One of the most important factors determining human health, the proper functioning of his body and well-being is a competent diet. Rational nutrition is a balanced diet, taking into account the physiological characteristics of a particular person and his needs for various substances. It helps maintain health and largely determines the quality of life. We will help you develop an individual menu for weight loss, as well as organize the delivery of all the products necessary for this.
The concept of rational nutrition
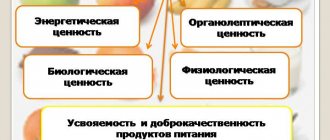
Balanced diet
- This is not a simple diet balanced in micro- and macronutrients. This is a complete diet that satisfies all the body’s energy needs, tailored to meet age and gender characteristics, the presence of chronic or concomitant diseases, genetic disorders and enzymopathies.
This concept cannot be specified - it always remains purely individual in relation to each person. After all, what is “rational” for one patient may not only not be suitable, but also be extremely dangerous for another: for example, although a 3-times-a-day diet is considered the most physiological, it is fundamentally unsuitable for a patient with adrenal depletion, not not to mention the extreme manifestation of this condition - Addison's disease.
In addition, genetics is also important: for example, the presence of defects in the genes of the folate cycle entails a violation of the utilization of the well-known and quite sensational amino acid homocysteine - and such people are advised to limit animal products containing a precursor in the reactions of its synthesis.
On the other hand, a purely plant-based diet is also contraindicated in case of polymorphisms in other genes - in this situation, vegetarians and vegans are at risk not only for vitamin B12 deficiency, but also for many others. So, say, if the transition of carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, which is concentrated in plant products, is disrupted, you can eat a kilogram of carrots - but this will be of little use (at least in the context of the formation of retinol).
Basics of rational nutrition
And yet we will have to start with theory: after all, it is important to understand not only what we eat, but also for what purpose we do it.
There must be balance in all processes of our body - after all, it is towards internal homeostasis that it so tirelessly strives throughout its life. Let's call this a lever or driving force, which forces the activation of the synthesis of certain hormones and at the same time reduce the formation of others (for example, with an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood, insulin is actively produced by the beta cells of the pancreas, while the conductor coordinating this hectic metabolic orchestra sends a clear signal: stop glucagon production). Entering the body, crossing its borders in the form of barriers of the skin and mucous membranes stimulates a reciprocal immune response - and all because our smart body, in fact, craves one main goal: peace and order on its vascular streets with parenchymal houses.
Nutrition is no exception.
— the rule of balance is unchanged for him. We eat in order to live (although statistics in recent years indicate a completely opposite trend of interpretation) - in other words, the amount of incoming food products, which, after splitting and digestion, are burned in the furnaces of cells, forming energy, must fully satisfy the body’s expenses, and they really huge.
Few people have thought that most processes, no matter how disadvantageous it is for the body, occur with a loss of energy - even such a primitive mechanism as the transport of glucose, perhaps the most common nutrient: given the large size of its molecule, it simply will not pass through the cage gate, getting stuck in the doorway. Unfortunately, this carbohydrate cannot carry out its functions in the blood - therefore, specific carriers come to the rescue, carrying or transporting it into the cells on their shoulders, thereby providing them with the necessary raw materials.
Fat-soluble substances and gases can freely penetrate through the lipid layer of the membrane - but we cannot eat only them! So, energy is the basis of everything.
However, what will happen if we receive more energy than we are able to expend? Considering the greed of our body and its desire to accumulate (who knows when that very rainy day will come), the balance will invariably be shifted - the so-called positive energy balance develops. And then everything follows the well-worn scenario: depositing fatty tissue as a safety net in case of an apocalypse.
The balance of nutrients is no less important: in classical dietetics the following ratio is given for proteins, fats and carbohydrates - 1: 1: 4. Although, we emphasize: in many ways, these numbers will depend on age and the chosen diet.
The diet should be varied
: mono-diets are a thing of the past. The more sources of nutrients, vitamins and minerals, the more likely it is that the body will be in minimal deficiency states. Turn your plates into a rainbow of colors - typically brightly colored fruits and vegetables are not only a great source of fibre, but also contain quite a bit of antioxidants. In addition, digestion begins even before the first bite enters the oral cavity and the subsequent irritation of the taste buds: that is why the appearance of the dish, its smell and table setting are so important. The complex reflex phase of secretion is the initial link that should not be excluded from the chain of digestion and absorption.
Drink enough water
- no matter how banal this rule may sound, in practice it turns out that many happily neglect it. Water is the basis of life: most digestive secretions consist of more than 97% of it. In the composition of blood plasma, water accounts for 91 to 93% - impressive, right?
Often, restriction in water consumption is motivated by the occurrence of edema. Here it is important to dig deeper and find the main reason for their appearance: and it is clearly not connected (directly so exactly) with water. Pay attention to possible endocrine pathologies - in particular, the functioning of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands. Sometimes the cause is disorders of the cardiovascular system.
Try to drink at least one glass immediately after waking up - and then just start brewing coffee. Moreover, its temperature should be equal to room temperature - remember that excessively cold temperatures can sufficiently cause spasms and generally disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
An approximate formula for calculating the daily water requirement:
Weight (in kg) *30 (ml)
The basics of healthy eating - the path to longevity
Home » Medical prevention » The basics of a healthy diet - the path to longevity
Ministry of Health of the Astrakhan Region
GBUZ JSC "Center for Medical Prevention"

«BASICS OF HEALTHY EATING - THE PATH TO LONGEVITY"
Healthy nutrition is nutrition that ensures human growth, normal development and vital activity, promotes health and prevents diseases. By eating right today, you take care of your health for many years. Healthy nutrition is one of the elements of a healthy lifestyle and the most important components of beauty and health. Sticking to a healthy diet isn't that difficult. Start switching to a healthy diet gradually. If you adhere to the basic rules of a healthy diet, then most diseases will bypass you, and your spirits and energy will never run out.
Basic rules of healthy eating
- It is necessary to ensure that the caloric content of the diet corresponds to the energy expenditure of the body and monitor body weight.
- Your food should contain all the substances necessary for a full life: proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, mineral salts and trace elements, i.e. nutrition should be varied and properly balanced.
- Eat calmly, in small pieces and chew each piece well.
- Divide your daily diet into 4-5 small meals (about 1 glass), instead of 2-3 large meals.
- Do not consume (or minimize the consumption of) harmful foods such as mayonnaise, ketchup, fast food, alcohol, etc.
- Limit the consumption of simple carbohydrates (sugar, sweet carbonated drinks) - no more than 30-40g per day. In some cases, sugar can be replaced with honey.
- Limit your salt intake. Use iodized salt instead of regular salt.
- Eat more fresh vegetables and fruits. Aim to include whole grains, legumes and nuts in your daily diet.
- Drink about 2 liters of water per day. Do not drink with food or drink immediately after meals (drink 30 minutes before meals and 30 minutes after meals). Do not drink a lot of water at night - no more than 200 ml.
- Have dinner no later than 4 hours before bedtime. About 2 hours before bedtime, you can drink a glass of low-fat kefir, yogurt or yogurt.
Body weight is the main indicator of energy balance. Energy needs depend on your type of activity and overall physical activity. You can determine whether your weight is normal using your body mass index (BMI). To calculate your BMI, you need to divide your weight in kilograms by the square of your height (kg/m2) .
- If the BMI value is from 18.5 to 25, then your weight is normal, which means you are consuming enough calories.
- BMI less than 18.5 – underweight. This can lead to exhaustion of the body and disruption of the functioning of all organs; it is worth increasing the amount of food consumed.
- A BMI from 25 to 30 is a sign of being overweight. It is urgent to reduce portions and increase physical activity, otherwise you risk obesity.
REMEMBER! An adult can rely on BMI.
A child's underweight or overweight must be diagnosed by a doctor!
Cooking healthy food
Whether food is healthy depends largely on how you prepare it. From the same products you can prepare both healthy and unhealthy food. The whole secret is in the balance of ingredients, breaking up meals, and cooking methods. Don't say that you don't like something - just try preparing this product differently!
When preparing dishes, use only vegetable oils (sunflower, olive, etc.) and gentle heat treatment (steam, grill, bake, boil, stew without adding oil).
Healthy Plate Principles
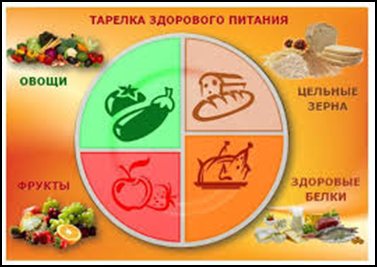
- 20% - fresh fruits or berries;
- 25% - grains or legumes;
- 25% - sources of healthy protein
- (meat, fish, seafood, eggs, cottage cheese);
- 30% - vegetables (fresh vegetable salad or vegetable stew);
- 200-250 ml – drink (water, tea, juice).
The basis of the diet consists of vegetables (except potatoes), fruits, grains and legumes, the amount of which should not be less than 500g. per day. In order to increase the amount of dietary fiber (fiber) in the diet, it is recommended to consume baked goods made from whole grains, as well as with the addition of bran.
PROTEINS are the most important components of food. Proteins of plant and animal origin should be present in food in equal proportions, approximately 30-40g. some and as many others.
Animal proteins ( meat, fish, cottage cheese, eggs, cheese) contain about 20% pure protein. The daily intake of such products should be up to 150-200g. Red meat (lamb, beef, pork) is not recommended to be consumed more than twice a week; it is better to replace it with chicken, turkey (without skin), and even better - fish.
Plant proteins (grain products, cereals, legumes, mushrooms, sunflower and pumpkin seeds and nuts). Eat 1 serving of these products per day: you can prepare a separate dish or add them to any other dish (salad, omelet, vegetable side dish, soup, etc.).
CARBOHYDRATES – supply the human body with energy. Proteins are divided into simple and complex. Our body needs them the most, as they serve as the main source of energy.
Simple carbohydrates (sugar, sweets and drinks based on it), they require no more than 50g per day.
Complex carbohydrates are present in starchy foods (bread, cereal, pasta, as well as vegetables and fruits). A healthy person needs to consume 350g of carbohydrates per day.
FATS – have high energy value. They are more than 2 times higher than the energy value of proteins and carbohydrates, which means that foods containing fat are the most high-calorie.
Animal fats (saturated), high consumption leads to obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. It is recommended to limit the consumption of fatty meat, butter, as well as the exclusion of meat and sausage products (sausages, sausages, carbonates, etc.) and offal (liver, tongue, etc.).
Vegetable fats (unsaturated ) enter the body along with vegetable oils - olive, soybean, sunflower or corn. 1-2 tbsp is enough. spoons of this oil per day (30g).
It is IMPORTANT that your daily diet should include:
proteins – 15%, fats – 30%, carbohydrates – 55%.
FOOD FIBER is practically not digested. However, they significantly affect the processes: digestion, absorption of food, and are also important for the intestinal microflora. Dietary fiber is found in vegetables and fruits, unrefined grains such as rolled oats, and bran.
LIMIT CONSUMPTION OF TABLE SALT to 5g, i.e. 1 teaspoon. It is necessary to limit/eliminate the consumption of canned products, pickled and salty foods, and you should also abandon the habit of adding salt to an already prepared dish.
Alcoholic drinks should be limited/excluded from the diet, since they do not contain nutritional value for the body.
MONITOR YOUR HEALTH, EAT VARIOUSLY.
HEALTHY EATING – HEALTHY LIFE
The material was prepared by the preparation and replication department
medical information materials of the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution JSC "CMP" - 2020
Rational diet
- Breakfast is everything.
Your first meal should be balanced, rich in fat and protein - this combination will make you full, and you won't even remember about food until lunch.
At the same time, the usual cereals, fruit juices, croissants and other confectionery products, except for another nuclear attack against the cells of the pancreas, will bring neither benefit nor saturation. In a word, a complete sugar bomb.
We recommend
“Balanced nutrition: the right diet and the right foods” Read more
We recommend considering the options for keto breakfasts: they ideally satisfy the feeling of hunger and do not just pickle the worm, but actually put it into a state of suspended animation. Use avocado, bacon, olives, cod liver, and eggs, salmon or poultry are great sources of protein. Add unsweetened coffee or cocoa and a small cup of your favorite berries - and you are guaranteed a stable emotional background, the key to which is the absence of hypoglycemia swings.
- Forget about the existence of the food pyramid
- at least until it is revised. Or better yet, create a new one!
What do you think occupies a dominant position in the old one? Surprisingly, these are grain crops.
Undoubtedly, the same cereals have many useful properties, but let's be honest: in the realities of the modern world, people are surrounded (literally) by their abundance. Take the same wheat (or rather its proteins - gliadins, which, together with other proteins similar in structure and functions, are united under the general name “gluten”) - wherever its components are added - the spectrum has long ceased to be limited to bakery products. The widespread use of gluten has also led to a predictable result: more and more, various groups of the population are diagnosed with gluten hypersensitivity - both in adults and in children.

Food hygiene, that branch of science that a priori should move ahead along with various advanced technologies, is stuck in a deep and very ancient hole of the past. But the responsibility for your health still lies not so much on the shoulders of science, but on your own.
- Fractional meals
- the same outdated regime, applicable only to professional athletes and in a number of diseases. A healthy person, and even more so a person striving with all his might to lose weight, should completely forget about snacks - as an adaptation during a smooth transition, you can leave one, but with the condition that it will be fatty.
- Avoid eating fruit as a meal on its own
— the fructose they contain bypasses all saturation pathways (this is achieved, in particular, due to the absence of a response signal to its entry in the form of insulin secretion from the pancreas). That is why it will not only not dull the feeling of hunger, but, like a match falling on a stack of dry firewood, will make it flare up with even greater force.
- Try to eat at certain times
- again, the digestion process does not rely on purely mechanical rubbing and absorption of food in the gastrointestinal tract.
What should be the diet?
The rules of rational nutrition will be ineffective without adherence to the regime. This is important because the human body is largely subject to rhythms and lives in accordance with them. A rational diet involves the following nuances:
- Meals are strictly at the same time every day, according to an individual regimen. You cannot skip a planned meal or have an unplanned one. Over time, the body will adapt to the regime and begin to signal hunger strictly before scheduled meals.
- Eating before bed, at night, is prohibited. This can cause problems falling asleep, poor absorption of nutrients from food, upset stomach, and weight gain. The rule “not to eat after 18:00” is relevant for those who go to bed around 21-22 hours. For the rest, the rule “do not eat 3-4 hours before bedtime” is true, no matter what time you plan to go to bed.
- There should be at least 3 meals, ideally 4-5 per day, including snacks. Rare (1-2 times a day) and plentiful meals cause health problems and can provoke a set of extra pounds.
Children's nutrition
Rational nutrition is no less important for children - especially in the context of treatment and prevention of diseases, maintaining optimal conditions for the growth and development of the child, in the maturation and final differentiation of tissues and systems of his body.

An adequate supply of minerals is necessary - their deficiency has a huge range of multidirectional adverse factors on the cognitive functions, growth and processes of development of the child as a person. For example, a lack of iron, leading to hypoxia or oxygen starvation, reduces the activity of liver enzyme systems (and this is subject to their already inadequate activity), and also slows down the processes of cell division. In addition, the exchange of serotonin, dopamine, and other neurotransmitters is also inhibited.
Study
: Micronutrients for child growth and development
Iodine deficiency, which is widespread, leads to disorders of cartilage tissue, slows down skeletal growth and impairs its maturation. A decrease in the activity of the thyroid gland is also accompanied - for example, insufficient formation of such a hormone as triiodothyronine (T3) inhibits the division of nerve cells (or rather their precursors), and the process of myelination of nerve fibers is disrupted.
In general, it is recommended to eat three meals a day and two additional snacks. At the same time, the latter also need to be made as healthy as possible - replace sweets and chocolate with low-carb homemade sweets, berries and nuts.
Remember
: instilling correct eating habits in childhood is much easier than getting rid of them in adulthood (the neural connections are already formed).
Functions of proper nutrition

The first function of nutrition aims to provide our body with energy. Let's describe it as follows. Each day, you eat the amount of food you need to perform your daily activities, including working out at the gym. If you don’t finish eating, your strength will leave you in the middle of the day, you will feel tired, exhausted, and you won’t have enough energy for the gym. Overeat - excess nutrients will affect your well-being. You will experience bloating, belching, flatulence, you will begin to feel sleepy, and it is strictly not recommended to exercise in the gym while sleepy and on a full stomach. Overeating will also affect the level of subcutaneous fat, which will then have to be burned.
The second function of nutrition is the timely provision of the body with nutritional components. These are proteins, fats, carbohydrates and mineral elements. The purpose of such provision is to create conditions for the effective construction of new cellular forms and structures, as well as to maintain the appropriate energy balance in them.
The third function of nutrition is based on the continuous provision of our body with biologically important substances that it requires for the full functioning of vital processes. Simply put, they are vitamins, since they are obtained with food and act as components of various hormones and enzymes.
The fourth function of nutrition is the formation and strengthening of immunity. Numerous studies have proven that the reaction of the immune system to bacteria, infections and their aggression entering the body directly depends on the quality of the food you eat. And also, on the amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in it.
Now you most likely have a logical question: “How should you eat to ensure the correct functioning of the body and all its systems?” And here we come to the fact that the basis of proper and rational nutrition is made up of three principles: moderation, variety and regimen. We will talk about them further.
Rational nutrition standards
In general, any balanced diet should contain
:
- Protein sources
: meat, eggs, fish, seafood, legumes (remember the need to pre-soak them).
Perfect fit
:
- Salmon (32 g/100 g product)
- Beef (28 g/100 g product)
- Chicken (25 g/100 g product)
- Rabbit meat (23 g/100 g product)
- Shrimp (20 g/100 g product)
- Squid (17 g/100 g product))
- Eggs (12g/100g product)
- Sources of fiber
: vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs, cereals, nuts.
- Sources of healthy fats and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
. Fatty fish (herring, trout, mackerel) will also help with this.
- It is recommended to add probiotic-rich foods
- sauerkraut and other fermentation products. It’s not for nothing that the answer to the main (after Shakespeare’s “to be or not to be”) question has not been received: do we control the microbiome or does it control us?
Energy value of food
Energy value of food
- an indicator that displays the amount of energy released by the body when absorbing incoming products. This is calorie content.
The energy value for different classes of biological compounds is different:
- Fats - 9.29 kcal/g.
- Proteins - 4.1 kcal/g.
- Carbohydrates - 4.1 kcal/g.
Even without going into biochemical reactions, it is already clear from these data that the most advantageous source of energy - that is, the fuel on which the cellular engines operate - is the oxidation of fats. Thus, when burned, they contribute to the release of twice as much energy as other classes of organic compounds.
However, in fairness, it is worth noting that not all cells are capable of recycling them. So, let’s say, red blood cells, which simply lack those very production furnaces called “mitochondria,” simply cannot oxidize fatty acids.
Proteins, fats and carbohydrates

As we have already understood, the distribution of food into portions throughout the day implies the distribution of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. To do this, you need to know the rate, ratio and proportions of consumption of these components. This raises the corresponding question: when, in what quantity and in what ratio should they be taken?
The principles of healthy and proper nutrition suggest distributing proteins, fats and carbohydrates as follows: carbohydrate intake should mainly occur in the first half of the day, protein intake in the morning is small, but by the second half of the day it should be increased. The amount of fat should decrease by the afternoon. Why is this so? This is due to the fact that throughout the day we need energy to perform all kinds of tasks, including working out in the gym. Carbohydrates are a source of energy, so during the day, the emphasis is on them. Fats are also a source of energy, but you need to consume them much less than carbohydrates. When it comes to night, and energy costs decrease, in turn, the need to provide muscles with building material, which, as we know, is protein, increases. From this we can draw the appropriate conclusion: taking protein in the first half of the day instead of carbohydrates will not be able to provide your body with energy, and you will not feel full of energy. By taking carbohydrates in the second half of the day, when energy costs are reduced, they will not be spent on doing work and will be deposited in adipose tissue. It's simple. The emphasis on carbohydrates decreases from morning to evening, and the emphasis on proteins increases from morning to evening.
Recommendations for a balanced diet
- Don't rely entirely on apps that calculate your calories.
foods you eat: remember that they work quite subjectively, using average values. It is much more important to provide adequate physical activity, which would reinforce and complement the results of proper nutrition.
- Don't create red lists or taboos
: there is a high probability of failure. A balanced diet should become a way of life for you, and not just another hard labor in the form of a short-term diet.
- Try to personalize your diet
- especially in the presence of pathologies from various organs and systems. Contact specialists in the field of nutrition: they will help you not only compensate for deficiencies (if any), but also choose the right course and stick to it in the future.
Remember
: Your health is only in your hands!
Healthy nutrition menu
The first day
| Breakfast | Omelet in melted butter GHI with cherry tomatoes and aged cheese; leafy vegetables; unsweetened apple or pear. |
| Dinner | Creamy cauliflower soup, baked salmon; vegetable salad. |
| Dinner | Mixed grilled vegetable salad. |
Second day
| Breakfast | Casserole using coconut flour and soft cream cheese; lightly salted salmon, coffee with the addition of a piece of coconut oil/GHI. |
| Dinner | Baked lamb and seasonal vegetable salad. |
| Dinner | Quinoa and low-fat fish baked with your favorite spices. |
Day three
| Breakfast | Avocado toast with poached egg, homemade chicken liver pate; a handful of your favorite berries. |
| Dinner | Rabbit meat on a bed of spinach. |
| Dinner | Pumpkin cream soup |
Day four
| Breakfast | Zucchini fritters with psyllium, ricotta cheese, olives. |
| Dinner | Falafel with green salad, peach. |
| Dinner | Couscous with green lettuce and baked mushrooms. |
Day five
| Breakfast | Red fish, whole grain bread, a few pieces of GHI butter - your perfect toast is ready. Add two slices of bitter dark chocolate and tart coffee. |
| Dinner | Offal with brown rice and cherry tomatoes. |
| Dinner | Tilapia baked with spicy spices. |
Day six
| Breakfast | Omelet with bacon and cheese, berries, cocoa or coffee. |
| Dinner | Seafood pasta and leafy vegetable salad. |
| Dinner | Baked chicken breast with cauliflower. |
Day seven
| Breakfast | Cheese pancakes with coconut or almond flour, avocado slices. |
| Dinner | Boiled beef with couscous. |
| Dinner | Grilled vegetables. |
Healthy nutrition menu for the week
Rational nutrition involves a daily balanced diet.
A balanced diet menu should include:
- Whole wheat bread;
- Cereals;
- Lean meats;
- Eggs;
- Fresh vegetables and fruits;
- Fermented milk products with low fat content.
I offer a balanced nutrition menu for healthy women who want to lose extra pounds and change their eating habits.
Monday
Breakfast
- Oatmeal with low-fat milk;
- A few nuts of any kind;
- Honey;
- Tea or coffee.
2nd breakfast
- 1 banana;
- A glass of kefir.
Dinner
- Soup (at your discretion);
- Fish or chicken cutlet;
- Vegetable salad dressed with olive oil.
Afternoon snack
- Chocolate – 20 g;
- Tea.
Dinner
- Steamed fish;
- Fruit salad with yogurt.
Tuesday
Breakfast
- Buckwheat porridge cooked in water;
- 1 tsp. honey;
- Tea or coffee.
2nd breakfast
- Fruits;
- 6% fat yogurt.
Dinner
- Soup;
- Stewed pork with vegetables;
- Tea.
Afternoon snack
Tea with marshmallows or marmalade.
Dinner
- Cottage cheese with raisins;
- Fruits.
Wednesday
Breakfast
- Omelette;
- Coffee or tea;
- Honey;
- A piece of bran bread.
2nd breakfast
Cottage cheese with low-fat sour cream.
Dinner
- Soup;
- Stewed fish;
- The vinaigrette;
- Coffee or tea.
Afternoon snack
- Fruits;
- Half a marshmallow.
Dinner
- Boiled chicken;
- Steamed broccoli.
Thursday
Breakfast
- Cereal flakes with yogurt;
- Tea or coffee.
2nd breakfast
Hot sandwich without mayonnaise.
Dinner
- Soup;
- Beef goulash;
- Vegetable salad.
Afternoon snack
Fruit salad.
Dinner
Stewed fish with vegetables.
Friday
Breakfast
- Rice porrige;
- Coffee or tea.
2nd breakfast
Citrus juice with cracker.
Dinner
- Soup;
- Canned stewed meat;
- Vegetable salad.
Afternoon snack
- Dried fruits;
- Cocoa.
Dinner
- Cottage cheese casserole;
- Tea.
Saturday
Breakfast
- Cheesecakes made from low-fat cottage cheese;
- Sour cream;
- Coffee.
2nd breakfast
Fruits or berries.
Dinner
- Soup;
- Fish;
- Garnish: rice.
Afternoon snack
- Orange juice;
- Biscuit.
Dinner
Grilled meat with vegetables.
Sunday
Breakfast
- Cottage cheese casserole;
- Coffee or tea.
2nd breakfast
Fruit salad or tea with dried fruits.
Dinner
- Grilled meat;
- Vegetable salad.
Afternoon snack
- Tomato juice;
- Cheese;
- Bread.
Dinner
- Canned stewed meat;
- Sauerkraut.
As you can see, rational nutrition does not require large financial costs and excessive effort. You just need to choose healthy foods and don’t starve yourself or overeat.