced adaptation that can leave you with low energy levels, really bad breath, an inability to concentrate effectively, and severe vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Additionally, research does not show that fat loss is greater during ketosis compared to a diet of equal calories but with many more carbohydrates. When it comes to polysaccharides, use your common sense—a few servings of fruit, plenty of vegetables (which provide few calories but tons of nutrients), some starches and grains (or a lot if you're very active) each day should help your body provide nutrients needed for optimal performance.
Physicochemical characteristics
Pure starch is a white semi-crystalline substance, tasteless and odorless, insoluble in cold water with hot forming of starch slurry. Starch is hydrolyzed only to -D-glucose, but it is not a chemically homogeneous compound - it actually consists of two fractions:
Typically unbranched amylose, consisting of glucose units linked together by oxygen atoms through -1,4-glycosidic bonds. Amylose is insoluble in cold water, but soluble in hot water, possibly with partial degradation. branched amylopectin, in which additional -1,6-glycosidic linkages are present and their number is estimated to be approximately 4%. Amylopectin dissolves in cold water (which is required, however, before a strong starch dispersion is obtained, for example by treatment with dimethyl sulfoxide). However, it should be noted that such processing should be considered as a chemical modification of starch. Interestingly, waxy starches (potatoes, corn, rice), despite containing only amylopectin, are insoluble in cold water.
Also available commercially are pregelatinized “CS” starches—cold water solubles—which are actually starch slurries dried using drying rollers.
The proportion of individual fractions in starch depends on its botanical origin. The amylose content according to various literary sources is: 10–35%, 14–27%, 10–20%, the rest is amylopectin. The proportion of amylose in starch from the most popular raw materials is: potatoes - 21%, corn - 28%, waxy corn - 0%, wheat - 28%, tapioca - 17%.
Starch can be detected with iodine or Lugol's fluid, which contains iodine. A 1% aqueous solution of starch is used to detect molecular iodine. Under the influence of iodine, starch acquires a blue-violet (starches containing amylose) or brown-red (starches containing exclusively amylopectin) color. This is due to differences in the ability to bind iodine before amylose and amylopectin, which are 20% and 0.2%, respectively. The degree of polymerization is another factor determining iodine-binding capacity, and only >200 chains are characterized by high iodine-binding capacity.
During acid hydrolysis, starch breaks down into increasingly shorter polysaccharide chains, forming in turn:
amyldextrins (stained blue with I 2 ) erythrodextrins (stained red with I 2 ) achrodextrin (not stained with I 2 ) maltose and glucose.
Polysaccharides You Should Eat More of
If you are serious about eating a carbohydrate-heavy diet, then you need to know which foods contain complex carbohydrates. Be sure to include them as a regular part of your diet:
- Grains are good sources of fiber, as well as potassium, magnesium and selenium. Choose less processed whole grains, such as buckwheat and whole wheat pasta.
- Fiber-rich fruits such as apples, berries and bananas (avoid canned fruits as they usually contain added syrup).
- Vegetables rich in fiber. Eat more of any vegetables, including broccoli, leafy greens and carrots.
- Legumes. In addition to fiber, they are good sources of folic acid, iron and potassium.
Selecting slow polysaccharides can take some trial and error. But taking an inquisitive look at the labels of the foods you buy can help you start making healthier choices that will activate your body and protect it from long-term complications.
Complex carbohydrates food list - we reveal secrets and give advice on Pitanie4Zdravie.ru
Benefits of Resistant Starch
Resistant starch is too valuable to forget and has many beneficial properties. Here are the main ones:
Resistant starch supports beneficial intestinal microflora and inhibits pathogenic ones
Butyrate, which is formed when resistant starches are broken down by enzymes of beneficial bacteria, serves as food for them. Good microflora develops, while suppressing the growth of pathogenic microflora.
Participates in the regulation of blood sugar levels
One of the most important properties. Resistant starches are “slow” carbohydrates. They are broken down by bacterial enzymes, mainly into short-chain acids and a small amount of glucose, unlike regular starches, which produce simple sugars. The effect of resistant starches on blood sugar and insulin levels is being actively studied. It has been proven that adding this type of starch to food helps stabilize sugar levels at low levels and increases insulin sensitivity.
This property is especially important for those who are overweight, suffering from diabetes and prediabetes. Starch breaks down slowly and gives a gradual release of glucose into the blood
Thanks to this, the level of insulin does not increase, which “helps” increase fat reserves. Moreover, preventing a sharp rise in sugar also manifests itself at the next meal. For example, if you eat food with resistant starch for breakfast, your blood sugar will not spike at lunchtime.
It has been proven that tissue sensitivity to insulin decreases by 40% when body weight exceeds 35-40% of normal.
Increased insulin sensitivity (or decreased insulin resistance) occurs with regular consumption of foods containing resistant starch.
This effect of resistant starches is also important for all people in terms of preventing disease and maintaining overall health.
Resistant starch helps in weight loss
Along with fiber and protein, resistant starch provides a lasting feeling of fullness and a minimum of calories. We get about 2 kilocalories from 1 gram of resistant starches, while from 1 gram of digestible starches we get 4.2 kcal. Resistant starches promote the involvement of fat reserves in metabolism.
Improves absorption and bioavailability of minerals
The elements we need, such as calcium and iron, are usually in a bound state and therefore difficult to absorb. We often experience a deficiency of these important elements. When starch is fermented by intestinal microflora, conditions are created for better absorption of minerals. Studies have shown a significant increase in the absorption of iron and calcium, phosphorus and zinc in the colon.
Improves intestinal motility
Irregular bowel movements, constipation or diarrhea can often be reduced by including resistant starch in the diet. It supports beneficial intestinal microflora - one of the main conditions for healthy digestion. Beneficial bacteria actively prevent diarrhea and help form proper stool.
Prevention of bowel cancer
One of the main reasons to include resistant starch foods in your diet is to prevent colon cancer. Mortality from intestinal cancer is in third place on the planet among malignant tumors. A lot of research work is being done in this direction around the world.
Damage to the DNA of intestinal cells and mutations lead to the formation of cancer cells. It has been revealed that the constant intake of butyrate into the colon triggers a program of self-destruction of altered cells. If there is little butyrate in the intestines and our microbiome is “hungry,” then it cannot protect us from cancer cells. By consuming foods containing resistant starch, we support our microbiome and, thus, our health.
BMI (BODY MASS INDEX) CALCULATOR ONLINE
The body mass index was developed by the Belgian sociologist and statistician Adolphe Quetelet back in 1869. Since then, calculating body weight has become much easier than estimating by eye or asking friends: “I haven’t gotten fat, have I?” But there are also disadvantages here: body mass index does not give a 100% result. The free online BMI calculator (which will help you calculate your body mass index) should be used for indicative purposes only. For example, athletes and those who regularly go to the gym will have an inaccurate mass index because muscle literally weighs more than fat.
Interesting: BMI norms in different countries can differ markedly from each other. If you believe the WHO (World Health Organization) body mass index tables, it is not difficult to understand that the average is considered the norm. But this does not mean that a person with an average BMI would not be considered “overweight” in the conventional sense.
Body mass index: analysis of results
So, you have calculated your body mass index using our calculator. Our BMI calculator is maximally adapted to the characteristics of residents of Europe and Russia. Now it's time to interpret the data and find out the results. So:
- 16 or less – pronounced weight deficiency,
- 16 – 17.9 – insufficient body weight,
- 18 – 24.9 – normal weight,
- 25 – 29.9 – overweight (preobesity),
- 30 – 34.9 – 1st degree obesity,
- 35 – 39.9 – 2nd degree obesity,
- 40 or more – grade 3 obesity (morbid).
Calculating BMI taking into account age leads to the following results:
- The normal BMI, depending on age in children, ranges from 15 to 18;
- 19-24 years: normal BMI is 19.5 for women and 21.4 for men;
- 25-34 years: Normal BMI is 23.2 for women and 21.6 for men;
- 35-44 years: Normal BMI is 23.4 for women and 22.9 for men;
- 45-54 years: Normal BMI is 25.2 for women and 25.8 for men;
- after 55 years: the normal BMI is 27.3 for women and 26.6 for men.
Let us remind you once again that these data are approximate. But given the magnitude of the error, certain conclusions can be drawn: body weight is normal or far from it. BMI norms may vary depending on standards and trends. Until 1998, in the USA, a BMI of up to 27.8 kg/m² was considered normal, but after 1998 the standards were changed, and the BMI norm recommended by doctors began to end at 25 kg/m².
How to Use Potato Starch + Healthy Substitutes
Potato starch is not an expensive product and is sold in grocery stores, health stores and online. Some products labeled as "potato starch" actually have "potato flour" as the only ingredient, so be sure to read the label carefully. If you buy potato starch, you need to make sure that it is non-GMO and made only from organic potatoes.
Potato starch is commonly used to thicken sauces, stews, soups, custards and puddings. It is also often used in gluten-free and Easter baking
If you are using potato starch as a thickener for a hot liquid, it is important to ensure that it does not boil because this will make it difficult to thicken. If you don't have potato starch on hand, you can't substitute potato flour.
Potato flour has a distinct potato flavor and also has a heavier consistency.
Arrowroot starch is a healthy substitute that has many beneficial properties. Non-GMO cornstarch is also gluten-free and is a more nutrient-dense alternative to potato starch. While cornstarch is preferred for thickening dairy-based liquids, arrowroot works well with acidic liquids. Corn starch and arrowroot can be used in place of potato starch in a one-to-one ratio (8).
Glycemic index of foods

We must not forget about the glycemic index. It is known that nutritionists and biochemists have determined the amount of glucose that enters the bloodstream after consuming certain carbohydrates.

The glycemic index (GI) is a characteristic of a certain product, which shows how much it can increase blood glucose levels compared to pure glucose. A glycemic index of more than 70 is considered high, and a glycemic index of less than 35 is considered low.
A table with such products is known to a wide audience and does not reflect the rate of increase in blood glucose levels, but its total amount relative to the standard. The same potato, despite the large amount of complex carbohydrates, is a type of food with a very high glycemic index.
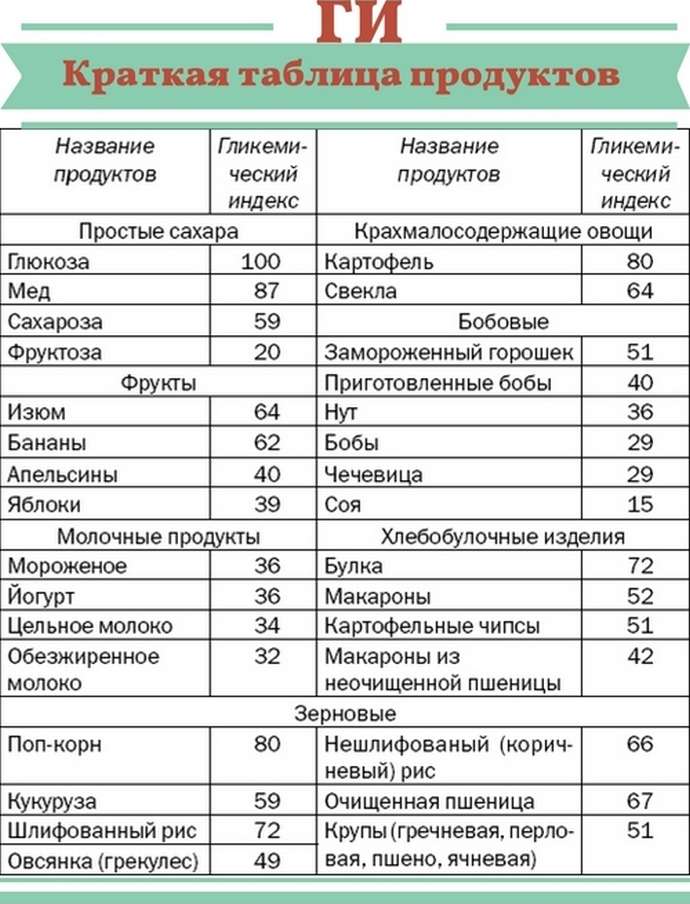
There is one very simple rule about the glycemic index. If you use products directly from the garden or without heat treatment and refining, then the glycemic index of such vegetables and fruits is lower.
The index may change depending on various factors:
- Degree of ripeness. For example, the glycemic index of bananas that have not yet ripened is lower than that of overripe ones.
- Use with other products. When processed, acid (citric, acetic or tartaric) lowers the Glycemic Index. Fat and the presence of large amounts of fiber also reduce GI levels.
- Treatment. The higher the glycemic index, the greater the amount of heat treatment that vegetables or fruits undergo.
- In fruits, the amount of carbohydrates and the level of the glycemic index are not related to sweetness. It happens that the acid is masked and is not heard in the presence of a large amount of fructose.
Glycemic index of complex carbohydrates in berries and fruits:
- Low glycemic index 55 and below - apples, grapefruits, lemons, cranberries, raspberries, apricots, persimmons, plums, strawberries, pears, grapes, peaches.
- Average 59-69 - melon, banana.
- High over 70 - watermelon.
Glycemic index level in vegetables:
- Very low glycemic index 15 and below - onions, bell peppers, cucumbers, mushrooms, cabbage, zucchini, greens, broccoli.
- Low - carrots, eggplant, tomato, beets.
- High - potatoes, corn, pumpkin.
Glycemic index content of nuts and grains
- Low glycemic index below 55 - soy, buckwheat, lentils, almonds, cashews, peanuts, sunflower seeds, peanuts, almonds, brown rice, buckwheat, green peas, beans.
- Average glycemic index 59-69 - millet, oats.
- High over 70 - pearl barley, semolina, white rice.
Complex carbohydrates contained in prepared foods have their own glycemic index:
- Low - yogurt, durum wheat pasta, dark chocolate, milk, cottage cheese, boiled potatoes, pizza, ketchup, mayonnaise.
- Medium - instant oatmeal, popcorn, marmalade, chips,
- High - white flour bread, ice cream, waffles, sugar, jam, corn flakes.
Note!
Knowledge about the glycemic index is useful for those who want to competently build their diet in order to lose weight or for the purpose of correcting dietary nutrition for diabetes.

When food with a high glycemic index enters the body, blood glucose levels rise sharply. The next stage is the release of insulin into the blood.
Insulin is a protein hormone of the pancreas that regulates carbohydrate metabolism in the body and makes glucose available to cells.
Insulin converts excess glucose into glycogen and fat deposits. A vicious vicious circle occurs. If you eat a portion of fast carbohydrates, they quickly turn into glucose and are just as quickly transported into cells through a greater release of insulin.
Thus, the sugar level in the bloodstream drops again and the person feels hungry. Thus, the total calorie content increases and you will not be able to lose weight. The situation is worse for patients with diabetes. In this case, an increase in glucose that is not utilized can lead to serious complications.
Slow polysaccharides, entering the human body, dissolve into monomers slowly, because the structure of their molecules is longer, the bonds are stronger. Insulin is produced fractionally, without causing a sudden drop in blood sugar.











