Share:
Fiber is one of the most important components of any diet. Its absence or excess leads to detrimental consequences for the human gastrointestinal tract. How much fiber should you consume for a healthy diet? Which fiber sources should you choose? Which products contain the most of it, and which do not have it at all? What are the benefits of fiber and is there any harm, as well as what are the functions and properties of this element of the human diet - you will learn about all this from our article.
Fiber - what is it in simple terms?
Fiber is a type of complex carbohydrate, plant fiber formed from parts of plants. Cabbage leaves, bean and seed skins, plant stems and grains are all examples of fiber.

In addition to fiber, which is formed under natural conditions, there is also a food additive of the same name. It is also a complex carbohydrate formula that cannot be broken down in the gastrointestinal tract, and is used for dietary purposes (source - Wikipedia).
Dietary plant fibers are not digested by enzymes in the digestive tract. Beneficial intestinal microflora is responsible for their processing.
If fiber is not absorbed by our body, then what is its benefit? First of all, fiber helps food move out of the digestive system faster. The longer food is digested inside the gastrointestinal tract, the more difficult it is to eliminate it later without consequences, such as gas or bloating. Fiber speeds up this process and helps the body cleanse itself naturally.
That is why fiber is indicated for those who have intestinal problems.
Diet rich in fiber

A diet rich in fiber is very beneficial for health. But it is important to switch to a new nutrition program gradually, adding 5 g of the substance per day. A faster transition may cause bloating, cramping, and diarrhea. Also, nutritionists from the University of Michigan advise slightly reducing the amount of caffeine-containing drinks while taking fiber. Caffeine acts on the body as a diuretic, and fluid loss due to the consumption of large amounts of fiber is fraught with constipation.
Dietary fiber will help replenish your diet; you don’t have to immediately resort to taking dietary supplements. To do this, you should pay attention to fruits and berries. Ideally, they should be consumed in small portions throughout the day. The next recommendation from nutritionists is to start the day with oatmeal or bran with berries. As for protein foods, in addition to meat, it is important to include plant proteins (beans, beans, lentils) in your diet, which are also excellent sources of fiber. For a fiber-rich dinner, broccoli, collard greens, corn, whole grain pasta, and brown rice are ideal options.
Types of fiber - cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, pectin
Fiber is classified according to its content in different products or their parts. Let's look at the main types of fiber.
Cellulose
It is the main component of plant cell walls. Cellulose is an insoluble type of fiber. It can be found in wheat flour that has not yet been sifted, in bran, in cabbage leaves, in the pod of young peas, in the peel of green beans, in broccoli leaves or Brussels sprouts, in the peel of cucumbers, peppers and apples. Cellulose facilitates the activity of the colon , absorbing all excess moisture.
Hemicellulose
This species is found in bran, grain, beet pulp, Brussels sprouts or mustard sprouts. All subtypes of this type of fiber have the ability to dissolve.
Hemicellulose, like the first type, absorbs liquid, facilitating intestinal function.
These two types help processed waste leave the intestines faster and prevent conditions and diseases such as constipation, colitis due to spasms of intestinal smooth muscles, as well as varicose veins, hemorrhoids, colon cancer, and diverticulosis.
Lignin
The third, insoluble type, is found in cereals, such as bran, or in eggplant, strawberries, radishes and peas. Moreover, the lignin content in those vegetables and fruits that have already been sitting for some time is much higher than in fresh ones. The main property of lignin is considered to be its special viscosity - it prevents the absorption of harmful substances, which helps food leave the intestines faster. In addition, due to the ability to bind to bile acids, the amount of cholesterol in the blood decreases.
Pectin and gums
Both of these types are soluble and are found in oat porridges, potatoes, beans, peas, as well as in berries - strawberries and strawberries. There is a lot of pectin in apples and citrus fruits.
This type of fiber controls the process of food digestion not only in the stomach, but also in the small intestine.
Like lignin, pectin and gums combine with bile acids, lowering cholesterol and actively absorbing fat. In addition, the substances slow down the process of glucose absorption , which becomes a salvation for patients with diabetes (source - NCBI).
Fiber tablets
In addition to natural fiber, scientists have developed in the laboratory a formula of an easily accessible substance - activated fiber, which is taken in tablets in the dosage required for your body.
This type of planned introduction of fiber into the diet contributes not only to the formation of a correct diet, but also increases the effectiveness of various diets , since activated fiber controls the supply of proteins in food and reduces the carbohydrate component.
Hence, tangible and constant weight control.
What does the body need: benefits
Fiber is essentially carbohydrates , or to be more precise, simply dietary fiber or ballast substances. This means that, like water and mineral salts, fiber does not provide the body with energy, but at the same time plays an important role in its life. So how is it good for the body?
Dietary (plant) fiber, which is found primarily in low- or very low-sugar plant foods, is usually combined with other nutrients.
By the way, in a study by Pilar Buil-Cosiales, it was found that consuming fiber-containing fruits from cardiovascular diseases by 41%
So we hope that opponents of fruits (and there are such people, and their names are legion) will come to their senses, read the article about fructose and conquer their raging fear of bananas , apples and pears.
Types and where many are found
Dietary fiber comes in two main types: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber is the pulp of fruits and vegetables, while insoluble fiber is the peel and husk. Both types are useful and necessary for our body .
Most plant foods contain these two forms of fiber simultaneously. We will tell you more about each of them, how they are eaten, and also what they contain:
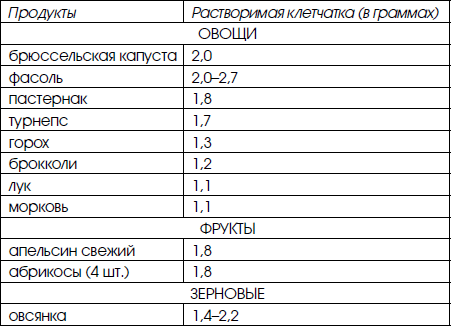
- Soluble dietary fiber
They turn into a viscous gel in the intestines, which slows down the movement of food contents and significantly inhibits the enzymatic processing of carbohydrates. What is the list of vegetables rich in this type of fiber:
- Pectin . It is found in large quantities in apples, carrots, citrus fruits, cabbage and, oddly enough, in native potatoes . Pectin helps lower cholesterol levels and slows down the absorption of sugar, which makes it indispensable for diabetics.
Gum . Contained in oatmeal and dried beans (peas, beans, beans, lentils). Like pectin, this type of fiber affects the digestibility of food.
- Lignin . It is found in greatest quantities in cereals (oats, rye, barley). Another source of lignin is stale vegetables (this does not mean spoiled, but slightly wilted products).
- Insoluble dietary fiber
This is the so-called a coarse, large type of fiber, which, on the contrary, accelerates the movement of food contents through the gastrointestinal tract, has a laxative effect (used to prevent constipation), modulates pH in the colon, and is also a prebiotic ( restores microflora ).
Which vegetables and fruits have a lot of this fiber?
To begin with, we note that insoluble dietary fiber is divided into: cellulose and hemicellulose . Where there is a lot of them: bran, unprocessed grains (buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley, bulgur), legumes, nuts, seeds, green beans, cauliflower, broccoli, greens, peels of fruits and vegetables.
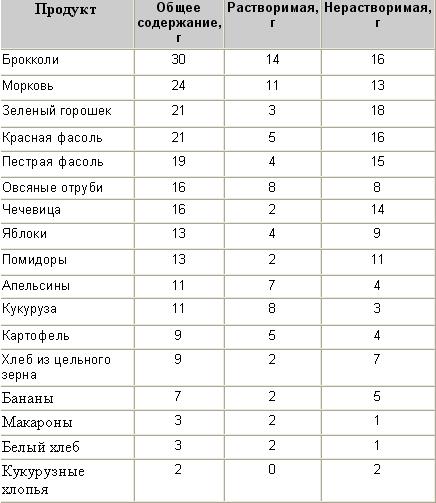
Also, soluble fiber is found in some fruits: prunes, raisins, avocados, berries, bananas , quince and peaches peels.
According to dietetics, with proper nutrition, the total amount of soluble fiber should be at least 3/4 of the total amount.
Both types of fiber tend to increase the volume of food content, thereby increasing satiety (reducing appetite), but at the same time inhibiting the absorption of nutrients . Their undoubted advantage is that they prevent the peak increase in blood glucose concentrations.
Butt without squats: is it possible?
What are the benefits of fiber?

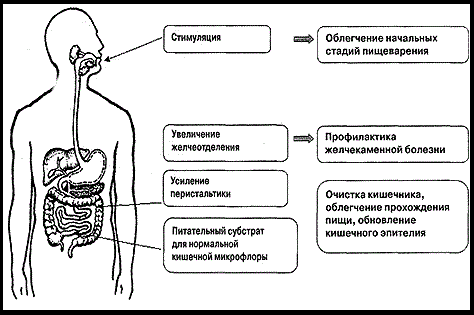
Recent research in the field of nutrition has shown that the benefits of fiber for the human body are not only in normalizing intestinal function by accelerating the elimination of waste, but also in cleansing the body of toxins and waste.
This is why so many products made from wholemeal flour have appeared on store shelves. People consciously switch to such a diet, since “rough food” helps to lose weight and improve gastrointestinal processes.
In addition to its function as the body’s main sorbent, fiber has other beneficial properties:
- Fills you up quickly, which is important when dieting.
- Tames excessive appetite.
- Improves the secretory functions of the stomach.
- Restores peristalsis of the large and small intestines.
- Reduces the risk of developing malignant neoplasms of the colon.
- Enriches the body with vitamins, minerals and other useful microelements.
- It is “food” for beneficial intestinal bacteria.
- Slows down the rate of increase in blood glucose.
- Reduces blood cholesterol levels.
Fiber also helps normalize blood pressure and reduce the likelihood of stroke and myocardial infarction (source: US National Library of Medicine).
Possible harm from fiber
Possible harm from fiber can be reduced to zero if you consume it in moderation and not on an empty stomach. It is best to consume foods containing fiber along with some liquids, for example, if you eat oat porridge, then the first course of this meal should be vegetable soup.
The abundant use of fiber in the diet contributes to changes in intestinal motility, which leads to constipation or diarrhea, increased fermentation and putrefaction.
Such reactions cause:
- bloating;
- spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen;
- intestinal obstruction;
- hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes.
It is also not recommended to consume dietary fiber in large quantities for stomach and duodenal ulcers during periods of exacerbation.
Daily norms
Researchers say the average woman consumes about 13 grams of fiber daily, and men about 17 grams. Meanwhile, nutritionists have found that fiber is so important for humans that it should be present in the diet every day. At the same time, men under 50 years old should consume approximately 38 grams of fiber per day, older ones - about 30 grams. Women under 50 years of age are recommended to consume about 25 g of the substance daily, and 21 g per day is enough for women over 50. It is not difficult to provide yourself with these portions if your daily diet contains whole fruits and vegetables, nuts and seeds.
The required amount of fiber for children is determined taking into account age categories: children under 3 years old should receive 19 g of the substance per day, 4-8 years old - about 25 g per day, girls 9-18 years old - 26 g each, boys 9-13 years old – 31 g each, boys 14-18 years old – 38 g each.
Nutritionists say that the ratio of insoluble to soluble fiber should be 75% to 25%. But since many products (rolled oats, bran, flax seeds and others) contain two types of dietary fiber, you should not specifically calculate the proportions.
Table - sources of fiber in foods

The largest supply of fiber is found in the outer shells of foods: peels, leaves, stems, etc. The highest fiber content product is considered to be whole grain bran - about 44.0% per 100 g.
From the table you will find out which other foods contain fiber and in what quantity:
| Product | Amount of fiber (percentage) |
| Bran | 44 |
| Nuts (especially almonds) | 15 |
| Green pea | 12 |
| Whole grain products | From 8.5 to 9.6 |
| Legumes | 7 |
| Raisin | 6,8 |
| Greenery | 3,8 |
| Carrot | 3,1 |
| Broccoli | 3 |
| Cabbage | 2,9 |
| Apples, potatoes, wheat flour | 2 |
| Rice | 0,8 |
Note! Vegetables and fruits are considered the most balanced foods in terms of fiber and other nutrients. Animal products often contain no fiber at all, or the content is negligible.
Fiber and...
…cholesterol
Dietary fiber helps lower cholesterol levels. The process of digesting food requires bile acids, which are partly composed of sterol. To improve digestion, the liver pulls cholesterol from the blood to create bile acids, thereby reducing the concentration of so-called “bad” cholesterol.
…heart health
A link has also been found between fiber intake and the risk of heart attack. In people whose diet is based on foods rich in fiber, the risk of heart disease is reduced by 40%. And just increasing your daily fiber intake by 7 grams is enough to reduce your risk of heart attack by 7%.
…blood sugar
Research has shown a connection between fiber and blood glucose levels. American scientists have noticed that increased consumption of fiber can reduce glucose levels. In addition, the risk of developing diabetes is reduced in people who consume enough fiber daily. Soluble fiber helps slow the breakdown of carbohydrates and the absorption of glucose, which helps control blood sugar levels.
…cancer

Research conducted in 2011 showed a potential relationship between the amount of fiber consumed and the risk of cancer. Then a group of scientists conducted a control experiment on animals, and this time the researchers found that such a connection still exists, but only if the correct microflora is present in the intestines. In this case, the fiber reacts with bacteria in the lower part of the large intestine. Fermentation produces a reactant called butyrate. It is this substance that causes self-destruction of cancer cells.
But this is not the only type of cancer that is affected by fiber. Recently, scientists from Nebraska announced the results of another study. In their opinion, fiber, oddly enough, can also prevent lung cancer. The study found that 68 percent of those who consumed 18 grams or more of fiber per day had excellent lung health. Also, lovers of foods containing fiber turned out to be the best in another test - for lung capacity. Scientists do not yet know how to explain this relationship.
…longevity
According to many scientists, the secret of longevity lies in dietary fiber. And American epidemiologists believe that high-fiber foods can reduce mortality rates. And they add: wheat fiber and whole grain products are especially beneficial for humans. A 14-year follow-up showed that people whose diets included these foods had a 19 percent lower risk of death. By the way, some studies suggest that in ancient times the diet of our ancestors included at least 60 g of dietary fiber per day.
…allergy
In addition to all this, it is believed that fiber also plays a role in preventing food allergies. This theory again stems from the relationship between fiber and gut bacteria.
Scientists suggest that people with impaired intestinal microflora are prone to food allergies, in particular those caused by peanuts, crustaceans and shellfish. And dietary fiber activates the proliferation of the clostridia bacterium, on which the proper functioning of the organ actually depends.
List of foods with healthy fiber for people with food allergies: apples, pears, melon, carrots, potatoes, rutabaga, broccoli, green beans, pumpkin, zucchini. Their plant fiber is presented in high concentration and at the same time they are hypoallergenic products.
…asthma
A similar explanation applies to the effectiveness of fiber in treating asthma. One reason autoimmune diseases develop is that when digestion fails, particles from the intestines enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation. An experiment conducted on rats showed that increased consumption of dietary fiber reduces asthmatic inflammation.
...weight loss
Keeping you feeling full for a long time, fiber helps you lose weight. Therefore, all diets for obese individuals should contain the maximum amount of dietary fiber. The average daily intake of dietary fiber in this case should be about 60 g. In this case, you can resort to the use of pharmaceutical fiber. You can drink it yourself: dilute a tablespoon of the substance with a glass of water and drink 30 minutes before meals (but no more than 6 tablespoons per day). A more pleasant way is to add the substance to ready-made dishes (soups, broths, yoghurts, salads). There is a diet, the essence of which is to drink a liter of kefir and 6 tablespoons of fiber per day. This dietary menu can be used as a 1-day fast or followed for several days.
…healthy skin
The fiber contained in plantain helps eliminate bacteria and fungi from the body that cause acne and rashes. So, at least, some researchers say. There are many other reasons why you should consume enough of this substance. For example, most fiber foods contain high concentrations of vitamins and other nutrients needed to maintain healthy skin.
Properties of fatty tissue
There is such a thing as adipose tissue - this is a mesh layer of skin, which is penetrated by collagen fibers and is located immediately under the skin itself (dermis). This mesh contains special “lobules of fat” that form our animal or subcutaneous fat.
@ Evgeniya adobe.stock.com (accumulation of fatty tissue)
What is fatty tissue needed for? This is connective tissue that provides shock absorption and thermal insulation to the body. In some cases (at different stages of obesity), the weight of fatty tissue can be from 10 kg, and the localization is different in men and women.
Women accumulate fatty tissue mainly in the thighs and buttocks, and men - in the chest and abdomen.
According to statistics, this connective tissue reaches its greatest thickness (up to 5 cm or more) in the hips, and the smallest thickness occurs in the eyelids and genitals.
The properties of fatty tissue include the following features:
- Energy. Fat is an important source of energy reserves in the body. Fat reserves are used up during periods of intense energy expenditure or during fasting.
- Thermal insulation. Heat is lost slowly through fat, which is useful in cold climates. The thicker the layer of fat, the less a person freezes at low temperatures. However, in excess amounts, fat spoils the figure, lowers self-esteem, and, in addition, adds problems in the “heart” part. Excess weight is a prerequisite for coronary heart disease, hypertensive crisis, diabetes mellitus and even skeletal-deforming osteoarthritis.
- Protection. Fat protects all internal organs from overheating and also increases skin elasticity. Shifting in different directions, the dermis seems to “slide” over the subcutaneous fat and has much less damage.
- Accumulation. Fat is the body’s reserve for “hungry” times. In addition to the fiber itself, the body accumulates other useful substances in subcutaneous fat. For example, estrogen hormones, which are important for the sexual function of the body, as well as vitamins A, D and E.
- Production of hormones. In addition to natural accumulation, fatty tissue is capable of independently producing important hormones. For example, leptin, which is responsible in our body for the feeling of satiety, etc.











