Protein is an important building material of our body. Every cell of the body consists of it, it is part of all tissues and organs. In addition, a special type of proteins plays the role of enzymes and hormones in a living organism.
In addition to its construction function, protein can also be a source of energy . And in case of excess protein, the liver “prudently” converts the protein into fats, which are stored as reserves in the body (how to get rid of such fat?).
The human body contains 22 amino acids : the body can synthesize 13 amino acids independently from existing building materials, and 9 of them it can only obtain from food.
In the process of assimilation by the body, proteins break down into amino acids, which in turn are supplied to different parts of the body to perform their basic functions. Proteins (in the form of amino acids) are part of the blood, are components of the hormonal system, the thyroid gland, influence the growth and development of the body, regulate the water and acid-base balance of the body.
general information
Proteins are found in both animal and plant foods. However, their value is not equal. As is known, among the amino acids supplied with protein foods, there are:
- replaceable , capable of being synthesized in the digestive tract;
- conditionally replaceable , which are produced only under certain conditions;
- irreplaceable , which the body can receive exclusively from the outside.
High protein animal products contain all essential amino acids in high concentrations. Plant foods are poorer in this regard; their amino acid composition may be incomplete, or the content of some essential amino acids may be insufficient.
Does this mean that protein needs should be met exclusively through animal foods? No, nutritionists recommend including both types of protein foods in your diet, and vegetable protein should account for at least half of the daily value.
Plant protein foods are essential in the diet because:
- In addition to protein, most animal products also contain saturated fats, which are harmful to blood vessels, the consumption of which should be limited.
- Plant foods rich in protein also contain carbohydrates, the content of which in the daily diet should be 3-4 times higher than proteins.
- In addition to proteins, many plant-based foods contain unsaturated fats, which are beneficial for the cardiovascular system.
- Most plant foods also contain fiber, which is necessary for normal intestinal function. Without its supply, constipation occurs and the body is poisoned by protein breakdown products.
Therefore, plant-based foods rich in protein must be present in the diet. Moreover, there is another important reason for their use.
Almost every product contains harmful substances in addition to beneficial substances. This is due to the unfavorable environmental situation, as well as to technologies for growing agricultural plants and animals. Harmful substances (pesticides from plants, hormones and antibiotics from meat foods, mercury and other pollution from the world's oceans from fish, etc.) gradually accumulate in the body, which can lead to the development of serious diseases. In order not to exceed the permissible levels of various harmful substances, it is necessary to eat as varied as possible.
If you give preference to 2-3 types of protein foods, eating the same thing every day, then there is a high risk of getting negative side effects from the toxic compounds they contain. The more different high-protein foods you have in your diet, the healthier your diet will be.
We bring to your attention the top protein products that must be present in an athlete’s diet.
Greek yogurt
There are many ways to introduce Greek yogurt into your diet. You can eat it on its own for breakfast or top it with a fruit salad. It is also good as a base for sauces and salad dressings.
When choosing Greek yogurt, look for options without additives, preservatives, colors or chemicals.
A 170g package of low-fat Greek yogurt contains 100 calories and 18g of protein. A 170g packet of full-fat Greek yoghurt contains about 144 kcal and 15 g of protein. Both options are good, but the choice depends on your dietary needs.
Greek yogurt is an excellent source of calcium and magnesium. It brings much more benefits to the body than regular dessert yogurt, as it contains a lot of proteins and few carbohydrates.
Tip #1. Mix Greek yogurt with lemon juice to make a delicious fish sauce.
Advice »2. Add a couple tablespoons of Greek yogurt and a few slices of fruit to your oatmeal to increase the calories and add a creamy flavor.
Tip #3. Blend Greek yogurt, protein powder, fresh fruit and ice to make a high-protein smoothie.
Tip #4. For those with a sweet tooth, combine Greek yogurt, a little honey and walnuts for a high-protein snack dessert.
Tip #5. Make a delicious salad dressing by combining Greek yogurt, olive oil, minced garlic, and salt and pepper to taste.
Red meat
Red meat is usually called the muscle tissue of mammals: beef, pork, lamb, rabbit, horse meat, etc.
Meat proteins are very valuable in composition; they contain all the essential amino acids in large quantities. In addition, unlike many other sources of protein, meat contains a significant amount of vitamins A, D, group B, and important microelements: iron, magnesium, zinc. Deficiency of vitamin B12, iron, and zinc is often observed in vegetarians, and this is due precisely to their refusal to eat meat. Connective tissues are very beneficial for joints. Orthopedists recommend that their patients include beef and pork shank aspic and dishes with gelatin in their menu more often.
The protein content of meat ranges from 16 g/100 g to 21 g/100 g. It could be called an ideal source of animal proteins, but there are reasons why its consumption should be limited:
- Red meat contains large amounts of saturated fat, which is harmful to the cardiovascular system. Even if pork or beef does not look fatty, it still contains a significant amount of saturated fat. Especially if there are layers of fat. Beef fat is the most harmful, it is the most refractory, its melting point is 50 ° C, which is 13 ° C higher than the temperature of the human body. So marbled beef, prized by gourmets, cannot be called healthy. Pork fat, contrary to popular belief, is less refractory and harmful; in small quantities it is even beneficial. The least amount of saturated fat is found in lean veal, fat-free rabbit and lamb.
- Consuming large amounts of meat increases the acidity of the body's internal environment. A shift in the acid-base balance to the acidic side is very harmful, it contributes to the development of serious diseases and shortens life expectancy.
- Meat contains many purines, which are converted into uric acid. This leads to overload of the kidneys, as well as to the deposition of uric acid salts in the joints, which causes a common disease among elderly meat-eaters - gout.
- Fried meat, especially its charred parts, contains carcinogens - substances that provoke the development of cancer. The same applies to smoked products. Therefore, it is recommended to stew, boil, bake it.
- The breakdown and assimilation of meat food requires significant time and energy consumption, so it cannot be eaten in large quantities. An eaten portion weighing more than 150 g of meat does not have time to be absorbed in the small intestine and enters the large intestine. The large intestine is the kingdom of bacteria; under their influence, the remains of meat food begin to rot, releasing toxins and poisoning the body.
Considering all of the above, we can conclude that red meat should not be the main supplier of protein in the diet. But you shouldn’t completely abandon it. It is recommended to consume it no more than 2 times a week, 100-150 g at a time, giving preference to low-fat varieties. When preparing, it is advisable not to use frying or smoking. The best side dish for meat is vegetables and herbs; the fiber they contain neutralizes many of the negative effects of eating meat dishes.
List of foods with “slow” protein
Slow proteins are characterized by the fact that they are absorbed by the body over a long period of time, require the expenditure of a large amount of energy, and have fewer calories than fast ones.
A special feature of eating this kind of protein is considered to be a late dinner, namely 2–3 hours before bedtime, since the body has time to digest the food overnight, while at the same time the muscles are fully enriched with amino acids. This type of protein is also good to use during periods when there is no possibility of eating for a long time, the feeling of hunger will be as undisturbing as possible.
Do not forget that vegetable proteins are considered to be among the slowest, in particular cereals, the grains of which are coated in a shell. It is recommended to soak them before use, then their digestibility increases significantly.
The basis of slow protein is casein, which is abundant in cottage cheese, but it should definitely be low-fat.
Slow proteins
Poultry meat
Meat from chickens, turkeys, geese, and ducks are also protein-rich foods. This is an excellent source of easily digestible proteins; 100 g of the product contains 18-20 g. In terms of amino acid composition, it is not inferior to red meat, but in terms of the content of vitamins and microelements, poultry meat is poorer. It can be included in the menu of athletes and bodybuilders every day, but with some reservations:
- In poultry factories, when raising broilers, antibiotics and all kinds of growth stimulants are used, among which there may be substances identical to female sex hormones. Therefore, you should not get carried away with chicken from supermarkets. It is better to give preference to poultry from personal plots.
- Poultry adipose tissue contains both saturated and unsaturated fats. They are mainly concentrated in the skin. Traces of drugs used in raising poultry also accumulate there. Therefore, it is recommended to remove the skin from the carcass. Chicken and turkey fillets have the least fat; these parts of the carcass are considered dietary. If the bird is not too fatty and is raised on natural feed, then sometimes you can boil it with the skin, then removing the fat from the broth, since the skin contains connective tissue that is beneficial for joints.
Like meat, poultry is not recommended to be eaten in large portions; more than 150 g at one time should not be consumed.
You may also find tables of high protein foods helpful.
How long does it take for slow and fast proteins to be absorbed?
Experts have proven that slow proteins are broken down into amino acids within 6–8 hours , since their calorie content is lower and more energy is spent, hence the longer time spent on absorption.
The standard representative of slow proteins is low-fat cottage cheese, which ranks first in this list in terms of the time it takes to feel full.
For fast proteins, 60–80 minutes are enough. From the available list of products, you can choose, for example, kefir, as an excellent recovery protein after physical activity, and egg white, as an energy drink before strength exercises.
Kefir is digested in just over an hour, so it is classified as a “fast” protein and is recommended for consumption after physical activity.
Fish
Fish is another protein-rich food. Depending on the type of fish, the protein content in it is 18-24 g for every 100 g. Fish proteins are easily digestible and contain all the essential amino acids. Fish also contains a lot of minerals: phosphorus, iodine, copper. Fish bones contain a large amount of phosphorus, so canned food is useful, in which the bones are softened and can be eaten. Fatty sea fish is especially valued due to the content of such useful substances as omega-3 fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins A, E, D.
Fish and seafood have traditionally served as the main source of animal protein for residents of sea coasts and, as a rule, the average life expectancy in such regions is higher than where meat is preferred.
However, such a healthy product as fish cannot be consumed in large quantities. Fatty fish should not be eaten more than twice a week, because... Even healthy fats should be consumed in moderation. Another reason for the restriction is due to the fact that fish can accumulate harmful substances used when growing in fish farms, as well as from polluted waters of the world’s oceans.
Chicken
Everyone knows that chicken forms the basis of the nutrition of athletes, but few have heard anything specific about its nutritional value. Dietary chicken meat is rich in proteins, vitamins A, B6, B12, iron and magnesium.
Chicken is an excellent choice for athletes who want to gain muscle mass, but need to watch every calorie. One chicken breast contains about 27 g of protein, only 152 kcal and 3 g of fat.
Tip #1. Add a sauce of 2 tablespoons sour cream and ¼ cup salsa to the chicken meat. This will increase the calorie content of the dish by 75 kcal and significantly improve its taste.
Tip #2. If your daily caloric intake is strictly limited, then add a mixture of hot sauce and chopped garlic to the chicken.
Tip #3. Make a simple high-protein salad with chicken, spinach, ½ cup cooked quinoa, crumbled almonds and onions, dressed with wine vinegar and olive oil.
Tip #4. Dice the cooked chicken and mix it with the quinoa and salsa. This is a simple, high-protein meal that's easy to grab in a grab-and-go container and perfect for lunch.
Tip #5. Healthy homemade nuggets recipe: dip chicken fillet pieces in egg coating and fry in a frying pan greased with olive oil.
Cottage cheese
Cottage cheese is considered one of the best sources of protein. The protein content in cottage cheese ranges from 16 g/100 g in a product with a fat content of 11% to 22 g/100 g in a low-fat product. Cottage cheese is also valuable for its high calcium content. Milk fat in large quantities is harmful to blood vessels, so it is recommended to choose cottage cheese with a low content.
To reduce costs, manufacturers often add soy protein and palm fat to cottage cheese, which are also not healthy. Therefore, you should look for places that sell a pure product, free of herbal additives.
Slow and fast proteins: what is the difference
In addition to the classification of proteins by origin (animal and plant), they can be divided into 2 types according to the speed of absorption:
- Slow - which take a long time to be broken down by the body, help prevent catabolic processes, lose weight, help you not feel hungry for a long time, while only eating a small amount of such protein food.
- Fast - they are absorbed accordingly, increase strength, energy, contribute to the rapid receipt of a charge of vigor, and promote a slow gain of muscle mass.
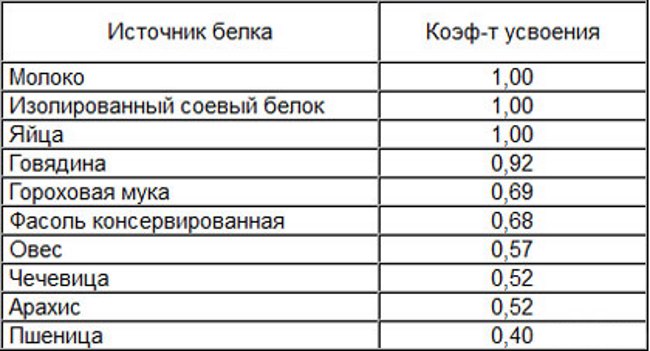
The determining indicator in designating the rate of absorption of protein products is the coefficient of the process of the same name in the body, which is calculated taking into account the composition of incoming amino acids and the completeness of digestion of protein compounds.
Foods rated 1.0 or less indicate that the food is the richest source of protein. And knowing the individual indicators of slow proteins, you can create a list of products that will easily help you gain weight and lose weight, because it is this protein that contributes to this.
Fast proteins and a list of products that suit them are a fast way to restore strength after workouts and a sharp boost of energy to increase their effectiveness.
How does cooking method affect protein digestibility?
The digestibility of protein directly depends on the method of cooking:
- Thermal influence when preparing dishes - here it is important not to overdo it with temperature and time, since there may be practically no vitamins left in the food, but the food should still be healthy.
In such cases, for slow proteins, in particular cereals, pre-soaking in water is suitable; this will make the protective film of the grains more pliable and thereby reduce the thermal effect in order to preserve vitamins.
A double boiler can come to the rescue with this, as it provides a gentle cooking mode for food.

Cooking protein foods in a steamer helps preserve their usefulness
- Grinding will speed up the absorption of protein and its completeness; blenders and meat grinders will be useful in the kitchen; the less fibrous, the faster the body digests and breaks down protein foods.
Daily protein intake
Each person needs an individual amount of protein daily. It depends on gender, weight and other factors. It is important not to overdo it and not eat only protein-rich foods. In any case, nutrition should be balanced and rational. Eating too much protein will not lead to increased muscle growth, although some people believe it will. Even 300 grams of pure protein per day will not cause the body to produce muscle tissue faster than possible.
Research says that for athletes and people who are trying to gain weight, the protein norm is equal to 1.5-2.5 g per 1 kg of weight. That is, with a weight of 70 kg, a man needs about 200 g of protein, a woman with a weight of 60 kg needs 165 g per 1 kg of weight. For weight maintenance or weight loss, this value is reduced by 10% or 20% respectively. But do not forget that this is purely individual, and you should rely on your feelings, observing changes in your figure and well-being. It is impossible to understand from the first day whether the diet has been chosen correctly; at least a month must pass, after which you can adjust your diet.










