General characteristics of fluorine
Fluorine has atomic number 9, and its atomic mass is 18.9984031. In the periodic table of chemical elements, fluorine is usually designated F. This component is poisonous. At its core, fluorine is a chemically active non-metal. It is a strong acidifier. Among all the elements from the halogen group, fluorine is the lightest. Under standard pressure temperature conditions, fluorine is a diatomic gas, pale yellow in color, with a pungent odor. Reminds me of ozone or chlorine. Fluorine formula-F2.
Story
The first fluorine compound, fluorite (fluorspar) CaF2, was described at the end of the 15th century under the name “fluor”.
In 1771, Karl Scheele obtained hydrofluoric acid. When the fluorite mineral CaF2 was treated with sulfuric acid, it released HF in the form of an aqueous solution. This event is considered in the history of chemistry as the discovery of fluorine. The analogy with chlorine was proposed in 1810 by Andre Ampère, and was supported by Humphry Davy. Davy studied the dissolution of glass in hydrofluoric acid. As a chemical element included in hydrofluoric acid, fluorine was predicted in 1810, and isolated in free form only 76 years later by Henri Moissan in 1886 by electrolysis of liquid anhydrous hydrogen fluoride containing an admixture of acidic potassium fluoride KHF2.
origin of name
The name “fluorine” (from ancient Greek φθόρος - “destruction, spoilage, harm”), proposed by Andre Ampère in 1810, is used in Russian and some other languages; in many countries names derived from Lat. fluorum (from fluere - “to flow”), - according to the ability of some fluorine compounds, for example fluorite (CaF2), to lower the melting point of metallurgical slag formed during the reduction of metals from ores, and increase its fluidity.
Finding fluorine in nature. Where is fluoride found?
In its free state, Tuesday can be found in the environment, as it is part of compounds with various elements. Under certain conditions, they break down to form fluoride ions.
Fluorine compounds can be found in soil, water, and food. This element is vital for human health, however, it also has negative qualities. The amount of fluoride in the body should not exceed the permissible daily norm, as this can lead to negative consequences. Doctors believe that 0.5 mmg to 1-2 mmg is enough for an adult. If more fluoride enters the body, complications may arise.
Acute poisoning[edit | edit code]
Sources F
Such poisoning is not uncommon. It usually occurs due to accidental ingestion of fluoride-containing insecticides or rodent control agents.
The first symptoms (salivation, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea) are associated with the local effect of fluoride compounds on the gastrointestinal mucosa. Systemic symptoms are varied and severe: nervous excitement (apparently caused by the calcium-binding effect of fluoride ions), hypocalcemia and hypoglycemia. Blood pressure decreases, which can be explained both by inhibition of the vasomotor center and by direct cardiotoxic effects. Breathing initially quickens, but then becomes depressed. Death usually occurs from respiratory arrest or heart failure. The lethal dose of sodium fluoride for humans is approximately 5 g, although it varies widely. Treatment boils down to intravenous administration of saline with glucose and gastric lavage with lime water (0.15% calcium hydroxide solution) or solutions of other calcium salts to bind fluoride ions. For tetany, calcium gluconate is administered intravenously. With the help of intensive infusion therapy, high diuresis is maintained.
Food sources of fluoride. What products can you get fluoride from?
Products more saturated with fluoride are black and green tea. Fluorine is also included in nuts. Animal products are also rich in it. These include sea fish, seafood, shellfish, shrimp, mussels, mackerel, and cod. The component is included in cereals: wheat, rye, oats, corn, rice. It can also be obtained from beans, peas, and other legumes. By-products are rich in fluoride no less. Beef, veal and liver are the main sources of this trace element. You can also get it from vegetables and fruits. The richest foods are apples, fruits, carrots, and pumpkins.
Beneficial properties of fluoride and its effect on the body
Fluorine performs many useful functions in the human body. It is responsible for strengthening the immune system. Tur also participates in metabolism and mineralization of bone tissue. Protects tooth enamel. Fluoride prevents the premature development of osteoporosis and strengthens the bone skeleton. Thanks to fluoride, hair and nails grow, it stimulates blood circulation throughout the body.
Fluoride is included in many toothpastes for a reason; it helps protect tooth enamel from the development of caries. Thanks to fluoride, bone healing after a fracture occurs more quickly. Also, these microelements take part in the formation of the skeleton and maintain its functioning throughout life. The presence of this component in the body reduces acidity and bacteria, causing problems with teeth.
Helps iron be better absorbed, it accelerates the process of removing radionuclides and heavy metal salts from the body. the beneficial properties of fluorine have been evaluated in medicine. Its compounds are included in new drugs, blood substitutes, and artificial heart valves.
Application
Fluorine is used to obtain:
- freons - widely used refrigerants;
- fluoroplastic - chemically inert polymers;
- SF6 gas - a gaseous insulator used in high-voltage electrical engineering;
- uranium hexafluoride UF6, used for separating uranium isotopes in the nuclear industry;
- sodium hexafluoroaluminate - an electrolyte for producing aluminum by electrolysis;
- metal fluorides (eg W and V), which have some beneficial properties;
Harm of fluoride to humans. Negative effects of fluoride on the body
Fluoride can cause harm only when a large dosage enters the body. If the daily requirement of microelements is regularly exceeded, a person develops a severe case of arthritis, fluorosis of bones and teeth. An excess of fluoride causes problems in the functioning of the endocrine system and suppresses the functioning of the thyroid and pineal glands. Because of this, metabolic processes in the body are disrupted.
Fluoride is inherently a powerful neurotoxin that promotes the accumulation of aluminum in the brain. This component can lead to the development of Alzheimer's disease and a number of nervous and mental disorders. However, not only an excess of fluoride is dangerous. If the body has too low a percentage of the component, caries, periodontal disease develops, and nails and hair begin to break.
Lack of fluoride in the body. What are the consequences of fluoride deficiency?
Fluoride is an essential component for maintaining human health. Despite the fact that a person needs a very small amount of the component, its deficiency is quite common. You can get less of a microelement if you stop getting enough drinking water. If the amount of microelement is insufficient, iron begins to be absorbed worse, which leads to the development of iron deficiency anemia and caries. The quality of tooth enamel also suffers, because fluoride is washed out by fluorapatites.
The main manifestations of fluoride deficiency are dental caries and osteoporosis. To avoid the development of caries, it is necessary to consume sufficient amounts of drinking water and foods containing fluoride. And also use toothpastes, gels, nail polishes, hair sprays that contain this microelement. However, it is important to understand that fluoride is not a cure for tooth decay. It only helps to avoid its development in the human oral cavity.
Physical properties
Under normal conditions it is a pale yellow gas. In low concentrations in the air, its odor resembles both ozone and chlorine. Very aggressive and poisonous.
Fluorine has an abnormally low boiling point (85.03 K, −188.12 °C) and melting point (53.53 K, −219.70 °C). This is due to the fact that fluorine does not have a d-sublevel and is not able to form one-and-a-half bonds, unlike other halogens (the bond multiplicity in other halogens is approximately 1.1).
Below the melting point it forms pale yellow crystals.
Electronic structure
Electronic configuration of fluorine atom: 1s22s22p5.
Fluorine atoms in compounds can exhibit an oxidation state of −1. Positive oxidation states in compounds are unknown, since fluorine is the most electronegative element.
The quantum chemical term of the fluorine atom is 2P3/2.
Molecule structure
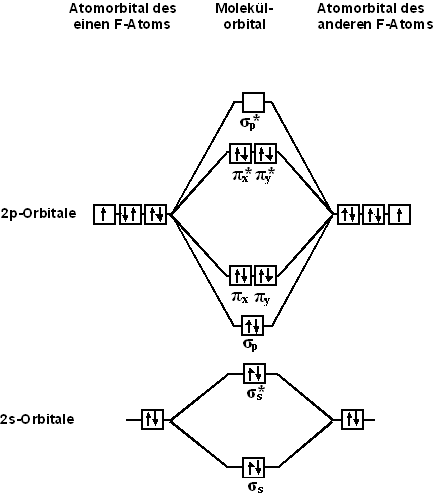
From the point of view of molecular orbital theory, the structure of a diatomic fluorine molecule can be characterized by the following diagram. The molecule contains 4 bonding orbitals and 3 antibonding orbitals. The bond order in a molecule is 1.
Crystals
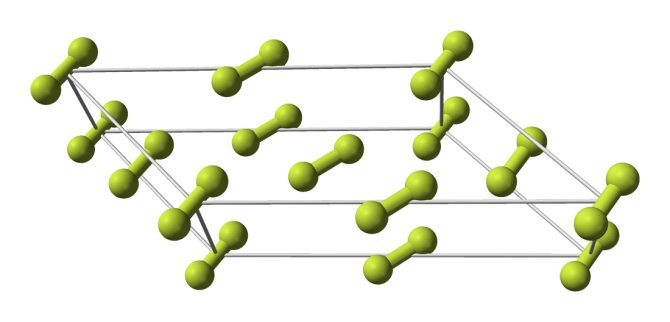
Fluorine forms molecular crystals with two crystal modifications stable at atmospheric pressure:
- α-fluorine, opaque, hard and brittle, exists at temperatures below 45.6 K, monoclinic crystal lattice, space group C
2/
c
, cell parameters
a
= 0.54780(12) nm,
b
= 0.32701(7 ) nm,
c
= 0.72651(17) nm, β = 102.088(18)°,
Z
= 4,
d
= 1.98 g/cm3 with a unit cell volume of 0.12726(5) nm3 (at 10 K); - β-fluorine, transparent and less dense and hard, exists in the temperature range from 45.6 K to the melting point of 53.53 K, cubic crystal lattice (primitive lattice), space group Pm
3
n
, cell parameters
a
= 0.65314 (15) nm,
Z
= 8,
d
= 1.81 g/cm3 with a unit cell volume of 0.27862(11) nm3 (at 48 K), the lattice is isotypical of the O2 γ-phase and the N2 δ-phase. It should be noted that in an early (but the only one conducted before 2021) experiment on the structure of β-fluorine, the x-ray density of the crystal was estimated to be 1.70(5) g/cm3, and this density of solid fluorine is cited in most reference books. A more accurate modern measurement gives 1.8104(12) g/cm3.
The phase transition between these crystalline fluorine phases is more exothermic than the solidification of liquid fluorine. The orthorhombic phase has not been detected in solid fluorine, unlike all other halogens. α-fluorine molecules are directionally disordered. The length of the F-F bond in molecules is 0.1404(12) nm.
Even at such low temperatures, the interaction of fluorine crystals with many substances leads to an explosion.
Isotopic composition
Main article: Isotopes of fluorine
Fluorine is a monoisotopic element: in nature there is only one stable isotope of fluorine, 19F. There are 17 more known radioactive isotopes of fluorine with a mass number from 14 to 31, and one nuclear isomer - 18mF. The longest-lived radioactive isotope of fluorine is 18F, with a half-life of 109.771 minutes, an important source of positrons used in positron emission tomography.
Nuclear properties of fluorine isotopes
| Isotope | Relative mass, a. eat. | Half life | Type of decay | Nuclear spin | Nuclear magnetic moment |
| 17F | 17,0020952 | 64.5 s | β+ decay in 17O | 5/2 | 4,722 |
| 18F | 18,000938 | 1.83 hours | β+ decay in 18O | 1 | |
| 19F | 18,99840322 | Stable | — | 1/2 | 2,629 |
| 20F | 19,9999813 | 11 s | β− decay in 20Ne | 2 | 2,094 |
| 21F | 20,999949 | 4.2 s | β− decay in 21Ne | 5/2 | |
| 22F | 22,00300 | 4.23 s | β− decay in 22Ne | 4 | |
| 23F | 23,00357 | 2.2 s | β− decay in 23Ne | 5/2 |
Magnetic properties of nuclei
The nuclei of the 19F isotope have half-integer spin, so these nuclei can be used for NMR studies of molecules. The 19F NMR spectra are quite characteristic of organofluorine compounds.
Excess fluoride in the body. What happens when there is an excess of a microelement?
If a person drinks too much water that contains fluoride, exceeding its norm in the body, then he may develop the following ailments:
- Pathological changes in bone structure;
- the appearance of chalky stains on the teeth;
- violation of enamel strength;
- development of dental fluorosis;
- frequent nausea;
- vomit;
- disruption of the central nervous system;
- decreased blood pressure;
- failure of metabolic processes in the body;
- slowing down blood clotting;
- development of bone fluorosis.
The greatest risk of excess fluoride from drinking water is observed in the northern regions of Russia, as well as in those places where aluminum production enterprises are located.
How to avoid the dangerous effects of fluoride on the body?
You should check with your utility company to see if your water is treated with fluoride. If the answer is yes, then refuse to cook in aluminum cookware, since fluorine forms a dangerous compound with this component that can cause the development of disease in the human body. Also, do not use tap water for cooking or drinking. Doctors recommend that pregnant women and children not consume foods prepared in such water; for them, exposure to fluoride is especially dangerous. To avoid the negative effects of fluoride, use mineral water for cooking.
Receipt
Laboratory method for obtaining fluorine The
industrial method for obtaining fluorine includes the extraction and enrichment of fluorite ores, sulfuric acid decomposition of their concentrate with the formation of anhydrous HF and its electrolytic decomposition.
To obtain fluorine in the laboratory, the decomposition of certain compounds is used, but all of them are not found in nature in sufficient quantities, and they are obtained using free fluorine.
Laboratory method
- In laboratory conditions, fluorine can be obtained using the installation shown. A copper vessel 2 with holes in the bottom is placed in a copper vessel 1 filled with KF·3HF melt. A thick nickel anode is placed in vessel 2. The cathode is placed in vessel 1. Thus, during the electrolysis process, fluorine gas is released from tube 3, and hydrogen from tube 4. An important requirement is to ensure the tightness of the system; for this, plugs made of calcium fluoride with lubricant of lead(II) oxide and glycerin are used .
- In 1986, while preparing for a conference to celebrate the 100th anniversary of the discovery of fluorine, Karl Christe discovered a method for the purely chemical production of fluorine using the reaction in a hydrogen fluoride solution of K2MnF6 and SbF5 at 150 °C:
2K2MnF6 + 4SbF5 → 4KSbF6 + 2MnF3 + F2↑
Although this method has no practical application, it demonstrates that electrolysis is not necessary; in addition, all components for these reactions can be obtained without the use of fluorine gas.
Also, for the laboratory production of fluorine, you can use heating cobalt(III) fluoride to 300 °C, decomposition of silver fluorides and some other methods.
Industrial method
Industrial production of fluorine is carried out by electrolysis of a melt of acidic potassium fluoride KF 2HF (often with the addition of lithium fluoride), which is formed when the KF melt is saturated with hydrogen fluoride to a content of 40-41% HF. The electrolysis process is carried out at temperatures of about 100 °C in steel electrolyzers with a steel cathode and a carbon anode.
The benefits of fluoride for human teeth. Do I need to treat my teeth with fluoride?
Many people don't even think about the fact that they are not getting enough fluoride. It is necessary to consult with a doctor and check the condition of your teeth to make sure that they have enough microelements. People who take medications that cause dry mouth should have their teeth treated with fluoridation to improve their resistance to tooth decay. This procedure will also be useful for those who suffer from diseases that cause dry mucous membranes.
It is advisable to additionally treat teeth with fluoride for those who have receding gums. With this problem, bacteria have a greater chance of getting on the surface of the tooth, which leads to the development of caries and cracks. This procedure is especially necessary for people who have installed braces. Metal plates can cause cavities. It is also worth strengthening your teeth if you are undergoing radiation therapy to the head or neck. This type of therapy damages the salivary glands, leading to dry mouth.

What types of special fluoride dental treatments are there?
You can treat your teeth with fluoride at a dental clinic or yourself at home. However, it is better to trust professionals who will not harm your teeth. The dentist will remove excess saliva and then apply a special film or varnish containing fluoride to the jaw. Some dentists use a mouthguard that is filled with gel or foam. It should be kept for no more than a few minutes. After the procedure, you cannot eat or drink anything for about half an hour, and smoking is also prohibited.
Rate
Fluorine